Course: Physics 1 Module 1: Electricity and Magnetism
... • Electromagnetism describes the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Electromagnetism is essentially the foundation for all of electrical engineering. We use electromagnets to generate electricity, store memory on our computers, generate pictures on a television screen, diagnose illnesse ...
... • Electromagnetism describes the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Electromagnetism is essentially the foundation for all of electrical engineering. We use electromagnets to generate electricity, store memory on our computers, generate pictures on a television screen, diagnose illnesse ...
V - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Whenever electric charges move, an electric current is said to ...
... Whenever electric charges move, an electric current is said to ...
MAX680/MAX681 +5V to ±10V Voltage Converters
... is as a dual charge-pump voltage converter that provides positive and negative outputs of two times a positive input voltage. For applications where PC board space is at a premium, the MAX681, with its capacitors internal to the package, offers the smallest footprint. The simple circuit shown in Fig ...
... is as a dual charge-pump voltage converter that provides positive and negative outputs of two times a positive input voltage. For applications where PC board space is at a premium, the MAX681, with its capacitors internal to the package, offers the smallest footprint. The simple circuit shown in Fig ...
Electromagnetism
... Charges fill space with an electric field. Static electricity is associated with the gain or loss of electrons. Electromagnetic forces can attract or repel. Opposite electrical charges attract each other, and like electrical charges repel each other. Electric current is the flow of electrons. A comp ...
... Charges fill space with an electric field. Static electricity is associated with the gain or loss of electrons. Electromagnetic forces can attract or repel. Opposite electrical charges attract each other, and like electrical charges repel each other. Electric current is the flow of electrons. A comp ...
Electronics () - Lyle School of Engineering
... • There was a vague idea that the negative charge electron, while it was in between the two positive nuclei, could attract both of them and hold them together – But when it moved away from the inter-atomic position in its normal rotations around the nuclei, the nuclei would repel each other and push ...
... • There was a vague idea that the negative charge electron, while it was in between the two positive nuclei, could attract both of them and hold them together – But when it moved away from the inter-atomic position in its normal rotations around the nuclei, the nuclei would repel each other and push ...
document
... Prob. 2.38: A metal sphere of radius R carries a total charge Q. What is the force of repulsion between the northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere? ...
... Prob. 2.38: A metal sphere of radius R carries a total charge Q. What is the force of repulsion between the northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere? ...
Document
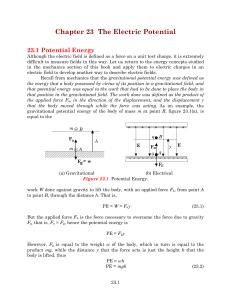
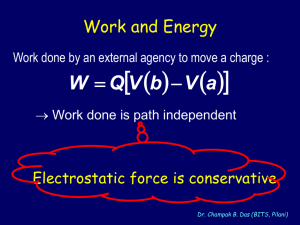
... charge distribution, the electric force acting on the test charge is q0 E. When the test charge is moved in the field by some external agent, the work done by the field on the charge is equal to the negative of the work done by the external agent causing the displacement This is analogous to the sit ...
... charge distribution, the electric force acting on the test charge is q0 E. When the test charge is moved in the field by some external agent, the work done by the field on the charge is equal to the negative of the work done by the external agent causing the displacement This is analogous to the sit ...
An Advanced Model of Partial Discharge in Electrical Insulation
... cavity (shape, size etc.), as well as on the coupling of the discharge and external circuit (local impedances, frequency, generator harmonics, generator impedance, etc.) [9–11]. During the current pulse, there changes surface density of the spark free charge δs on cavity walls, Figure 4a. That charg ...
... cavity (shape, size etc.), as well as on the coupling of the discharge and external circuit (local impedances, frequency, generator harmonics, generator impedance, etc.) [9–11]. During the current pulse, there changes surface density of the spark free charge δs on cavity walls, Figure 4a. That charg ...
