course outline - Modesto Junior College
... A4. determine if a given improper integral is convergent or divergent and evaluate it if convergent. B1. calculate the arc length of a given function between two given values. B2. determine the area of a surface of revolution. B3. solve application problems from science, engineering, economics and/o ...
... A4. determine if a given improper integral is convergent or divergent and evaluate it if convergent. B1. calculate the arc length of a given function between two given values. B2. determine the area of a surface of revolution. B3. solve application problems from science, engineering, economics and/o ...
Electric Fields
... The Coulomb constant ke has a value of 8.9876 x 109 N・m2/C2 and can be written where e0 is the permittivity of free space with a value 8.8542 x 10–12 C2/N・m2 ...
... The Coulomb constant ke has a value of 8.9876 x 109 N・m2/C2 and can be written where e0 is the permittivity of free space with a value 8.8542 x 10–12 C2/N・m2 ...
Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home Work
... Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home Work Problems ...
... Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home Work Problems ...
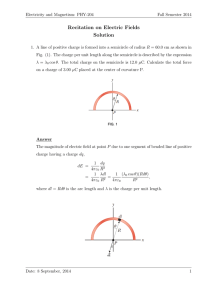
Recitation on Electric Fields Solution
... parallel to the axis of the ring and dE⊥ perpendicular to the axis. Figure (b) shows the electric field contributions from two segments on opposite sides of the ring. Because of the symmetry of the situation, the perpendicular components of the field cancel and only the parallel components will contri ...
... parallel to the axis of the ring and dE⊥ perpendicular to the axis. Figure (b) shows the electric field contributions from two segments on opposite sides of the ring. Because of the symmetry of the situation, the perpendicular components of the field cancel and only the parallel components will contri ...
Chapter 19: Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
... 16. An insulating sphere has a uniform surface charge density, and exerts a force on a point charge that is placed nearby but outside the sphere. The insulating sphere is then replaced by an otherwise identical conducting sphere. Consider the behavior of insulating and conducting materials when answ ...
... 16. An insulating sphere has a uniform surface charge density, and exerts a force on a point charge that is placed nearby but outside the sphere. The insulating sphere is then replaced by an otherwise identical conducting sphere. Consider the behavior of insulating and conducting materials when answ ...
Fields/Forces
... The electric field at a point near a charge is equal to the force that an imaginary +1 C of charge would receive if placed at the point. The unit of electric field is Newton per Coulomb. The electric force on a charge in an electric field is equal to the electric field’s strength times the size of t ...
... The electric field at a point near a charge is equal to the force that an imaginary +1 C of charge would receive if placed at the point. The unit of electric field is Newton per Coulomb. The electric force on a charge in an electric field is equal to the electric field’s strength times the size of t ...
Homework #5 assignment
... Reading assignment: Griffiths sections 8.2 and 9.1 Problem 1. (a) Consider two equal point charges q at the points (x, y, z) = (0, 0, a) and (0, 0, −a). Find the Maxwell stress tensor everywhere on the infinite xy plane equidistant from the two charges. Use rectangular coordinates. (b) By integratin ...
... Reading assignment: Griffiths sections 8.2 and 9.1 Problem 1. (a) Consider two equal point charges q at the points (x, y, z) = (0, 0, a) and (0, 0, −a). Find the Maxwell stress tensor everywhere on the infinite xy plane equidistant from the two charges. Use rectangular coordinates. (b) By integratin ...
Grade 11 Physics – Course Review Part 2
... (The separation of the plates has nothing to do with this force.) 7. The net force on it will be: Fnet = FE + Fg = 1.536 x 10 – 12 - 1.6 x 10 – 13 (9.8) = - 3.2 x 10 – 14 N (downward) giving an acceleration of a = Fnet ÷ m = 0.20 m/s2, downward. 8. Both electric fields and magnetics fields surround ...
... (The separation of the plates has nothing to do with this force.) 7. The net force on it will be: Fnet = FE + Fg = 1.536 x 10 – 12 - 1.6 x 10 – 13 (9.8) = - 3.2 x 10 – 14 N (downward) giving an acceleration of a = Fnet ÷ m = 0.20 m/s2, downward. 8. Both electric fields and magnetics fields surround ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.