PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 19/Page 1 Today
... Average motion of electrons: Drift velocity - Without an electric field (or no potential difference), charges feel no force, and hence just move with random motion (because of their thermal energy). - But, if we apply an electric field (there is a potential difference) in the conductor, there still ...
... Average motion of electrons: Drift velocity - Without an electric field (or no potential difference), charges feel no force, and hence just move with random motion (because of their thermal energy). - But, if we apply an electric field (there is a potential difference) in the conductor, there still ...
Resistor - eLisa UGM
... • When the blob at the top (the cell body) is stimulated, it causes Na+ ions to rush into the top of the tail (axon). This electrical pulse will then travel down the axon, like a flame burning down from the end of a fuse, with the Na+ ions at each point first going out and then coming back in. If 10 ...
... • When the blob at the top (the cell body) is stimulated, it causes Na+ ions to rush into the top of the tail (axon). This electrical pulse will then travel down the axon, like a flame burning down from the end of a fuse, with the Na+ ions at each point first going out and then coming back in. If 10 ...
The Electric Field
... • Electric field is a concept, allowing to understand the action of the electric force. • The directions of the electric field at a point source is the direction of the electric force exerted on a small positive charge. • Electric flux through a surface is a product of the electric field magnitude a ...
... • Electric field is a concept, allowing to understand the action of the electric force. • The directions of the electric field at a point source is the direction of the electric force exerted on a small positive charge. • Electric flux through a surface is a product of the electric field magnitude a ...
Electric Potential Energy
... of 1000 Volts: • Uba = qVba = (1.60 x 10-19 C)(1000 V) = 1.60 x 10-13 J = 1000 eV (electron volts) = 1 keV (kilo electron volt) One electron-volt (1 eV) is the kinetic energy gained by an elemental charge (electron or proton) when it is accelerated through a potential difference of one Volt. 1 eV ...
... of 1000 Volts: • Uba = qVba = (1.60 x 10-19 C)(1000 V) = 1.60 x 10-13 J = 1000 eV (electron volts) = 1 keV (kilo electron volt) One electron-volt (1 eV) is the kinetic energy gained by an elemental charge (electron or proton) when it is accelerated through a potential difference of one Volt. 1 eV ...
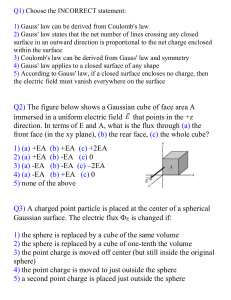
Gauss` Law
... radius r enclosing an isolated charged particle. Suppose the enclosing Gaussian surface is changed to a larger Gaussian sphere of radius 2r. Is the net flux through the new Gaussian sphere greater than, less than, or equal to i? ...
... radius r enclosing an isolated charged particle. Suppose the enclosing Gaussian surface is changed to a larger Gaussian sphere of radius 2r. Is the net flux through the new Gaussian sphere greater than, less than, or equal to i? ...
Electrostatics
... A drum is basically a metal roller covered by a layer of photoconductive material. This layer is made out of a semiconductor t i l Thi l i d t f i d t such as selenium, germanium h l i i or silicon. What makes elements like selenium so cool is that they can conduct electricity in some cases, but n ...
... A drum is basically a metal roller covered by a layer of photoconductive material. This layer is made out of a semiconductor t i l Thi l i d t f i d t such as selenium, germanium h l i i or silicon. What makes elements like selenium so cool is that they can conduct electricity in some cases, but n ...
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
... Projectile with mass M strikes the ground 5 times sooner than the one with mass 5M. b) Projectile with mass M strikes the ground 5 times farther than the one with mass 5M. c) Both projectiles strike the ground at the same time. d) Both projectiles strike the ground at the same distance. e) The answe ...
... Projectile with mass M strikes the ground 5 times sooner than the one with mass 5M. b) Projectile with mass M strikes the ground 5 times farther than the one with mass 5M. c) Both projectiles strike the ground at the same time. d) Both projectiles strike the ground at the same distance. e) The answe ...
Physics 7701: Problem Set #9
... density λ is located perpendicular to the x–y plane in the first quadrant at (x0 , y0 ). The intersecting planes x = 0, y ≥ 0 and y = 0, x ≥ 0 are conducting boundary surfaces held at zero potential. Consider the potential, fields, and surface charges in the first quadrant. (a) The well-known potent ...
... density λ is located perpendicular to the x–y plane in the first quadrant at (x0 , y0 ). The intersecting planes x = 0, y ≥ 0 and y = 0, x ≥ 0 are conducting boundary surfaces held at zero potential. Consider the potential, fields, and surface charges in the first quadrant. (a) The well-known potent ...
Chapter 1 Notes: Electric Charges and Forces
... Chapter 2 Notes: Electric Fields What is an electric field, and where does it come from? The influence of electrical forces is seen when various objects (such as plastic or rubber rods, or tapes) are observed to attract and repel each other. We have described these objects as being “charged.” It has ...
... Chapter 2 Notes: Electric Fields What is an electric field, and where does it come from? The influence of electrical forces is seen when various objects (such as plastic or rubber rods, or tapes) are observed to attract and repel each other. We have described these objects as being “charged.” It has ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.