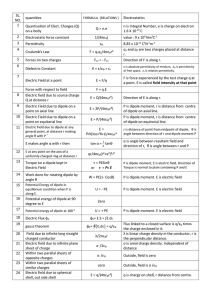
Charges, currents & reference frames
... moving within a magnetic field created by the other charge and there is an attractive force between the charges which the observer describes as magnetic in origin. There is both an increased electrostatic repulsive force and a new magnetic attractive force compared with the stationary observer frame ...
... moving within a magnetic field created by the other charge and there is an attractive force between the charges which the observer describes as magnetic in origin. There is both an increased electrostatic repulsive force and a new magnetic attractive force compared with the stationary observer frame ...
The electric field
... A. When there are more electric field lines leaving a gaussian surface than entering it then there is a net negative charge enclosed by the surface. B. Gauss's law can be used to find the electric field if the total charge inside a closed surface is known even if the distribution of that charge is n ...
... A. When there are more electric field lines leaving a gaussian surface than entering it then there is a net negative charge enclosed by the surface. B. Gauss's law can be used to find the electric field if the total charge inside a closed surface is known even if the distribution of that charge is n ...
BilaksPhysiks
... -3Q will help us find expressions for the electric field in the regions ab.
• Sketch the charge configuration of the spherical shell
considering all sources of electric field (combine your
...
... -3Q will help us find expressions for the electric field in the regions a
Tuesday, Sept. 13, 2011
... • Draw the appropriate gaussian surface, making sure it passes through the point you want to know the electric field • Use the symmetry of charge distribution to determine the direction of E at the point of gaussian surface • Evaluate the flux • Calculate the enclosed charge by the gaussian surf ...
... • Draw the appropriate gaussian surface, making sure it passes through the point you want to know the electric field • Use the symmetry of charge distribution to determine the direction of E at the point of gaussian surface • Evaluate the flux • Calculate the enclosed charge by the gaussian surf ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE FINAL REVIEW Multiple Choice Protons and
... 35. Two charges separated by one meter exert a one N force on each other. If the charges are pushed to a ¼ meter separation, the force on each charge will be a. 1 N b. 2 N c. 4 N d. 8 N e. 16 N 36. A race car moving away from you sounds ____ frequency than it really is a. ...
... 35. Two charges separated by one meter exert a one N force on each other. If the charges are pushed to a ¼ meter separation, the force on each charge will be a. 1 N b. 2 N c. 4 N d. 8 N e. 16 N 36. A race car moving away from you sounds ____ frequency than it really is a. ...
document
... fuse box and branches out to appliances, wall socket and lights. Circuit breakers – small piece of metal that bends when it gets hot, opening circuit and stopping current flow. Electronic fuse - small piece of metal that melts if current becomes to high, opening circuit ...
... fuse box and branches out to appliances, wall socket and lights. Circuit breakers – small piece of metal that bends when it gets hot, opening circuit and stopping current flow. Electronic fuse - small piece of metal that melts if current becomes to high, opening circuit ...
Chapter 18 - Purdue Physics
... equal to the energy required to move all the packets of charge from one plate to the other Section 18.4 ...
... equal to the energy required to move all the packets of charge from one plate to the other Section 18.4 ...
Chapter 1
... d) both are positive or both are negative The fact that the balls repel each other only can tell you that they have the same charge, but you do not know the sign. So they can be either both positive or both negative. Follow-up: What does the picture look like if the two balls are oppositely charged? ...
... d) both are positive or both are negative The fact that the balls repel each other only can tell you that they have the same charge, but you do not know the sign. So they can be either both positive or both negative. Follow-up: What does the picture look like if the two balls are oppositely charged? ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide
... LT 1: I can explain moving and static electrical charges (the behavior of charged objects). 1. Draw a simple series circuit with a light bulb as your load, a battery as your energy source, and include a switch. Diagram should include a battery- wire from one battery terminal (-) to the light- ligh ...
... LT 1: I can explain moving and static electrical charges (the behavior of charged objects). 1. Draw a simple series circuit with a light bulb as your load, a battery as your energy source, and include a switch. Diagram should include a battery- wire from one battery terminal (-) to the light- ligh ...
WinFinalSoln
... (a) Velocity selector: When a charged particle travels through crossed E and B fields (both of which fill the region below), the trajectory will be undeflected (continuing in a straight line) only if the velocity has a certain relationship to E and B. This setup effectively “selects” particles with ...
... (a) Velocity selector: When a charged particle travels through crossed E and B fields (both of which fill the region below), the trajectory will be undeflected (continuing in a straight line) only if the velocity has a certain relationship to E and B. This setup effectively “selects” particles with ...
Chapter 1
... d) both are positive or both are negative The fact that the balls repel each other only can tell you that they have the same charge, but you do not know the sign. So they can be either both positive or both negative. Follow-up: What does the picture look like if the two balls are oppositely charged? ...
... d) both are positive or both are negative The fact that the balls repel each other only can tell you that they have the same charge, but you do not know the sign. So they can be either both positive or both negative. Follow-up: What does the picture look like if the two balls are oppositely charged? ...
Electrostatics
... Coulomb’s law Coulomb’s Law: The magnitude of the force between two point charges is proportional to the h i ti l t th product of their charges and inversely proportional to the inversely proportional to the square of their separation. ...
... Coulomb’s law Coulomb’s Law: The magnitude of the force between two point charges is proportional to the h i ti l t th product of their charges and inversely proportional to the inversely proportional to the square of their separation. ...
Maxwell`s equations
... These equations specify the response of bound charge and current to the applied fields and are called constitutive relations. ...
... These equations specify the response of bound charge and current to the applied fields and are called constitutive relations. ...
Gravitational Relativity Proposed by David Penny The only intrinsic
... Gravitational Relativity Proposed by David Penny 1. The only intrinsic property of matter is electric charge. There is no relativistic change of intrinsic electric charge with velocity in any relative frame of reference. 2. Electric charges emit longitudinal electric waves. Positive charges transmit ...
... Gravitational Relativity Proposed by David Penny 1. The only intrinsic property of matter is electric charge. There is no relativistic change of intrinsic electric charge with velocity in any relative frame of reference. 2. Electric charges emit longitudinal electric waves. Positive charges transmit ...
PH504lec0910-9
... There are no equilibrium positions away from the x-axis. This question has a complication which is easy to miss in that you have to be very careful concerning the signs of the three terms which contribute to the P.E. For example in the region -a
... There are no equilibrium positions away from the x-axis. This question has a complication which is easy to miss in that you have to be very careful concerning the signs of the three terms which contribute to the P.E. For example in the region -a
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.