Ch. 15: Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... paper, or a balloon sticking to a wall. Three thousand years ago, a thousand years ago, and up until just a few hundred years ago, this behavior must have seemed odd, almost magical. We now understand that it is simply explained as the transfer of some electrons between the two rubbed objects, resul ...
... paper, or a balloon sticking to a wall. Three thousand years ago, a thousand years ago, and up until just a few hundred years ago, this behavior must have seemed odd, almost magical. We now understand that it is simply explained as the transfer of some electrons between the two rubbed objects, resul ...
one mark questions
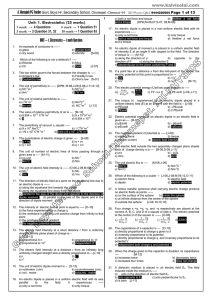
... 10. The unit of electric field intensity is ------ [O-06,J-08,M-09] a) NC-2 b) NC c) Vm-1 d) Vm 11. The direction of electric field at a point on the equatorial line due to an electric dipole is -----a) along the equatorial line towards the dipole b) along the equatorial line away from the dipole c) ...
... 10. The unit of electric field intensity is ------ [O-06,J-08,M-09] a) NC-2 b) NC c) Vm-1 d) Vm 11. The direction of electric field at a point on the equatorial line due to an electric dipole is -----a) along the equatorial line towards the dipole b) along the equatorial line away from the dipole c) ...
Electric current and circuits
... 1. The sum of the currents entering a junction, must equal the sum of the currents leaving that junction (result of charge conservation). ...
... 1. The sum of the currents entering a junction, must equal the sum of the currents leaving that junction (result of charge conservation). ...
See also "SPINNING MAGNETIC FIELDS"
... current is observed flowing through that circuit. It is assumed that the permanent magnet is made of an electrically conducting material, thus forming the part of the closed electrical circuit. If a steady electromagnet is used instead of the permanent magnet, then an appropriate coaxial conductor, ...
... current is observed flowing through that circuit. It is assumed that the permanent magnet is made of an electrically conducting material, thus forming the part of the closed electrical circuit. If a steady electromagnet is used instead of the permanent magnet, then an appropriate coaxial conductor, ...
lecture1423903135
... Static Electric Fields: Electrostatics can be defined as the study of electric charges at rest. Electric fields have their sources in electric charges. The fundamental & experimentally proved laws of electrostatics are Coulomb’s law & Gauss’s theorem. Coulomb’s law & Electric field Intensity Stateme ...
... Static Electric Fields: Electrostatics can be defined as the study of electric charges at rest. Electric fields have their sources in electric charges. The fundamental & experimentally proved laws of electrostatics are Coulomb’s law & Gauss’s theorem. Coulomb’s law & Electric field Intensity Stateme ...
electromagnetic theory - SK Engineering Academy
... Electric flux: The lines of electric force is known as electric flux. It is denoted by . = Q ( charge ) Coulomb. Electric flux density : Electric flux density or displacement density is defined as the electric flux per unit area. Q D= A 2.State Gauss’s law. The electric flux passing through any ...
... Electric flux: The lines of electric force is known as electric flux. It is denoted by . = Q ( charge ) Coulomb. Electric flux density : Electric flux density or displacement density is defined as the electric flux per unit area. Q D= A 2.State Gauss’s law. The electric flux passing through any ...
AAT3697 数据资料DataSheet下载
... input is set by the RSET resistor connected between the ADPSET pin and ground. Refer to Table 1 for recommended RSET values for a desired constant current charge level. The presence of voltage on the adapter input is indicated by the ADPP# pin function. This indicator pin uses an internal open drain ...
... input is set by the RSET resistor connected between the ADPSET pin and ground. Refer to Table 1 for recommended RSET values for a desired constant current charge level. The presence of voltage on the adapter input is indicated by the ADPP# pin function. This indicator pin uses an internal open drain ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.