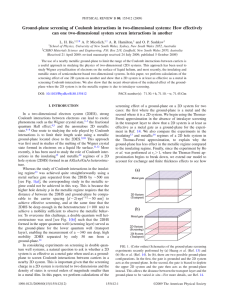
Wave Propagation through Vegetation at 3.1 GHz and 5.8 GHz
... branches, the size and shape of these are important. For low frequencies — when the wavelength is much larger than the scattering body — leaves and branches have only a small interaction to the electromagnetic field, which means that surface irregularities have no — or minor — influence on the atten ...
... branches, the size and shape of these are important. For low frequencies — when the wavelength is much larger than the scattering body — leaves and branches have only a small interaction to the electromagnetic field, which means that surface irregularities have no — or minor — influence on the atten ...
Optimal Design of 245kV SF6 Bushing by Using Genetic
... demands on bushings, as the dimension of bushings is relatively small compared with the equipment that connects by bushings. Besides that, the manufacturing, design and operation of bushings should exceed the requirements of its applications during the lifetime. It is a challenge to complete such a ...
... demands on bushings, as the dimension of bushings is relatively small compared with the equipment that connects by bushings. Besides that, the manufacturing, design and operation of bushings should exceed the requirements of its applications during the lifetime. It is a challenge to complete such a ...
Laboratory studies of waves and instabilities in dusty plasmas
... become a dynamical variable and represent an additional degree of freedom unavailable to a classical plasma. Charged dust particles in a plasma introduce unique potential structures and significantly alter the short and long range forces which can affect the short and long range ordering of the dust ...
... become a dynamical variable and represent an additional degree of freedom unavailable to a classical plasma. Charged dust particles in a plasma introduce unique potential structures and significantly alter the short and long range forces which can affect the short and long range ordering of the dust ...
Thesis Manuscript - Materials Physics Center
... is illuminated from the inside, in transmission mode, the cup turns red, showing its glowing ruby colour. This effect is due to the presence of small gold and silver particles in the glass, around 5 − 60 nm in size [2]. The same effect is also responsible for the colours of stained glass, very popul ...
... is illuminated from the inside, in transmission mode, the cup turns red, showing its glowing ruby colour. This effect is due to the presence of small gold and silver particles in the glass, around 5 − 60 nm in size [2]. The same effect is also responsible for the colours of stained glass, very popul ...
Michael Faraday Physicist www.AssignmentPoint.com Michael
... briefly set up a circuit to study whether a magnetic field could regulate the flow of a current in an adjacent wire, but he found no such relationship. This experiment followed similar work conducted with light and magnets three years earlier that yielded identical results. During the next seven yea ...
... briefly set up a circuit to study whether a magnetic field could regulate the flow of a current in an adjacent wire, but he found no such relationship. This experiment followed similar work conducted with light and magnets three years earlier that yielded identical results. During the next seven yea ...
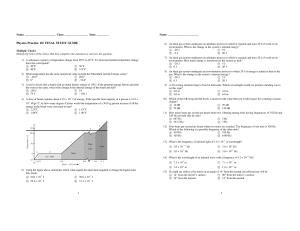
AP Phys B FRQ - Blue Valley Schools
... A particle with unknown mass and charge moves with constant speed v = 1.9 x 106 mIs as it passes undeflected through a pair of parallel plates, as shown above. The plates are separated by a distance d = 6.0 x I o- m, and a constant potential difference V is maintained between them. A uniform magneti ...
... A particle with unknown mass and charge moves with constant speed v = 1.9 x 106 mIs as it passes undeflected through a pair of parallel plates, as shown above. The plates are separated by a distance d = 6.0 x I o- m, and a constant potential difference V is maintained between them. A uniform magneti ...
Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance in Bimetallic Core
... Various applications for LSPRs are in optics, photo catalysis, medicine and photovoltaics. For our research, we use the Mie Theory to analyze the LSPR properties of bimetallic core-shell nanoparticles in the shape of a sphere and consisting of Drude metals. We have come to see that there is a specia ...
... Various applications for LSPRs are in optics, photo catalysis, medicine and photovoltaics. For our research, we use the Mie Theory to analyze the LSPR properties of bimetallic core-shell nanoparticles in the shape of a sphere and consisting of Drude metals. We have come to see that there is a specia ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.