Document
... When charges move, the disturbance in the E-field affects other charges. An E-field can store charge. An E-field can be channeled An E-field teamed with a magnetic field can move through empty space. ...
... When charges move, the disturbance in the E-field affects other charges. An E-field can store charge. An E-field can be channeled An E-field teamed with a magnetic field can move through empty space. ...
Gauss' Law Review & Summary
... Using Gauss' law and, in some cases, symmetry arguments, we can derive several important results in electrostatic situations. Among these are: 1. An excess charge on an isolated conductor is located entirely on the outer surface of the conductor. 2. The external electric field near the surface of ...
... Using Gauss' law and, in some cases, symmetry arguments, we can derive several important results in electrostatic situations. Among these are: 1. An excess charge on an isolated conductor is located entirely on the outer surface of the conductor. 2. The external electric field near the surface of ...
twopointcharges01 by AJC2012
... (b) Is the force on the +q charge by the +Q charge greater than, less than or equal to the force on the +Q charge by the +q charge? Explain. ...
... (b) Is the force on the +q charge by the +Q charge greater than, less than or equal to the force on the +Q charge by the +q charge? Explain. ...
Electric Field (Continued)
... B) The electric field is zero somewhere on the x axis to the left of the +4q charge. C) The electric field is zero somewhere on the x axis to the right of the –2q charge. D) The electric field is zero somewhere on the x axis between the two charges, but this point is nearer to the –2q charge. E) The ...
... B) The electric field is zero somewhere on the x axis to the left of the +4q charge. C) The electric field is zero somewhere on the x axis to the right of the –2q charge. D) The electric field is zero somewhere on the x axis between the two charges, but this point is nearer to the –2q charge. E) The ...
Lecture Power Points Chapter 16 Physics: Principles
... Electric Charges: Positive and Negative Charge comes in two types, like charges repel and opposite charges attract Benjamin Franklin coined the terms Positive and Negative, in line with his theory that there is single “electrical fluid”, that flows in response to some kind of pressure, from positiv ...
... Electric Charges: Positive and Negative Charge comes in two types, like charges repel and opposite charges attract Benjamin Franklin coined the terms Positive and Negative, in line with his theory that there is single “electrical fluid”, that flows in response to some kind of pressure, from positiv ...
HW6 - University of St. Thomas
... in the middle as shown in the diagram at right (the grey color indicates the “meat” of each conductor). The inner shell has a total charge of -2q, but the outer shell is neutral. The point charge does not touch the conductors. Find expressions for the electric field in all regions (r
... in the middle as shown in the diagram at right (the grey color indicates the “meat” of each conductor). The inner shell has a total charge of -2q, but the outer shell is neutral. The point charge does not touch the conductors. Find expressions for the electric field in all regions (r
Chapter 25: Electric Potential Energy
... Energy concepts allow us to consider the behavior of charges in an electric field. ...
... Energy concepts allow us to consider the behavior of charges in an electric field. ...
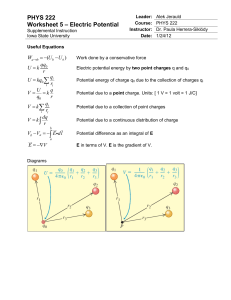
PHYS 222 Worksheet 5 Electric Potential
... (c) A negative point charge q = -0.200 µC is moved from b to a. Calculate the work done on the point charge by the electric field W q0 V q(Va Vb ) (0.2)(106 )(370) 7.4(105 ) J 4) How much excess charge must be placed on a copper sphere 25.0 cm in diameter so that the potential of ...
... (c) A negative point charge q = -0.200 µC is moved from b to a. Calculate the work done on the point charge by the electric field W q0 V q(Va Vb ) (0.2)(106 )(370) 7.4(105 ) J 4) How much excess charge must be placed on a copper sphere 25.0 cm in diameter so that the potential of ...
Lecture #25 - UCF Physics
... Count the amount of charge in coulombs that pass where you are standing in one second. This amount of charge, divided by the time of passage is defined as the CURRENT. The current is measured in AMPERES and we use the symbol I. One ampere is a current of one coulomb per ...
... Count the amount of charge in coulombs that pass where you are standing in one second. This amount of charge, divided by the time of passage is defined as the CURRENT. The current is measured in AMPERES and we use the symbol I. One ampere is a current of one coulomb per ...
Ch17 Review
... Understand the basic properties of electric charges. Differentiate between insulators and conductors. Distinguish between charging by contact and charging by induction. Calculate electric force using Coulomb’s Law. Compare electric force to gravitational force. Apply the superposition pr ...
... Understand the basic properties of electric charges. Differentiate between insulators and conductors. Distinguish between charging by contact and charging by induction. Calculate electric force using Coulomb’s Law. Compare electric force to gravitational force. Apply the superposition pr ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.