Module 4 UNDERSTANDING ELECTRICITY AND
... What is electricity? In today’s world we grow up in an environment where electrical power is everywhere around us and we sometimes accept this unquestioningly ... we take it for granted. 6 a.m. Another weekday. The clock-radio blares, but you lie in bed a few minutes longer, listening to the news an ...
... What is electricity? In today’s world we grow up in an environment where electrical power is everywhere around us and we sometimes accept this unquestioningly ... we take it for granted. 6 a.m. Another weekday. The clock-radio blares, but you lie in bed a few minutes longer, listening to the news an ...
Goal of this chapter is to learn the how to calculate the magnetic field
... is: ⃗μ =I ⃗A ). When materials are placed in magnetic field, the magnetic dipole moments in the materials will be re-arranged or changed and change the magnetic field around it. • Very similar to dielectric materials (with dielectric constant, K) placed in electric field, ⃗E . (Recall that: in capac ...
... is: ⃗μ =I ⃗A ). When materials are placed in magnetic field, the magnetic dipole moments in the materials will be re-arranged or changed and change the magnetic field around it. • Very similar to dielectric materials (with dielectric constant, K) placed in electric field, ⃗E . (Recall that: in capac ...
mjk_icopsO1.pps - Mark J. Kushner
... Electric field emission from the trigger electrode initiates the discharge. Densities of 1011 cm-3 are produced by the trigger pulse. Avalanche in the main gap is anode directed due to cathode preionization. After gap closure, avalanche is cathode directed. “Prearrival” of avalanche at anode ...
... Electric field emission from the trigger electrode initiates the discharge. Densities of 1011 cm-3 are produced by the trigger pulse. Avalanche in the main gap is anode directed due to cathode preionization. After gap closure, avalanche is cathode directed. “Prearrival” of avalanche at anode ...
1 - gtbit
... 34. Find out the current density and electric field intensity for aluminum conductor with conductivity σ= 3.82 x 10 7 Seimen /m and the mobility of electron μe = 0.0014 m2/ (Volt-sec) and drift velocity = 5.3 x 10-4 m/s. [E = 0.3786 V/m, J = 1.446x 107 Amp/m2] ...
... 34. Find out the current density and electric field intensity for aluminum conductor with conductivity σ= 3.82 x 10 7 Seimen /m and the mobility of electron μe = 0.0014 m2/ (Volt-sec) and drift velocity = 5.3 x 10-4 m/s. [E = 0.3786 V/m, J = 1.446x 107 Amp/m2] ...
Using the “Clicker”
... To ensure that the ions arriving at step 3 have the same velocity, the ions pass through a velocity selector, a region with uniform electric and magnetic fields. The electric field comes from a set of parallel plates, and exerts a force of FE qE on the ions. The magnetic field is perpendicular to ...
... To ensure that the ions arriving at step 3 have the same velocity, the ions pass through a velocity selector, a region with uniform electric and magnetic fields. The electric field comes from a set of parallel plates, and exerts a force of FE qE on the ions. The magnetic field is perpendicular to ...
ENE 429 Antenna and Transmission Lines
... and a dielectric with relative permittivity of 1200 has a 12. V potential difference across the plates. Calculate (a) the capacitance, and (b) the magnitude of the charge density on one of the ...
... and a dielectric with relative permittivity of 1200 has a 12. V potential difference across the plates. Calculate (a) the capacitance, and (b) the magnitude of the charge density on one of the ...
A When thinking about current flow, think about fluid flow.
... •Define resistance as the ratio of the voltage to the current ...
... •Define resistance as the ratio of the voltage to the current ...
Lecture XVIII_XIX
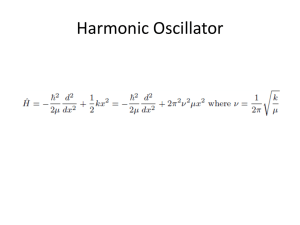
... be approximated by a parabola near the bottom of the well. The parabolic potential leads to harmonic oscillations. • At high excitation energies the parabolic approximation is poor (the true potential is less confining), and does not apply near the dissociation limit. • Must therefore use a asymmetr ...
... be approximated by a parabola near the bottom of the well. The parabolic potential leads to harmonic oscillations. • At high excitation energies the parabolic approximation is poor (the true potential is less confining), and does not apply near the dissociation limit. • Must therefore use a asymmetr ...
http://www.wccm-eccm-ecfd2014.org/admin/files/filePaper/p2949.pdf
... larization and electric field forces at the bubble and spike frontiers of both A and B cases clearly reveals that the electric field force is dominant over the polarization force on the tip positions of bubble and spike. On the other hand, the polarization force is obviously much greater than the el ...
... larization and electric field forces at the bubble and spike frontiers of both A and B cases clearly reveals that the electric field force is dominant over the polarization force on the tip positions of bubble and spike. On the other hand, the polarization force is obviously much greater than the el ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.