Measurement of the Electric Field Uniformity in an Electrostatic
... must be antisymmetric about the mechanical center and therefore has only odd order coef®cients in an expansion in x. The measured data has even order coef®cients which are of comparable importance over the measurement range. Symmetry of the electrodes implies these even order coef®cients cannot be a ...
... must be antisymmetric about the mechanical center and therefore has only odd order coef®cients in an expansion in x. The measured data has even order coef®cients which are of comparable importance over the measurement range. Symmetry of the electrodes implies these even order coef®cients cannot be a ...
+ Cl
... A 0.100 molality (mol/kg) solution of NaCl has a freezingpoint depression of -0.348 oC, whereas the expected decrease in the freezing point is -0.186 oC. The van’t Hoff factor in this case is 1.87. If there were no ion pairing, we would expect the van’t Hoff factor for NaCl to be 2.00. Similarly, ac ...
... A 0.100 molality (mol/kg) solution of NaCl has a freezingpoint depression of -0.348 oC, whereas the expected decrease in the freezing point is -0.186 oC. The van’t Hoff factor in this case is 1.87. If there were no ion pairing, we would expect the van’t Hoff factor for NaCl to be 2.00. Similarly, ac ...
Physics Week 3(Sem. 2)
... negative terminal. The field exerts a force on the free electrons in the wire, and they respond by moving through the wire. The resulting from of charge is called an electric current. The current is defined as the amount of charge per unit time that crosses an area of the wire. Thus the equ ...
... negative terminal. The field exerts a force on the free electrons in the wire, and they respond by moving through the wire. The resulting from of charge is called an electric current. The current is defined as the amount of charge per unit time that crosses an area of the wire. Thus the equ ...
Charge Pump, Loop Filter and VCO for Phase Lock
... Total simulation from phase frequency detector to loop filter is shown in figure 7 and value of loop filter is shown in figure 8 . ...
... Total simulation from phase frequency detector to loop filter is shown in figure 7 and value of loop filter is shown in figure 8 . ...
20.2 Electric Current and Ohm
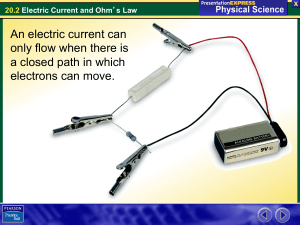
... The continuous flow of electric charge is an electric current. • Charge flows only in one direction in direct current (DC). A flashlight and most other battery-operated devices use direct current. • Alternating current (AC) is a flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction. Electr ...
... The continuous flow of electric charge is an electric current. • Charge flows only in one direction in direct current (DC). A flashlight and most other battery-operated devices use direct current. • Alternating current (AC) is a flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction. Electr ...
SANKEN ELECTRIC MLD685D
... The information included herein is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, SANKEN ELECTRIC CO., LTD assumes no responsibility for its use ; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. ...
... The information included herein is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, SANKEN ELECTRIC CO., LTD assumes no responsibility for its use ; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. ...
physics 251: test study sheet
... 2. Analyze the motion of charged particles moving in electric and/or magnetic fields. In particular, analyze the operation of a synchrotron, velocity selector, and mass spectrometer. 3. Find the size and direction (Force RHR #2) of the magnetic force exerted upon a straight wire carrying a current i ...
... 2. Analyze the motion of charged particles moving in electric and/or magnetic fields. In particular, analyze the operation of a synchrotron, velocity selector, and mass spectrometer. 3. Find the size and direction (Force RHR #2) of the magnetic force exerted upon a straight wire carrying a current i ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.