Use for “null set” (no solutions)
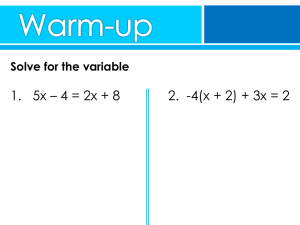
... If given a choice, most of us would rather work a problem in whole numbers rather than fractions or decimals. We’re going to look at a little gimmick that will “clear the factions” from an equations. We’re going to look at lots of examples. (It’s always a good idea to check your answers by substitut ...
... If given a choice, most of us would rather work a problem in whole numbers rather than fractions or decimals. We’re going to look at a little gimmick that will “clear the factions” from an equations. We’re going to look at lots of examples. (It’s always a good idea to check your answers by substitut ...
Sections 6.3, 10.4, and Slope Field
... dy f x g y dx dy To solve, we treat as a fraction. dx Put the y’s on the left with dy, put x’s on the right with dx, and integrate each side. ...
... dy f x g y dx dy To solve, we treat as a fraction. dx Put the y’s on the left with dy, put x’s on the right with dx, and integrate each side. ...
Document
... 1. For constant l, number of nodes along r increases with increasing n. 2. For l=n, all nodes are in the angular coordinates (2p, 3d, etc.). ...
... 1. For constant l, number of nodes along r increases with increasing n. 2. For l=n, all nodes are in the angular coordinates (2p, 3d, etc.). ...
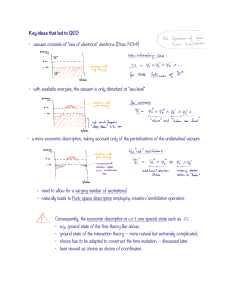
Time-dependent perturbation theory
... of the problem lies in establishing that the change is sudden enough. This is achieved by estimating the actual time taken for the Hamiltonian to change, and the periods of motion associated with the state |n! and with its transitions to neighboring states. ...
... of the problem lies in establishing that the change is sudden enough. This is achieved by estimating the actual time taken for the Hamiltonian to change, and the periods of motion associated with the state |n! and with its transitions to neighboring states. ...
HOMEWORK 5 DUE: Fri., Apr. 30 NAME: DIRECTIONS: • STAPLE
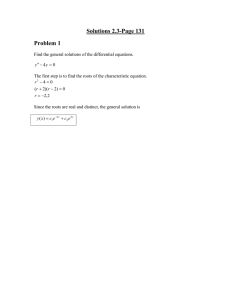
... Since W (et , e−t , e2t , e−2t ) 6= 0 these form a fundamental set of solutions. Problem 4: (2 points) Find the general solution to the differential equation y (5) + 5y (4) − 2y (3) − 10y (2) + y (1) + 5y = 0. The characteristic equation is given by m5 + 5m4 − 2m3 − 10m2 + m + 5 = 0. The possible ra ...
... Since W (et , e−t , e2t , e−2t ) 6= 0 these form a fundamental set of solutions. Problem 4: (2 points) Find the general solution to the differential equation y (5) + 5y (4) − 2y (3) − 10y (2) + y (1) + 5y = 0. The characteristic equation is given by m5 + 5m4 − 2m3 − 10m2 + m + 5 = 0. The possible ra ...
Exam 3
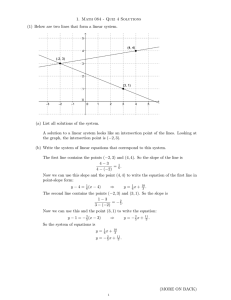
... APPM 2360: Section exam 3 July 8, 2011. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: (1) your name, (2) your instructor’s name, and (3) a grading table. Text books, class notes, and calculators are NOT permitted. A one-page crib sheet is allowed. Problem 1: (20 points) (a) Find the general solution for the ...
... APPM 2360: Section exam 3 July 8, 2011. ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: (1) your name, (2) your instructor’s name, and (3) a grading table. Text books, class notes, and calculators are NOT permitted. A one-page crib sheet is allowed. Problem 1: (20 points) (a) Find the general solution for the ...