chapter25
... Use integrals for evaluating the total potential at some point Each element of the charge distribution is treated as a point charge If the electric field is given Start with the definition of the electric potential Find the field from Gauss’ Law (or some other process) if ...
... Use integrals for evaluating the total potential at some point Each element of the charge distribution is treated as a point charge If the electric field is given Start with the definition of the electric potential Find the field from Gauss’ Law (or some other process) if ...
Notes - Electrostatics_2pp
... of 580 N/C. What is the maximum possible electric flux through the surface? The maximum possible flux occurs when the electric field is parallel to the normal of the rectangular surface (that is, when the angle between the direction of the field and the direction of the normal is zero). Then, ...
... of 580 N/C. What is the maximum possible electric flux through the surface? The maximum possible flux occurs when the electric field is parallel to the normal of the rectangular surface (that is, when the angle between the direction of the field and the direction of the normal is zero). Then, ...
Problem Set 6
... Explain why a lightbulb almost always burn out just as they are turned on and not after they have been on for some time. Question D The heating element in a toaster is made of Nichrome wire. Immediately after the toaster is turned on, is the current in the wire increasing, decreasing, or staying con ...
... Explain why a lightbulb almost always burn out just as they are turned on and not after they have been on for some time. Question D The heating element in a toaster is made of Nichrome wire. Immediately after the toaster is turned on, is the current in the wire increasing, decreasing, or staying con ...
Static Electricity and Charge Accumulation
... The capacitance of the vessel is calculated as before (typically assume equivalent spherical vessel). The static energy stored in the vessel is then calculated from E=Q2/2C. Examples 7-9 and 7-10 demonstrate using this relationship. ...
... The capacitance of the vessel is calculated as before (typically assume equivalent spherical vessel). The static energy stored in the vessel is then calculated from E=Q2/2C. Examples 7-9 and 7-10 demonstrate using this relationship. ...
Powerpoint
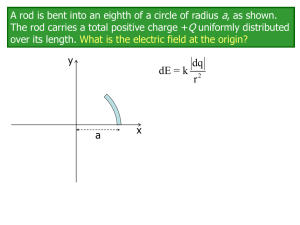
... A rod is bent into an eighth of a circle of radius a, as shown. The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You coul ...
... A rod is bent into an eighth of a circle of radius a, as shown. The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You coul ...
PowerPoint
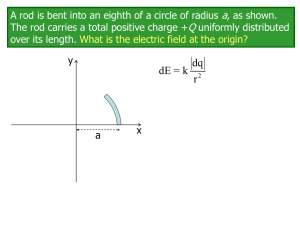
... A rod is bent into an eighth of a circle of radius a, as shown. The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You coul ...
... A rod is bent into an eighth of a circle of radius a, as shown. The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You coul ...
Document
... where s is the distance from the negative electrode. The electric potential, like the electric field, exists at all points inside the capacitor. The electric potential is created by the source charges on the capacitor plates and exists whether or not charge q is inside the capacitor. ...
... where s is the distance from the negative electrode. The electric potential, like the electric field, exists at all points inside the capacitor. The electric potential is created by the source charges on the capacitor plates and exists whether or not charge q is inside the capacitor. ...
19_ConcepTests_Clickers - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... The two +Q charges give a resultant E field that is down and to the right. The –Q charge has an E field up and to the left, but smaller in magnitude. Therefore, the total electric field is down and to the right. Follow-up: What if all three charges reversed their signs? ...
... The two +Q charges give a resultant E field that is down and to the right. The –Q charge has an E field up and to the left, but smaller in magnitude. Therefore, the total electric field is down and to the right. Follow-up: What if all three charges reversed their signs? ...
Lecture13reallynew
... •Solution to this “paradox”: divergence is non-zero at the origin: applying definition of divergence to small sphere around origin and only a fraction of these field lines emerge into the cone; therefore divergence theorem works, if origin (source of field lines) is properly treated ...
... •Solution to this “paradox”: divergence is non-zero at the origin: applying definition of divergence to small sphere around origin and only a fraction of these field lines emerge into the cone; therefore divergence theorem works, if origin (source of field lines) is properly treated ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... In the Einstein model for a solid, atoms are treated as one-dimensional quantum mechanical oscillators that can each accept an arbitrary number of energy units above the ground state. Recall that the multiplicity Ω(N, q) = (q + N − 1)!/(q!(N − 1)!) gives the number of states available to a system co ...
... In the Einstein model for a solid, atoms are treated as one-dimensional quantum mechanical oscillators that can each accept an arbitrary number of energy units above the ground state. Recall that the multiplicity Ω(N, q) = (q + N − 1)!/(q!(N − 1)!) gives the number of states available to a system co ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.