Analog Communication
... • FM receivers contain limiter circuits that deliberately restrict the amplitude of the received signal. • Any amplitude variations occurring on the FM signal are effectively clipped by limiter circuits. • This amplitude clipping does not affect the information content of the FM signal, since it is ...
... • FM receivers contain limiter circuits that deliberately restrict the amplitude of the received signal. • Any amplitude variations occurring on the FM signal are effectively clipped by limiter circuits. • This amplitude clipping does not affect the information content of the FM signal, since it is ...
AM Principles_Lecture2
... • Low level AM produces the AM signal at a very low power level. High power amplifiers increase the power to the desired level. Less efficient linear amplifiers must be used to amplify the AM signal. • High level AM is produced by amplitude modulating the final amplifier stage in a transmitter. More ...
... • Low level AM produces the AM signal at a very low power level. High power amplifiers increase the power to the desired level. Less efficient linear amplifiers must be used to amplify the AM signal. • High level AM is produced by amplitude modulating the final amplifier stage in a transmitter. More ...
Radio Signals and Fundementals
... T1B09 -- Why should you not set your transmit frequency to be exactly at the edge of an amateur band or sub-band? A. To allow for calibration error in the transmitter frequency display B. So that modulation sidebands do not extend beyond the band edge C. To allow for transmitter frequency drift D. ...
... T1B09 -- Why should you not set your transmit frequency to be exactly at the edge of an amateur band or sub-band? A. To allow for calibration error in the transmitter frequency display B. So that modulation sidebands do not extend beyond the band edge C. To allow for transmitter frequency drift D. ...
Angle Modulation Part 2
... of the RX which proportional to the square of modulation index. Angle modulation is resistant to propagation-induced selective fading since amplitude variations are unimportant and are removed at the receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (mi ...
... of the RX which proportional to the square of modulation index. Angle modulation is resistant to propagation-induced selective fading since amplitude variations are unimportant and are removed at the receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (mi ...
EET 2351 Lecture 2 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... Baseband signals Carrier Modulation of Baseband Signals Types of Modulation Methods Frequency, Spectrum, and Bandwidth Generation of Baseband Signals ...
... Baseband signals Carrier Modulation of Baseband Signals Types of Modulation Methods Frequency, Spectrum, and Bandwidth Generation of Baseband Signals ...
Part II Data Transmission
... (discussed on Part III), two channels with bandwidth of 6 MHz each can be used for data transmission ...
... (discussed on Part III), two channels with bandwidth of 6 MHz each can be used for data transmission ...
11 2018 Your First Radio
... transceiver is to store the frequency in a memory channel. A disadvantage of the "rubber duck" antenna supplied with most handheld radio transceivers is it does not transmit or receive as effectively as a full-sized antenna. A good reason NOT to use a "rubber duck" antenna inside your car is tha ...
... transceiver is to store the frequency in a memory channel. A disadvantage of the "rubber duck" antenna supplied with most handheld radio transceivers is it does not transmit or receive as effectively as a full-sized antenna. A good reason NOT to use a "rubber duck" antenna inside your car is tha ...
sidebands
... The first step in generating an SSB signal is to suppress the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. This type of signal is called a double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSSC) signal. No power is wasted on the carrier. A balanced modulator is a circuit used to produce the sum and diffe ...
... The first step in generating an SSB signal is to suppress the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. This type of signal is called a double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSSC) signal. No power is wasted on the carrier. A balanced modulator is a circuit used to produce the sum and diffe ...
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS
... signal consists of the original carrier, a lower side frequency, flsf = fc - fm, and an upper side frequency, fusf = fc + fm. ...
... signal consists of the original carrier, a lower side frequency, flsf = fc - fm, and an upper side frequency, fusf = fc + fm. ...
Efficiency of AM modulation
... the original current pulses are made proportional to the modulating voltage. This process is known as flywheel effect of the tuned circuit, and it works best with a tuned circuit whose Q is not too low. In AM transmitter, amplitude modulation can be generated at any point after the radio frequency ...
... the original current pulses are made proportional to the modulating voltage. This process is known as flywheel effect of the tuned circuit, and it works best with a tuned circuit whose Q is not too low. In AM transmitter, amplitude modulation can be generated at any point after the radio frequency ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... AM Vs FM systems In both systems a carrier wave is modulated by an audio signal to produce a carrier and sidebands. The technique can be applied to various communication systems eg telephony and telegraphy ...
... AM Vs FM systems In both systems a carrier wave is modulated by an audio signal to produce a carrier and sidebands. The technique can be applied to various communication systems eg telephony and telegraphy ...
review to communication system
... Any original signals, regardless of whether it is analog/digital, referred as base band signals. In Comm Sys, some info signals may be transmitted directly by themselves over the medium or using modulation. Putting the original signal directly to the medium is called base band transmission. ...
... Any original signals, regardless of whether it is analog/digital, referred as base band signals. In Comm Sys, some info signals may be transmitted directly by themselves over the medium or using modulation. Putting the original signal directly to the medium is called base band transmission. ...
Chapter 6 - Good Operating Practices
... • Used to connect amateur stations with the internet. • Uses the internet protocol known as VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol). • Gateway stations can be used to link repeaters where two distant repeaters share signals using VoIP. • Popular amateur VoIP linking systems are IRLP and Echolink – KØRGR ...
