4.3 Notes - Seymour ISD
... They contain many free electrons Metals are good conductors Temperature influences resistance of the flow What happens to the energy when resistance is present in electrical systems? ...
... They contain many free electrons Metals are good conductors Temperature influences resistance of the flow What happens to the energy when resistance is present in electrical systems? ...
4.3 Notes - Seymour ISD
... Resistance- measure of the ability of an electrical device to oppose flow of charge through a device Measured in OHMS (Ω) ...
... Resistance- measure of the ability of an electrical device to oppose flow of charge through a device Measured in OHMS (Ω) ...
ch_24_poss_elmo
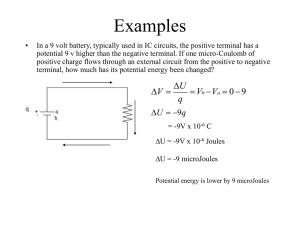
... In a 9 volt battery, typically used in IC circuits, the positive terminal has a potential 9 v higher than the negative terminal. If one micro-Coulomb of positive charge flows through an external circuit from the positive to negative terminal, how much has its potential energy been changed? ...
... In a 9 volt battery, typically used in IC circuits, the positive terminal has a potential 9 v higher than the negative terminal. If one micro-Coulomb of positive charge flows through an external circuit from the positive to negative terminal, how much has its potential energy been changed? ...
Electric potential energy Point charge potential Zero potential
... can be found by superposing the point charge potentials of infinitesimal charge elements ...
... can be found by superposing the point charge potentials of infinitesimal charge elements ...
q 1 - Mr. Cervantes Science Classes
... positive and negative. Rubbing certain electrically neutral objects together (e.g., a glass rod and a silk cloth) tends to cause the electric charges to separate. In the case of the glass and silk, the glass rod loses negative charge and becomes positively charged while the silk cloth gains negative ...
... positive and negative. Rubbing certain electrically neutral objects together (e.g., a glass rod and a silk cloth) tends to cause the electric charges to separate. In the case of the glass and silk, the glass rod loses negative charge and becomes positively charged while the silk cloth gains negative ...
Electricity
... negative to positive – An electric current will occur in a conductive metal when an electric potential exists – Electric potential is the difference between the charge at the – end and the + end – Electricity does work when the electrons flow in an electric current along a wire ...
... negative to positive – An electric current will occur in a conductive metal when an electric potential exists – Electric potential is the difference between the charge at the – end and the + end – Electricity does work when the electrons flow in an electric current along a wire ...
Name Date What is Electric Potential NRG and Electric Potential
... Once at the website, 1. Explore by placing a single positive 1 nC point charge in the middle of the screen. Move the voltage probe box to different locations near the charge. What happens to the voltage number? Does the number change at all? How does the color in the circle with the cross-hairs chan ...
... Once at the website, 1. Explore by placing a single positive 1 nC point charge in the middle of the screen. Move the voltage probe box to different locations near the charge. What happens to the voltage number? Does the number change at all? How does the color in the circle with the cross-hairs chan ...
Electrostatic - Portal UniMAP
... Neutrons and most materials have a net charge of zero or neutral. When certain types of objects are rubbed together, electrons from one object may be transferred to an object with a greater affinity for the electrons. When this happens, the object that gave up the electrons is positive, whereas the ...
... Neutrons and most materials have a net charge of zero or neutral. When certain types of objects are rubbed together, electrons from one object may be transferred to an object with a greater affinity for the electrons. When this happens, the object that gave up the electrons is positive, whereas the ...
Electricity
... The direction of the electric field at any point is defined to be the same direction as the direction of force on a positive test charge placed in the region at that point. Field lines point away from positive and toward negative charges. ...
... The direction of the electric field at any point is defined to be the same direction as the direction of force on a positive test charge placed in the region at that point. Field lines point away from positive and toward negative charges. ...
Electrostatics Test 2012
... regarding any force or torque applied to the water molecule. In this first instant, the net force will be___________, and in the first instant torque will be ____________. a. To the right, clockwise b. To the right, counter clockwise c. To the left, clockwise d. To the left, counterclockwise e. Zero ...
... regarding any force or torque applied to the water molecule. In this first instant, the net force will be___________, and in the first instant torque will be ____________. a. To the right, clockwise b. To the right, counter clockwise c. To the left, clockwise d. To the left, counterclockwise e. Zero ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.