Universidad de Puerto Rico
... Read the instructions carefully. Select the best answer. You are required to answer only 20 of the 25 questions. When you finish the exam you have to select and identify the 20 questions to be corrected by writing the question’s number in the square spaces provided in this page and write the answer ...
... Read the instructions carefully. Select the best answer. You are required to answer only 20 of the 25 questions. When you finish the exam you have to select and identify the 20 questions to be corrected by writing the question’s number in the square spaces provided in this page and write the answer ...
Lecture 8 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... •V is determined to within an arbitrary constant. •We can choose to set V=0 at any position (most often at “r=infinity”) •There is no absolute potential Rule: Electrostatic field lines always point to decreasing electric potential. Why? Note: electric potential V is not the same as electric potentia ...
... •V is determined to within an arbitrary constant. •We can choose to set V=0 at any position (most often at “r=infinity”) •There is no absolute potential Rule: Electrostatic field lines always point to decreasing electric potential. Why? Note: electric potential V is not the same as electric potentia ...
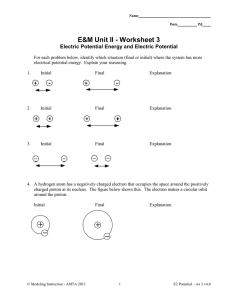
Honors Physics Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference
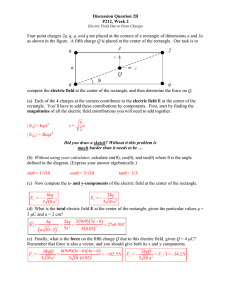
... (C) Find the work to move a 13.0 C from the origin to a point 50.0 cm from the origin on the positive x-axis. First note that you cannot simply move the charge along the x-axis since potential and electric field are infinity at the location of the two fixed charges. Thus we will have to move the ch ...
... (C) Find the work to move a 13.0 C from the origin to a point 50.0 cm from the origin on the positive x-axis. First note that you cannot simply move the charge along the x-axis since potential and electric field are infinity at the location of the two fixed charges. Thus we will have to move the ch ...
File
... The electric field vector, E, is tangent to the electric field lines at each point The number of lines per unit area through a surface perpendicular to the lines is proportional to the strength of the electric field in a given ...
... The electric field vector, E, is tangent to the electric field lines at each point The number of lines per unit area through a surface perpendicular to the lines is proportional to the strength of the electric field in a given ...
Semester 1 Final Review
... What is electricity? What is the difference between parallel and series circuits? What is the total charge of an object with 18 electrons and 17 protons?__________ An atom that loses electrons becomes positive/negative. An atom that gains electrons becomes positive/negative. ...
... What is electricity? What is the difference between parallel and series circuits? What is the total charge of an object with 18 electrons and 17 protons?__________ An atom that loses electrons becomes positive/negative. An atom that gains electrons becomes positive/negative. ...
I. Electric Charge
... Electric Charges In chemistry: matter is made up of atoms which are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons Electric charges of these particles: Protons – positive Electrons – negative Neutrons – neutral (no charge) ...
... Electric Charges In chemistry: matter is made up of atoms which are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons Electric charges of these particles: Protons – positive Electrons – negative Neutrons – neutral (no charge) ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.