Plant Structure and Function
... Cells are loosely packed with spaces between them in lower half of leaf near stomata openings ...
... Cells are loosely packed with spaces between them in lower half of leaf near stomata openings ...
Plants final review key - Hicksville Public Schools
... 13. The table below provides some information about common plant cell structures and their functions. In the table, there are three blank spaces. Fill in the three blank spaces by writing the name of the plant cell structure that performs the function described. ...
... 13. The table below provides some information about common plant cell structures and their functions. In the table, there are three blank spaces. Fill in the three blank spaces by writing the name of the plant cell structure that performs the function described. ...
(1) A - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... 13. The table below provides some information about common plant cell structures and their functions. In the table, there are three blank spaces. Fill in the three blank spaces by writing the name of the plant cell structure that performs the function described. ...
... 13. The table below provides some information about common plant cell structures and their functions. In the table, there are three blank spaces. Fill in the three blank spaces by writing the name of the plant cell structure that performs the function described. ...
Chapter 6 – Survey of Plants ()
... • (i) Possess vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). This accounts for the remaining characteristics • (ii) Possess true roots, stems, and leaves. • (iii) Large in size, growing well above the ground. • (iv) Not restricted to moist environments; well distributed over the Earth’s surface. Can even exist ...
... • (i) Possess vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). This accounts for the remaining characteristics • (ii) Possess true roots, stems, and leaves. • (iii) Large in size, growing well above the ground. • (iv) Not restricted to moist environments; well distributed over the Earth’s surface. Can even exist ...
Chapter 5 Questions
... 1. What two major groups do prokaryotes fall into? How are these two groups similar and how are they different? Be sure to include how energy is produced and how location of habitats differs between these two groups. Prokaryotes fall into two groups: bacteria and archaea. Bacteria (also known as eub ...
... 1. What two major groups do prokaryotes fall into? How are these two groups similar and how are they different? Be sure to include how energy is produced and how location of habitats differs between these two groups. Prokaryotes fall into two groups: bacteria and archaea. Bacteria (also known as eub ...
Moudry Fountain Grass
... a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. ...
... a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. ...
Life Cycle of a Plant
... The root pushes through the seed coat. The roots of the seedling grow down into the soil and the leaves and stem push out of the ground. The stem and its leaves grow toward the sunlight. The leaves make the plant’s food. The flowers form and bloom. New seeds are formed inside the flower or within th ...
... The root pushes through the seed coat. The roots of the seedling grow down into the soil and the leaves and stem push out of the ground. The stem and its leaves grow toward the sunlight. The leaves make the plant’s food. The flowers form and bloom. New seeds are formed inside the flower or within th ...
Classification and nomenclature of flower and ornamental plants
... A.1.2.1. Flowering shrub: They are grown for flowers. e.g. Rose, jasmines, oleanders, camellia etc. A.1.2.2. Foliage shrub: They are grown for their beautiful leaves. e.g. Croton, acalypha, aralia etc. A.1.2.3. Hedge: These are special type of shrubs planted in border, usually very closely for prote ...
... A.1.2.1. Flowering shrub: They are grown for flowers. e.g. Rose, jasmines, oleanders, camellia etc. A.1.2.2. Foliage shrub: They are grown for their beautiful leaves. e.g. Croton, acalypha, aralia etc. A.1.2.3. Hedge: These are special type of shrubs planted in border, usually very closely for prote ...
Sporophyte Stage - St. Ambrose School
... Non-Vascular Plants – Do not have tubes; water and nutrients are spread from one cell to another by osmosis or diffusion ...
... Non-Vascular Plants – Do not have tubes; water and nutrients are spread from one cell to another by osmosis or diffusion ...
NATIONAL MITRE 10 GARDEN CLUB
... weeds growing. Take care not to bury the crown. Water in well Also remember that birds will try to compete with you for your after planting. In early spring remove the flowers until the plant harvest – so ensure that you cover your plants carefully with has made plenty of leaf growth. netting. I fin ...
... weeds growing. Take care not to bury the crown. Water in well Also remember that birds will try to compete with you for your after planting. In early spring remove the flowers until the plant harvest – so ensure that you cover your plants carefully with has made plenty of leaf growth. netting. I fin ...
winged burning bush (Euonymus alatus) Homeowners Fact Sheet
... and there is little or no wind during application. Fall and winter applications will avoid or minimize impacts to native plants and animals. Foliar application Because this method involves applying herbicide mix to leaves. it should be considered mostly for large infestations where the risk to non-t ...
... and there is little or no wind during application. Fall and winter applications will avoid or minimize impacts to native plants and animals. Foliar application Because this method involves applying herbicide mix to leaves. it should be considered mostly for large infestations where the risk to non-t ...
elephant ears - Little Red Riding Hood Nursery
... ELEPHANT EARS BACKGROUND Elephant Ears have large, heart-shaped leaves which grow to almost 3 feet long and almost as wide. In the Pacific Islands, the plant is known as Taro and when ground up the bulb is known as “poi” which is eaten as their answer to bread. PLANTING The plant is known for its bol ...
... ELEPHANT EARS BACKGROUND Elephant Ears have large, heart-shaped leaves which grow to almost 3 feet long and almost as wide. In the Pacific Islands, the plant is known as Taro and when ground up the bulb is known as “poi” which is eaten as their answer to bread. PLANTING The plant is known for its bol ...