... • Used to connect amateur stations with the internet. • Uses the internet protocol known as VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol). • Gateway stations can be used to link repeaters where two distant repeaters share signals using VoIP. • Popular amateur VoIP linking systems are IRLP and Echolink – KØRGR ...
A CW Adapter for the Radio Shack HTX-10 Ten Meter
... adapter. All needed power is derived from the HTX-10. Tune a CW signal so that its audio pitch is approximately the same frequency as the adapter’s audio oscillator. Press the key to transmit. Adjust the rig’s mic gain control for desired power output. Either sideband may be selected for operation. ...
... adapter. All needed power is derived from the HTX-10. Tune a CW signal so that its audio pitch is approximately the same frequency as the adapter’s audio oscillator. Press the key to transmit. Adjust the rig’s mic gain control for desired power output. Either sideband may be selected for operation. ...
lecture09
... Amplitude Modulated (AM) Radio • Double sideband large carrier (DSC-LC) Carrier wave varied about mean value linearly with baseband message signal m(t) s(t ) Ac 1 k a m(t ) cos( 2 f c t ) Ac cos( 2 f c t ) Ac k a m(t ) cos( 2 f c t ) ka is the amplitude sensitivity, ka > 0 Modulati ...
... Amplitude Modulated (AM) Radio • Double sideband large carrier (DSC-LC) Carrier wave varied about mean value linearly with baseband message signal m(t) s(t ) Ac 1 k a m(t ) cos( 2 f c t ) Ac cos( 2 f c t ) Ac k a m(t ) cos( 2 f c t ) ka is the amplitude sensitivity, ka > 0 Modulati ...
Electronic-Circuit II Chap 4. Communication Systems
... • Amplitude modulation in oscillator circuit • Carrier wave is generated by an LC tank circuit of the oscillator • Modulating signal is directly fed in along with the fed-back carrier wave • Transistor in CE configuration • Parallel tuned L2 & C4 generates the necessary carrier wave ...
... • Amplitude modulation in oscillator circuit • Carrier wave is generated by an LC tank circuit of the oscillator • Modulating signal is directly fed in along with the fed-back carrier wave • Transistor in CE configuration • Parallel tuned L2 & C4 generates the necessary carrier wave ...
13 Technician Multi Mode
... Multi-Mode Radio Excitement Selectivity is the term that describes the ability of a receiver to discriminate between multiple signals. ...
... Multi-Mode Radio Excitement Selectivity is the term that describes the ability of a receiver to discriminate between multiple signals. ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Frequency modulation techniques 2011 February
... of a Fractional-N type synthesizer between two “end” frequencies ...
... of a Fractional-N type synthesizer between two “end” frequencies ...
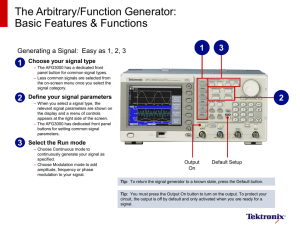
Intro-to-Signal-Generators-Fact
... the display and a menu of controls appears at the right side of the screen. – The AFG3000 has dedicated front panel buttons for setting common signal parameters. ...
... the display and a menu of controls appears at the right side of the screen. – The AFG3000 has dedicated front panel buttons for setting common signal parameters. ...
class05
... • Any non-periodic function (so frequency f0 0) can be expressed as an integral over frequency of sinusoidal waves having frequencies. The integral is called the Fourier transform of the function, and a plot of amplitude vs. frequency is called the Fourier spectrum of the function. • The Fourier sp ...
... • Any non-periodic function (so frequency f0 0) can be expressed as an integral over frequency of sinusoidal waves having frequencies. The integral is called the Fourier transform of the function, and a plot of amplitude vs. frequency is called the Fourier spectrum of the function. • The Fourier sp ...
Linearity - The University of Texas at Austin
... • Some characteristic of a carrier signal is varied in accordance with a modulating signal • For amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation, modulated signals can be expressed as y(t ) f (t ) cos(2 f c t (t )) f(t) is real-valued amplitude function fc is carrier frequency (t) is real-valued ...
... • Some characteristic of a carrier signal is varied in accordance with a modulating signal • For amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation, modulated signals can be expressed as y(t ) f (t ) cos(2 f c t (t )) f(t) is real-valued amplitude function fc is carrier frequency (t) is real-valued ...
angle modulation
... Phase Modulation • One of the properties of a sinusoidal wave is its phase, the offset from a reference time at which the sine wave begins. • We use the term phase shift to characterize such changes. • If phase changes after cycle k, the next sinusoidal wave will start slightly later than the time ...
... Phase Modulation • One of the properties of a sinusoidal wave is its phase, the offset from a reference time at which the sine wave begins. • We use the term phase shift to characterize such changes. • If phase changes after cycle k, the next sinusoidal wave will start slightly later than the time ...
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course
... T4A02 What could be used in place of a regular speaker to help you copy signals in a noisy area? A. A video display B. A low pass filter ...
... T4A02 What could be used in place of a regular speaker to help you copy signals in a noisy area? A. A video display B. A low pass filter ...
Single-sideband modulation
In radio communications, Single-SideBand modulation (SSB) or Single-SideBand Suppressed-Carrier (SSB-SC) is a refinement of amplitude modulation which uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal that has twice the bandwidth of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth doubling, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver.