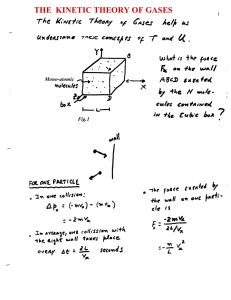
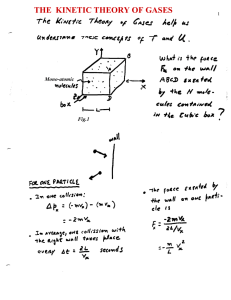
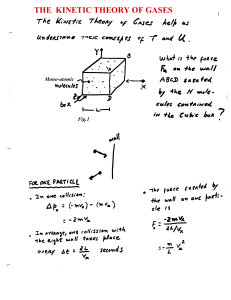
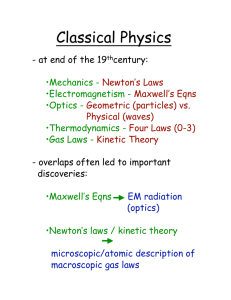
January 1998
... A piece of thin uniform unstretchable rope has length 2L and mass M . Its ends are attached to points at the same height separated by distance 2w, and the rope hangs between them under the influence of gravity (of course, w < L). Let us set up coordinates (x, y) in the plane of the rope, so that the ...
... A piece of thin uniform unstretchable rope has length 2L and mass M . Its ends are attached to points at the same height separated by distance 2w, and the rope hangs between them under the influence of gravity (of course, w < L). Let us set up coordinates (x, y) in the plane of the rope, so that the ...
06. Dynamics -- Energy 1. Energy
... • work = (force) × (distance moved) • For a constant force F, a small change in work dW is related to a small change in distance dx by dW = Fdx. • Many forms of energy, all interconvertible: (a) Chemical energy (b) Heat energy (c) Kinetic energy (d) Many others: electrical, potential, pressure, etc. ...
... • work = (force) × (distance moved) • For a constant force F, a small change in work dW is related to a small change in distance dx by dW = Fdx. • Many forms of energy, all interconvertible: (a) Chemical energy (b) Heat energy (c) Kinetic energy (d) Many others: electrical, potential, pressure, etc. ...
Learning Scales and Accommodations
... What evidence explains that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only changed from one form to another? Key Vocabulary Energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, mechanical energy, thermal energy, sound energy, electric energy, radiant energy, nuclear energy, energy transformation ...
... What evidence explains that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only changed from one form to another? Key Vocabulary Energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, mechanical energy, thermal energy, sound energy, electric energy, radiant energy, nuclear energy, energy transformation ...
Energy – Where does it come from and why does it produce waste?
... and coal), nuclear energy, falling water, geothermal, and solar energy. • Secondary Energy Resources: Those sources which are derived from primary resources such as electricity, fuels from coal, (synthetic natural gas and ...
... and coal), nuclear energy, falling water, geothermal, and solar energy. • Secondary Energy Resources: Those sources which are derived from primary resources such as electricity, fuels from coal, (synthetic natural gas and ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... creates sound. Without energy, we could not grow, move, or even stay alive! To understand energy and how it helps make life possible, we must learn that there are two kinds of energy: kinetic and potential. Kinetic “Kinetic” is another word for “motion.” Scientists use it to define energy that is mo ...
... creates sound. Without energy, we could not grow, move, or even stay alive! To understand energy and how it helps make life possible, we must learn that there are two kinds of energy: kinetic and potential. Kinetic “Kinetic” is another word for “motion.” Scientists use it to define energy that is mo ...
CHAPTER 6: THERMAL ENERGY
... Because the air in the room is a higher temperature than the butter, molecules in the air have more KE than the butter molecules. Energy is transferred from faster-moving molecules in the air to slower-moving butter molecules. ...
... Because the air in the room is a higher temperature than the butter, molecules in the air have more KE than the butter molecules. Energy is transferred from faster-moving molecules in the air to slower-moving butter molecules. ...
Energy Conversion and Rural Electrification
... relations between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy), and, by extension, of the relationships between all forms of energy. • For efficient conversion of energy from one form to another, knowledge of thermodynamic laws and principles is necessary • Com ...
