Ag Awareness – Plants
... This part makes seeds. Stem This part carries food and water through the plant. Leaf This part makes food for the plant. Root This part carries water from the soil to the plant. ...
... This part makes seeds. Stem This part carries food and water through the plant. Leaf This part makes food for the plant. Root This part carries water from the soil to the plant. ...
Pale and Black Swallow-worts
... tolerant and will thrive in a wide range of soil, moisture and light conditions, with the exception of extremely wet soils. Populations growing under dense wooded canopy may have inadequate resources to produce flowers or seeds. Swallow-wort dies back to the ground every winter. Its root crown fragm ...
... tolerant and will thrive in a wide range of soil, moisture and light conditions, with the exception of extremely wet soils. Populations growing under dense wooded canopy may have inadequate resources to produce flowers or seeds. Swallow-wort dies back to the ground every winter. Its root crown fragm ...
botany_plantphys_2008
... Biennial: A plant the requires two growing seasons to complete its lifecycle. Herbaceous perennial: A non-woody plant that lives for several years. It’s shoots die back every winter. Woody perennial: A tree or shrub ...
... Biennial: A plant the requires two growing seasons to complete its lifecycle. Herbaceous perennial: A non-woody plant that lives for several years. It’s shoots die back every winter. Woody perennial: A tree or shrub ...
CLASSIFICATION VOCABULARY 72L
... Ex Homo sapien= human The highest taxonomic group into which organisms are grouped; 1 of 5 biological categories: Monera or Protist or Plant or Fungi or Animal. Taxonomic group containing 1 or more species ...
... Ex Homo sapien= human The highest taxonomic group into which organisms are grouped; 1 of 5 biological categories: Monera or Protist or Plant or Fungi or Animal. Taxonomic group containing 1 or more species ...
plant form and function _1
... Why is it adaptive for some seeds to remain dormant before they germinate? Why did the development of the seed was a major factor in the success of plants? How do the flowers of wind-pollinated plants differ from the flowers of animal-pollinated plants? How might it be an advantage for a pla ...
... Why is it adaptive for some seeds to remain dormant before they germinate? Why did the development of the seed was a major factor in the success of plants? How do the flowers of wind-pollinated plants differ from the flowers of animal-pollinated plants? How might it be an advantage for a pla ...
2 - Capital High School
... What do plants need to survive? ____________ – make food through photosynthesis __________________ (CO2 and O2) ________________ and ____________________ Plant evolution The ancestor to today’s plants were similar to ___________________ Plants are divided into ___________ major groups ...
... What do plants need to survive? ____________ – make food through photosynthesis __________________ (CO2 and O2) ________________ and ____________________ Plant evolution The ancestor to today’s plants were similar to ___________________ Plants are divided into ___________ major groups ...
Weed of the Month (November 2009)
... mature size (Figure 2). Peppervine has inconspicuous green‑ ish‑white flowers opposite the leaves from June through August, and the berries appear from September into late fall. As a cluster of berries mature, their coloration gradually changes from green to white (Figure 3) to red to shiny blue-bla ...
... mature size (Figure 2). Peppervine has inconspicuous green‑ ish‑white flowers opposite the leaves from June through August, and the berries appear from September into late fall. As a cluster of berries mature, their coloration gradually changes from green to white (Figure 3) to red to shiny blue-bla ...
CONSERVATION
... • Remove or modify a specific disturbance to allow ecological process to bring about an independent recovery ...
... • Remove or modify a specific disturbance to allow ecological process to bring about an independent recovery ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... when a root’s position is altered. This causes the root to re-orient and turn downward. This response is adaptive because as a root grows, it encounters obstacles in the soil that it must grow around. Alternately, animals may partially uproot a plant. If the roots can continue to make their way into ...
... when a root’s position is altered. This causes the root to re-orient and turn downward. This response is adaptive because as a root grows, it encounters obstacles in the soil that it must grow around. Alternately, animals may partially uproot a plant. If the roots can continue to make their way into ...
Water Plant
... 1. All living things need water to live and grow. Plants are living things, therefore they need water to live and grow. 2. Plants require 16 specific chemical elements to grow and live, but not all plants require the same elements. 3. Feeding plants coffee grounds helps to keep bugs from eating the ...
... 1. All living things need water to live and grow. Plants are living things, therefore they need water to live and grow. 2. Plants require 16 specific chemical elements to grow and live, but not all plants require the same elements. 3. Feeding plants coffee grounds helps to keep bugs from eating the ...
4S D K - lhornec2e
... 1. All living things need water to live and grow. Plants are living things, therefore they need water to live and grow. 2. Plants require 16 specific chemical elements to grow and live, but not all plants require the same elements. 3. Feeding plants coffee grounds helps to keep bugs from eating the ...
... 1. All living things need water to live and grow. Plants are living things, therefore they need water to live and grow. 2. Plants require 16 specific chemical elements to grow and live, but not all plants require the same elements. 3. Feeding plants coffee grounds helps to keep bugs from eating the ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... Plant Reproduction Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on your answer document. 1.Plants who take two years to complete their life cycles are called a. sporophyte c. biennials b. annuals d. perennials 2.Which is a disadvantage of reproducing asexually a. one parent can quickly pro ...
... Plant Reproduction Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on your answer document. 1.Plants who take two years to complete their life cycles are called a. sporophyte c. biennials b. annuals d. perennials 2.Which is a disadvantage of reproducing asexually a. one parent can quickly pro ...
