Welcome to Phys 208! - UW-Madison Department of Physics
... Superposition with Electric Fields • At any point P, the total electric field due to a group of source charges equals the vector sum of electric fields of all the charges ...
... Superposition with Electric Fields • At any point P, the total electric field due to a group of source charges equals the vector sum of electric fields of all the charges ...
W = 9.6x10 -17 J B) The electron is decreasing it`s electric potential
... Some elements do this by giving away valence electrons K -> K+ + eSome elements do this by gaining valance electrons S + 2e- -> S2When a potassium atom (K) is placed next to a sulfur atom (S), they react and electrons flow from the potassium atom to the sulfur atom. This means, there must be an ele ...
... Some elements do this by giving away valence electrons K -> K+ + eSome elements do this by gaining valance electrons S + 2e- -> S2When a potassium atom (K) is placed next to a sulfur atom (S), they react and electrons flow from the potassium atom to the sulfur atom. This means, there must be an ele ...
Electricity_and_Magnetism
... difference in electric potential energy of the charges (electrons) between two points in a circuit. The amount of charge (Q), given by amount of electrons, is measured in Coulombs 1 electron has a charge of e=1.60 x 10-19C, so Q=Ne, where N is the # of electrons Voltmeters measure electric potential ...
... difference in electric potential energy of the charges (electrons) between two points in a circuit. The amount of charge (Q), given by amount of electrons, is measured in Coulombs 1 electron has a charge of e=1.60 x 10-19C, so Q=Ne, where N is the # of electrons Voltmeters measure electric potential ...
e - Mr. Schroeder
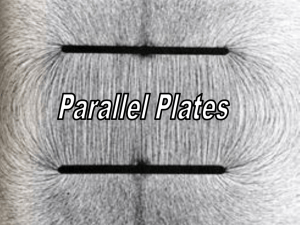
... 2. A pair of oppositely charged parallel plates are separated by 5.33 mm and connected to a 600 V source of potential difference. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates? ...
... 2. A pair of oppositely charged parallel plates are separated by 5.33 mm and connected to a 600 V source of potential difference. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates? ...
11.02.2015 - Erwin Sitompul
... axis, –q –3.2×10–19 C at x –3 m and q 4.8×10–19 C at x 3 m. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the net electric field produced at point P at y 4 m? ...
... axis, –q –3.2×10–19 C at x –3 m and q 4.8×10–19 C at x 3 m. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the net electric field produced at point P at y 4 m? ...
A -B
... Electrostatic copier. An electrostatic copier works by selectively arranging positive charges (in a pattern to be copied) on the surface of a nonconducting drum, then gently sprinkling negatively charged dry toner (ink) onto the drum. The toner particles temporarily stick to the pattern on the drum ...
... Electrostatic copier. An electrostatic copier works by selectively arranging positive charges (in a pattern to be copied) on the surface of a nonconducting drum, then gently sprinkling negatively charged dry toner (ink) onto the drum. The toner particles temporarily stick to the pattern on the drum ...
Electrons and Photons
... accelerated towards the anode and positive ions towards the cathode. When these highly accelerated positive ions strike the cathode, they eject electrons from the atoms of the cathode. These electrons are highly accelerated by the electric field. When they reach the anode with high velocity, fluores ...
... accelerated towards the anode and positive ions towards the cathode. When these highly accelerated positive ions strike the cathode, they eject electrons from the atoms of the cathode. These electrons are highly accelerated by the electric field. When they reach the anode with high velocity, fluores ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.