Worksheet 9.1 - contentextra
... of plants. The movement depends on cohesion and adhesion maintaining a constant column of water in the xylem. 11 The movement of organic molecules in plants is called translocation. Phloem sap includes mostly water, sugars, amino acids, plant hormones and mRNA. Its movement is explained by the press ...
... of plants. The movement depends on cohesion and adhesion maintaining a constant column of water in the xylem. 11 The movement of organic molecules in plants is called translocation. Phloem sap includes mostly water, sugars, amino acids, plant hormones and mRNA. Its movement is explained by the press ...
Cowhage (Mucuna prurita Hook.)
... For rain fed crop of mucuna seeds are sown in the month of June and harvested in the month of December otherwise, sowing is done in the month of August and harvesting done in the month of February in a irrigated land. Seeds are directly sown, for that seeds required at the rate of 5kg/ha. The land i ...
... For rain fed crop of mucuna seeds are sown in the month of June and harvested in the month of December otherwise, sowing is done in the month of August and harvesting done in the month of February in a irrigated land. Seeds are directly sown, for that seeds required at the rate of 5kg/ha. The land i ...
Growing and Overwintering Tender Varieties
... especially one you grew yourself. In Alaska, roses can be grouped into two major types: “hardy” and “tender.” These categories are specific to Alaska and based on growers’ experiences. Hardy roses will overwinter successfully in our cold climate. There are differences statewide on which varieties do ...
... especially one you grew yourself. In Alaska, roses can be grouped into two major types: “hardy” and “tender.” These categories are specific to Alaska and based on growers’ experiences. Hardy roses will overwinter successfully in our cold climate. There are differences statewide on which varieties do ...
Fireblight
... The most likely means of introduction is on infected planting material, which may or may not show symptoms. Primary infection usually occurs in spring through lenticels or wounds in young shoots, or through blossom. On some hosts, the disease then spreads down the shoot to the main stem, eventually ...
... The most likely means of introduction is on infected planting material, which may or may not show symptoms. Primary infection usually occurs in spring through lenticels or wounds in young shoots, or through blossom. On some hosts, the disease then spreads down the shoot to the main stem, eventually ...
Vanda and Ascocenda Culture
... repotting. Vandeceous orchids are heavy feeders. Plants in greenhouses should be given a solution of balanced fertilizer (20-20-20) once a week during the growing season. Outdoor plants require a heavier concentration of the same fertilizer. During the non-growing season, apply the same proportions ...
... repotting. Vandeceous orchids are heavy feeders. Plants in greenhouses should be given a solution of balanced fertilizer (20-20-20) once a week during the growing season. Outdoor plants require a heavier concentration of the same fertilizer. During the non-growing season, apply the same proportions ...
Chapter 35 Objectives
... b. Percent of dry weight as organic substances c. Percent of dry weight as inorganic minerals Know from Biology, Campbell book, pg. 711 2. Distinguish between macronutrient and micronutrient. Macronutrients are elements required by plants in relatively large amounts. Micronutrients are elements that ...
... b. Percent of dry weight as organic substances c. Percent of dry weight as inorganic minerals Know from Biology, Campbell book, pg. 711 2. Distinguish between macronutrient and micronutrient. Macronutrients are elements required by plants in relatively large amounts. Micronutrients are elements that ...
plant kingdom - introduction and classification
... PLANT KINGDOM - INTRODUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION PLANT KINGDOM ...
... PLANT KINGDOM - INTRODUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION PLANT KINGDOM ...
Fast Facts #3 Describing Plants
... extra food for the plant. Root hairs help increase the surface area of the root so it can absorb more water and nutrients. There are two types of roots: Fibrous Roots – consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass of roots (corn, grass, some trees) Taproots – consist of one large, ma ...
... extra food for the plant. Root hairs help increase the surface area of the root so it can absorb more water and nutrients. There are two types of roots: Fibrous Roots – consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass of roots (corn, grass, some trees) Taproots – consist of one large, ma ...
Fast Facts 3 - Anderson School District One
... extra food for the plant. Root hairs help increase the surface area of the root so it can absorb more water and nutrients. There are two types of roots: Fibrous Roots – consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass of roots (corn, grass, some trees) Taproots – consist of one large, ma ...
... extra food for the plant. Root hairs help increase the surface area of the root so it can absorb more water and nutrients. There are two types of roots: Fibrous Roots – consist of several main roots that branch off to form a mass of roots (corn, grass, some trees) Taproots – consist of one large, ma ...
Solanum pseudocapsicum - Australian Weeds and Livestock
... bright orange-red, like small tomatoes. . Fruits are attractive to children, but are poisonous to humans. . Reproduces by seed, spread by birds, et al. . Plants have been seen at markets, as novelty plants, incorrectly labeled, and sold as edible. . A native of South America. . Now found in many par ...
... bright orange-red, like small tomatoes. . Fruits are attractive to children, but are poisonous to humans. . Reproduces by seed, spread by birds, et al. . Plants have been seen at markets, as novelty plants, incorrectly labeled, and sold as edible. . A native of South America. . Now found in many par ...
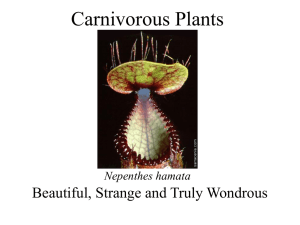
Carnivorous Plants - New England Carnivorous Plant Society
... they’re producers) • Utilize excess sugars from photosynthesis (which only requires sunlight, water, and CO2) as bait ...
... they’re producers) • Utilize excess sugars from photosynthesis (which only requires sunlight, water, and CO2) as bait ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.