... relations between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy), and, by extension, of the relationships between all forms of energy. • For efficient conversion of energy from one form to another, knowledge of thermodynamic laws and principles is necessary • Com ...
Introduction - WordPress.com
... relations between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy), and, by extension, of the relationships between all forms of energy. • For efficient conversion of energy from one form to another, knowledge of thermodynamic laws and principles is necessary • Com ...
... relations between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy), and, by extension, of the relationships between all forms of energy. • For efficient conversion of energy from one form to another, knowledge of thermodynamic laws and principles is necessary • Com ...
Notes on the First Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry CHEM 213W
... Suppose this were not the case. Then you could presumably find a process which produced more work than it absorbed heat. This extra work could be used to run a generator, which in turn could be used to produce more heat, which could run more of process, producing even more excess work, and so on. Th ...
... Suppose this were not the case. Then you could presumably find a process which produced more work than it absorbed heat. This extra work could be used to run a generator, which in turn could be used to produce more heat, which could run more of process, producing even more excess work, and so on. Th ...
Law conservation of energy worksheet
... The Law of Conservation of Energy. From students' everyday experience, e.g. of batteries going flat or car petrol tanks needing refilling, it is easy to believe that. Law of conservation of matter - definition of law of conservation of matter by The Free Dictionary. topExamples of the First Law of T ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy. From students' everyday experience, e.g. of batteries going flat or car petrol tanks needing refilling, it is easy to believe that. Law of conservation of matter - definition of law of conservation of matter by The Free Dictionary. topExamples of the First Law of T ...
Forms of Energy Basics What is energy? Energy makes change
... boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen in the freezer. It plays our favorite songs on the radio and lights our homes. Energy is needed for our bodies to grow and it allows our minds to think. Scientists define energy as the ability to do work. Modern civilization is p ...
... boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen in the freezer. It plays our favorite songs on the radio and lights our homes. Energy is needed for our bodies to grow and it allows our minds to think. Scientists define energy as the ability to do work. Modern civilization is p ...
Nature of Energy
... GPE = weight x height (unit is joules) The greater the weight of an object or the greater the height it is lifted, the greater is its GPE If you don’t have weight but have the mass, you must multiply the mass by 9.8 m/s2 in order to convert it to the weight in newtons. ...
... GPE = weight x height (unit is joules) The greater the weight of an object or the greater the height it is lifted, the greater is its GPE If you don’t have weight but have the mass, you must multiply the mass by 9.8 m/s2 in order to convert it to the weight in newtons. ...
Energy yo! - Sites@UCI
... Convection is heat energy moving as a fluid from hotter to cooler areas. Warm air at the ground surface rises as a thermal bubble, expends energy to expand, and therefore cools. ...
... Convection is heat energy moving as a fluid from hotter to cooler areas. Warm air at the ground surface rises as a thermal bubble, expends energy to expand, and therefore cools. ...
Lab #9 - Austin Community College
... gravitational potential energy. Gravitational potential energy also depends on mass, the more the better. The formula for gravitational potential energy is PE = mgh Although there are other kinds of energy, these two will be most important to us. The Total Energy of an object can therefore be expres ...
... gravitational potential energy. Gravitational potential energy also depends on mass, the more the better. The formula for gravitational potential energy is PE = mgh Although there are other kinds of energy, these two will be most important to us. The Total Energy of an object can therefore be expres ...
1 st Law of Thermodynamics - Mr Hartan`s Science Class
... • The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system increases over time. Entropy is the measure of the amount of disorder in a system. An increase in entropy arising from energy transformations reduces the energy available to do work. • The second law of thermodynamics explains th ...
... • The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system increases over time. Entropy is the measure of the amount of disorder in a system. An increase in entropy arising from energy transformations reduces the energy available to do work. • The second law of thermodynamics explains th ...
Section 12.1 Temperature and Thermal Energy
... One way to increase the temperature of an object is to place it in contact with a hotter object. Heat – energy that flows as a result of a difference in temperature. The symbol for heat is Q. Heat is a form of energy thus it is measured in Joules. It is the energy transferred because of a difference ...
... One way to increase the temperature of an object is to place it in contact with a hotter object. Heat – energy that flows as a result of a difference in temperature. The symbol for heat is Q. Heat is a form of energy thus it is measured in Joules. It is the energy transferred because of a difference ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.