Cacti Adaptations
... Roots are important to plants. •They absorb water and minerals from the soil. •They carry water and minerals to the stem. •They help to anchor the plant in the soil. •They store food and water for future use. ...
... Roots are important to plants. •They absorb water and minerals from the soil. •They carry water and minerals to the stem. •They help to anchor the plant in the soil. •They store food and water for future use. ...
affected by geological substratum
... in Table l. Some corrections to the published descriptions of Verbascum phoeniceum will be necessary: the overall size, said to be 30-100 cm, is in fact 27-113 cm; and petiole length of the basalleaves is not up to 4 cm but may reach 11.3 cm. Between the populations studied, significant differences ...
... in Table l. Some corrections to the published descriptions of Verbascum phoeniceum will be necessary: the overall size, said to be 30-100 cm, is in fact 27-113 cm; and petiole length of the basalleaves is not up to 4 cm but may reach 11.3 cm. Between the populations studied, significant differences ...
Unit 10: Soybean Diseases
... Small angular spots Appear yellow at first Later turn brown to black Diseased leaves eventually die and fall ...
... Small angular spots Appear yellow at first Later turn brown to black Diseased leaves eventually die and fall ...
Plant Love
... 1. Flowering plants are generally in one of two groups, monocots or dicots. Monocots are plants that have leaves with parallel veins, flowers with petals, sepals, and stamen in multiples of three. Dicots have leaves with branching veins, flowers with petals, sepals, and stamen in multiples of four o ...
... 1. Flowering plants are generally in one of two groups, monocots or dicots. Monocots are plants that have leaves with parallel veins, flowers with petals, sepals, and stamen in multiples of three. Dicots have leaves with branching veins, flowers with petals, sepals, and stamen in multiples of four o ...
Anatomy - FSU Biology
... 2. Draw and label the parts of the seedling. Identify the primary root and root hairs (if possible), seed coat, cotyledons, first true leaf, hypocotyl, and epicotyl of the seedling. ...
... 2. Draw and label the parts of the seedling. Identify the primary root and root hairs (if possible), seed coat, cotyledons, first true leaf, hypocotyl, and epicotyl of the seedling. ...
Amethyst Falls Wisteria
... climbing vine, it tends to be leggy near the base and should be underplanted with low-growing facer plants. It should be planted near a fence, trellis or other landscape structure where it can be trained to grow upwards on it, or allowed to trail off a retaining wall or slope. It grows at a fast rat ...
... climbing vine, it tends to be leggy near the base and should be underplanted with low-growing facer plants. It should be planted near a fence, trellis or other landscape structure where it can be trained to grow upwards on it, or allowed to trail off a retaining wall or slope. It grows at a fast rat ...
Information processing without brains – the power of
... Plants exhibit different developmental strategies than animals; these are characterized by a tight linkage between environmental conditions and development. As plants have neither specialized sensory organs nor a nervous system, intercellular regulators are essential for their development. Recently, ...
... Plants exhibit different developmental strategies than animals; these are characterized by a tight linkage between environmental conditions and development. As plants have neither specialized sensory organs nor a nervous system, intercellular regulators are essential for their development. Recently, ...
IJBT 5(2) 246-248
... L-I NAA was used. In this medium the callus doubled in size every 15 d with routine subcultures. Callus was found to be big, friable and white-pale green in colour. When nodal explants were grown in medium supplemented with low concentrations of NAA (1.0 mg L-') and BAP (0.1 mg L-'), they produced c ...
... L-I NAA was used. In this medium the callus doubled in size every 15 d with routine subcultures. Callus was found to be big, friable and white-pale green in colour. When nodal explants were grown in medium supplemented with low concentrations of NAA (1.0 mg L-') and BAP (0.1 mg L-'), they produced c ...
Look-out For Fusarium Root And Crown Rot Of Hostai\
... E oxysporum, and Fusariumsp. all caused disease to some extent, but root and crown rot always was most severe on plants inocu lated with the unidentified species—Fusarium sp. Therefore, we concluded that the root and crown rot of container-grown hosta plants in nurseries was caused primarily by this ...
... E oxysporum, and Fusariumsp. all caused disease to some extent, but root and crown rot always was most severe on plants inocu lated with the unidentified species—Fusarium sp. Therefore, we concluded that the root and crown rot of container-grown hosta plants in nurseries was caused primarily by this ...