Parts of a Plant
... axillary bud - a bud that develops in the axil. flower - the reproductive unit of angiosperms. flower stalk - the structure that supports the flower. internode - the area of the stem between any two adjacent nodes. lateral shoot (branch) - an offshoot of the stem of a plant. leaf - an outgrowth of a ...
... axillary bud - a bud that develops in the axil. flower - the reproductive unit of angiosperms. flower stalk - the structure that supports the flower. internode - the area of the stem between any two adjacent nodes. lateral shoot (branch) - an offshoot of the stem of a plant. leaf - an outgrowth of a ...
Lecture 29 Rise of Science in the 17th and 18th Century
... remained until his death. His labors have earned him the title of “Father of Taxonomy.” Linnaeus established groups of organisms, large and small, that depended upon structural or morphological similarities and differences. The basic taxonomic criteria for grouping plants was based on the morphology ...
... remained until his death. His labors have earned him the title of “Father of Taxonomy.” Linnaeus established groups of organisms, large and small, that depended upon structural or morphological similarities and differences. The basic taxonomic criteria for grouping plants was based on the morphology ...
Monocots vs Dicots
... Classification of Plants Plants are the fundamental building blocks of life on earth. Plants are life forms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. The scientific study has revealed at least 500,000 species of plants. The types of plants vary in size from microscopic algae, to huge sequoia trees more ...
... Classification of Plants Plants are the fundamental building blocks of life on earth. Plants are life forms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. The scientific study has revealed at least 500,000 species of plants. The types of plants vary in size from microscopic algae, to huge sequoia trees more ...
Chapter 6 Test Study Guide 6.1 Vocab: Root cap – protects the root
... Cambium – layer of cells that divide to produce new phloem and xylem Stoma – openings (pores) on the surface layers of the leaf; open and close to control when gases enter and leave the leaf (close to conserve water) Transpiration – process by which water evaporates from a plant’s leaves Embryo – a ...
... Cambium – layer of cells that divide to produce new phloem and xylem Stoma – openings (pores) on the surface layers of the leaf; open and close to control when gases enter and leave the leaf (close to conserve water) Transpiration – process by which water evaporates from a plant’s leaves Embryo – a ...
iii. plant classification
... modified to _prevent water loss______ and _minimize ice build-up______________________. In addition, gymnosperms (and angiosperms) have “flying sperm” or _pollen_____, so they are no longer tied to _water____ for reproduction. 3. Angiosperms – Have pollen, seeds, and fruit IV. ANGIOSPERMS - TRACHEOP ...
... modified to _prevent water loss______ and _minimize ice build-up______________________. In addition, gymnosperms (and angiosperms) have “flying sperm” or _pollen_____, so they are no longer tied to _water____ for reproduction. 3. Angiosperms – Have pollen, seeds, and fruit IV. ANGIOSPERMS - TRACHEOP ...
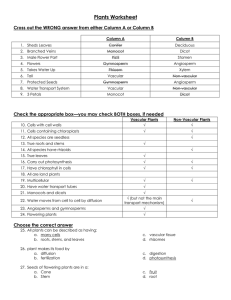
Plants Worksheet_answer key - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 33. The plant kingdom is divided into two groups based on how they: a. make food c. respond to light b. transport water and nutrients d. reproduce asexually 34. An angiosperm with two seed leaves inside its seed is classified as a: a. Monocot c. herbaceous plant b. Dicot d. gymnosperm 35. Transporti ...
... 33. The plant kingdom is divided into two groups based on how they: a. make food c. respond to light b. transport water and nutrients d. reproduce asexually 34. An angiosperm with two seed leaves inside its seed is classified as a: a. Monocot c. herbaceous plant b. Dicot d. gymnosperm 35. Transporti ...
PLANTS
... Held up by the style The style connects the stigma to the ovary The ovary contains the eggs ...
... Held up by the style The style connects the stigma to the ovary The ovary contains the eggs ...
Herbaceous plants
... • Annual plants live only one growing season • Their main purpose in life is to grow, bloom, produce seed, and die. • Can be grown easily from seed. • Many will continue to bloom and produce seed all summer. Others need to be prevented from going to seed (by removing spent flowers) for continuous bl ...
... • Annual plants live only one growing season • Their main purpose in life is to grow, bloom, produce seed, and die. • Can be grown easily from seed. • Many will continue to bloom and produce seed all summer. Others need to be prevented from going to seed (by removing spent flowers) for continuous bl ...
Slender Russian thistle (Salsola collina)
... Salsola collina is found in waste places, roadsides, railway areas, cultivated fields,disturbed natural and seminatural plant communities. Its distribution is patchy throughout northeastern and north central North America, and there are some patches within the four corners states. Salsola is drought ...
... Salsola collina is found in waste places, roadsides, railway areas, cultivated fields,disturbed natural and seminatural plant communities. Its distribution is patchy throughout northeastern and north central North America, and there are some patches within the four corners states. Salsola is drought ...
Plant Life Cycle - Mona Shores Public Schools
... This presentation was created following the Fair Use Guidelines for Educational Multimedia. Certain materials are included under the Fair Use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law. Further use of these materials and this presentation are restricted. Original presentation created by Linda Cherry, a tea ...
... This presentation was created following the Fair Use Guidelines for Educational Multimedia. Certain materials are included under the Fair Use exemption of the U.S. Copyright Law. Further use of these materials and this presentation are restricted. Original presentation created by Linda Cherry, a tea ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.