c spine - emlearn
... CASE DISCUSSION • A person arrives by ambulance to ED on a backboard and a cervical collar after an MVA. • Speed of 50km/hr • No LOC, no other injuries, no midline tenderness, BAL 0.20. • Does he need imaging? ...
... CASE DISCUSSION • A person arrives by ambulance to ED on a backboard and a cervical collar after an MVA. • Speed of 50km/hr • No LOC, no other injuries, no midline tenderness, BAL 0.20. • Does he need imaging? ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... cartilages of the ribs, and the superolateral corners of the manubrium exhibit clavicular notches for articulation with the clavicles. 16. There are 12 pairs of ribs. Most of them exhibit a head where they articulate with the body of a vertebra; a narrow neck; a rough tubercle where they articulate ...
... cartilages of the ribs, and the superolateral corners of the manubrium exhibit clavicular notches for articulation with the clavicles. 16. There are 12 pairs of ribs. Most of them exhibit a head where they articulate with the body of a vertebra; a narrow neck; a rough tubercle where they articulate ...
L3-female pelvis2015-04-17 06:407.1 MB
... AcGons of levator ani: 1. The muscles of the two sides form an efficient muscular sling that supports and maintains the pelvic viscera in posiGon. 2. They resist the rise in intra pelvic pressure ...
... AcGons of levator ani: 1. The muscles of the two sides form an efficient muscular sling that supports and maintains the pelvic viscera in posiGon. 2. They resist the rise in intra pelvic pressure ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Introduction to anatomy
... When you are describing a patient or the cadaver you have to keep the anatomical position in mind. By using this position and appropriate terminology, you can relate any part of the body precisely to any other part. The patient is lying on one side; we still use the anatomical position. He is in sup ...
... When you are describing a patient or the cadaver you have to keep the anatomical position in mind. By using this position and appropriate terminology, you can relate any part of the body precisely to any other part. The patient is lying on one side; we still use the anatomical position. He is in sup ...
Chapter 1 - UCLA Linguistics
... Without the action of inspiratory forces such as the external intercostals and the diaphragm, the lungs collapse back to their resting state. Normal expiration is entirely passive. The more the lungs are inflated, the greater their tendency to return to the resting position. This restoring force is ...
... Without the action of inspiratory forces such as the external intercostals and the diaphragm, the lungs collapse back to their resting state. Normal expiration is entirely passive. The more the lungs are inflated, the greater their tendency to return to the resting position. This restoring force is ...
Forensics - Salem Press
... Criminal Justice Issues: Evidence and forensics; investigation; technology Significance: Forensic science and forensic medicine, as they relate to the processing of crime scene evidence, have become increasingly important to the resolution of cases within the criminal justice system, particularly as ...
... Criminal Justice Issues: Evidence and forensics; investigation; technology Significance: Forensic science and forensic medicine, as they relate to the processing of crime scene evidence, have become increasingly important to the resolution of cases within the criminal justice system, particularly as ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
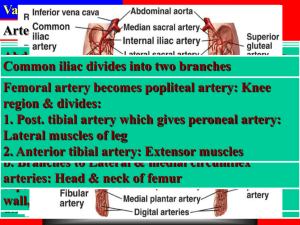
... Deltoid&shoulder viscosity arteries:Kidneys “thickness joint on b. wall: a. Common Located Greater in hepatic carotid at arterial and end aortic arch mm Hg) and ...
... Deltoid&shoulder viscosity arteries:Kidneys “thickness joint on b. wall: a. Common Located Greater in hepatic carotid at arterial and end aortic arch mm Hg) and ...
Notes on Axial Skeleton STUDENT Version
... Provides a protective cage for the vital organs of the thoracic cavity (heart, lungs, thymus, and great blood vessels) Supports the shoulders and upper limbs Provides attachment points for major muscles of the neck, back, chest, and shoulders In addition, the spaces between the ribs are occupi ...
... Provides a protective cage for the vital organs of the thoracic cavity (heart, lungs, thymus, and great blood vessels) Supports the shoulders and upper limbs Provides attachment points for major muscles of the neck, back, chest, and shoulders In addition, the spaces between the ribs are occupi ...
Blood supply of the brain
... layer of the dura and drain into the cranial venous sinuses • External Cerebral Veins • The superior cerebral veins pass upward over the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere and empty into the superior sagittal sinus. • The superficial middle cerebral vein drains the lateral surface of the cer ...
... layer of the dura and drain into the cranial venous sinuses • External Cerebral Veins • The superior cerebral veins pass upward over the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere and empty into the superior sagittal sinus. • The superficial middle cerebral vein drains the lateral surface of the cer ...
Meninges (singular Meninx)
... Function of CSF • Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord. • It helps cushion the central nervous system (CNS), acting in a similar manner to a shock absorber. • It also acts as a chemical buffer providing immunological protection and a transpor ...
... Function of CSF • Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord. • It helps cushion the central nervous system (CNS), acting in a similar manner to a shock absorber. • It also acts as a chemical buffer providing immunological protection and a transpor ...
heart
... the right atrium the blood which has become deoxygenated and taken up carbon dioxide during its circulation through the tissues of the body. From the right atrium this venous blood passes into the right ventricle, by which it is expelled into the pulmonary trunk to be conveyed to the lungs. As it ci ...
... the right atrium the blood which has become deoxygenated and taken up carbon dioxide during its circulation through the tissues of the body. From the right atrium this venous blood passes into the right ventricle, by which it is expelled into the pulmonary trunk to be conveyed to the lungs. As it ci ...
LEI examination points: • Lateral epicondyle, left and right
... • Medial femoral condyle, left and right - Find the joint line of the knee. Move the fingers approximately 2.5 cm (1 inch) proximal to this to locate the bony diffuse swelling on the medial femoral condyle - The thumb is pressed on the medial femoral condyle, sufficient to blanch the nail and the en ...
... • Medial femoral condyle, left and right - Find the joint line of the knee. Move the fingers approximately 2.5 cm (1 inch) proximal to this to locate the bony diffuse swelling on the medial femoral condyle - The thumb is pressed on the medial femoral condyle, sufficient to blanch the nail and the en ...
Mortuaries - Guidelines to Promote Safe Working
... per hour (vented to the exterior) with the air flow moving away from the operators’ breathing zone. 2. Local exhaust ventilation is provided over bone cutting saws or bandsaws used for sectioning of tissue. 3. All personnel who are in contact with the body or any specimens must use personal protecti ...
... per hour (vented to the exterior) with the air flow moving away from the operators’ breathing zone. 2. Local exhaust ventilation is provided over bone cutting saws or bandsaws used for sectioning of tissue. 3. All personnel who are in contact with the body or any specimens must use personal protecti ...
The Fifth Lumbar Vertebra - Aligned for Life Pilates
... The flexible spinal column is comprised of 26 bones – 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar (which make up the 24 articulating vertebrae), 1 sacral (which is usually made up of 5 fused vertebrae) and 1 coccygeal (which is also comprises 3 to 5 fused vertebrae). The spinal column’s primary roles and func ...
... The flexible spinal column is comprised of 26 bones – 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar (which make up the 24 articulating vertebrae), 1 sacral (which is usually made up of 5 fused vertebrae) and 1 coccygeal (which is also comprises 3 to 5 fused vertebrae). The spinal column’s primary roles and func ...
Chapter 18/Anatomy of blood vessels
... spleen, pancreas, intestines and liver. Blood flow is very adjustable. ...
... spleen, pancreas, intestines and liver. Blood flow is very adjustable. ...
Digital Necropsy of a Bottlenose Dolphin
... terrestrial mammals, certain aspects of their anatomy more closely resemble humans than fish. For example, a dolphin’s heart has four chambers and supplies oxygenated blood to both the lungs and the body. This is an important distinction between cetaceans and fish, which have a two-chambered heart a ...
... terrestrial mammals, certain aspects of their anatomy more closely resemble humans than fish. For example, a dolphin’s heart has four chambers and supplies oxygenated blood to both the lungs and the body. This is an important distinction between cetaceans and fish, which have a two-chambered heart a ...
Test Bank for The Muscular System
... 1. Which are the two major divisions of the human body? a. upper extremities and lower extremities b. axial body and upper extremities c. appendicular body and extremities d. axial body and appendicular body ANS: D 2. In kinesiology terminology, the arm is the body part that is located between a. th ...
... 1. Which are the two major divisions of the human body? a. upper extremities and lower extremities b. axial body and upper extremities c. appendicular body and extremities d. axial body and appendicular body ANS: D 2. In kinesiology terminology, the arm is the body part that is located between a. th ...
ANATOMY OF FEMALE REPRODUCTION ORGANS
... ovary in various phases of development. The structures include primordial follicles, maturing follicles, graffian follicle and corpus luteum. Atresia of structures results in formation of atretic follicles or corpus albicans. Medulla It consists of loose connective tissue few unstriped muscles, bloo ...
... ovary in various phases of development. The structures include primordial follicles, maturing follicles, graffian follicle and corpus luteum. Atresia of structures results in formation of atretic follicles or corpus albicans. Medulla It consists of loose connective tissue few unstriped muscles, bloo ...
Abdomen - Начало
... Relationship between the organs and peritoneum Due to intraembryonal processes the organs have different relationship with the peritoneum. 1. Intraperitoneal organs are entirely covered with peritoneum. They are connected to the abdominal wall with ligaments or meso, which ensures greater mobility. ...
... Relationship between the organs and peritoneum Due to intraembryonal processes the organs have different relationship with the peritoneum. 1. Intraperitoneal organs are entirely covered with peritoneum. They are connected to the abdominal wall with ligaments or meso, which ensures greater mobility. ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepepharmanatomy.wordpress.com Y
... response to signals from presynaptic neurons. The powerful medullary hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) activate the body to a flight-or-fight status in response to traumatic stress. They also increase heart rate and blood pressure, dilate the bronchioles, and chang ...
... response to signals from presynaptic neurons. The powerful medullary hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) activate the body to a flight-or-fight status in response to traumatic stress. They also increase heart rate and blood pressure, dilate the bronchioles, and chang ...
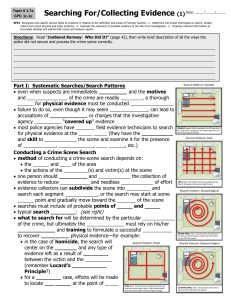
Searching For/Collecting Evidence (1) SFS1
... physical evidence is also collected in the autopsy room (for deceased victims): the medical examiner/coroner carefully examines the victim to establish a cause and manner of death (more on this later) tissues/organs are routinely retained for pathological/toxicological examination evidence c ...
... physical evidence is also collected in the autopsy room (for deceased victims): the medical examiner/coroner carefully examines the victim to establish a cause and manner of death (more on this later) tissues/organs are routinely retained for pathological/toxicological examination evidence c ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.