Little Devil Ninebark
... Little Devil Ninebark features showy clusters of white flowers with shell pink overtones at the ends of the branches in early summer. It has burgundy foliage throughout the season. The small serrated lobed leaves turn purple in fall. It produces red capsules from early to mid fall. The peeling tan b ...
... Little Devil Ninebark features showy clusters of white flowers with shell pink overtones at the ends of the branches in early summer. It has burgundy foliage throughout the season. The small serrated lobed leaves turn purple in fall. It produces red capsules from early to mid fall. The peeling tan b ...
Polystichum acrostichoides
... Rhizomes: Its rhizomes are dark evergreen, short, slender or stout, branching, creeping or erect, and scaly. It has several growing tips for forming multiple crowns. It also has a fibrous root system underground. Fronds: Its fronds (leaves) are arranged in circular, stiff, arching, tufted clumps tha ...
... Rhizomes: Its rhizomes are dark evergreen, short, slender or stout, branching, creeping or erect, and scaly. It has several growing tips for forming multiple crowns. It also has a fibrous root system underground. Fronds: Its fronds (leaves) are arranged in circular, stiff, arching, tufted clumps tha ...
Introduction: Irvingia gabonensis
... and are especially valued for fat and protein rich nuts. Irvingia is a nutritional important non-timber wood plant with edible parts such as fruits, nut and Kernel (Ladipo, 1996) I.gabonensis are socio-economically important food crop which range from their use as food, medicine and environmental co ...
... and are especially valued for fat and protein rich nuts. Irvingia is a nutritional important non-timber wood plant with edible parts such as fruits, nut and Kernel (Ladipo, 1996) I.gabonensis are socio-economically important food crop which range from their use as food, medicine and environmental co ...
Whiteflies - WordPress.com
... over the top of the top the crop that is being attacked. You can make your own by taking a piece of florescent yellow cardboard or plastic and coat it with petroleum jelly or tanglefoot. Then hang it on a wire or bamboo stick and insert it in the ground so it is about 6-12 inches above the effected c ...
... over the top of the top the crop that is being attacked. You can make your own by taking a piece of florescent yellow cardboard or plastic and coat it with petroleum jelly or tanglefoot. Then hang it on a wire or bamboo stick and insert it in the ground so it is about 6-12 inches above the effected c ...
Class Notes
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
Ch. 30
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
What are herbs and spices?
... • Oils usually sequestered in specialized pockets or glands on plants; oils produced by plant as aSractants or repellants (some compounds both aSract some visitors and repel others) • We use small amounts mixed with food for pleasant, rather than deterrent effect • Compounds must be of fairly lo ...
... • Oils usually sequestered in specialized pockets or glands on plants; oils produced by plant as aSractants or repellants (some compounds both aSract some visitors and repel others) • We use small amounts mixed with food for pleasant, rather than deterrent effect • Compounds must be of fairly lo ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... Seedless vascular plants became important as the swamps dried up and the global climate cooled. ...
... Seedless vascular plants became important as the swamps dried up and the global climate cooled. ...
AP Bio Lec Ch. - apbiologyclass
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
- Garden Resources
... There are not many keen gardeners that would not wish for a little extra space in their garden. This extra space would allow a more adequate range of plants and therefore a fuller display of colour from late winter right through to the following autumn. The traditional flower gardening year, is to u ...
... There are not many keen gardeners that would not wish for a little extra space in their garden. This extra space would allow a more adequate range of plants and therefore a fuller display of colour from late winter right through to the following autumn. The traditional flower gardening year, is to u ...
30_DetailLectOut
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
... o Oranges, plums, and grapes are fleshy fruits, in which the ovary wall softens during ripening. o Dry fruits include beans, nuts, and grains. o The dry, wind-dispersed fruits of grasses are major food staples for humans. o The cereal grains of wheat, rice, and maize are fruits with a dry outer cove ...
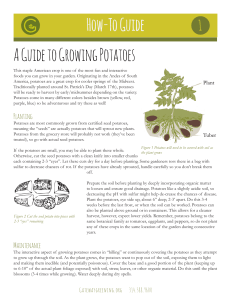
How-To Guide A Guide to Growing Potatoes
... Prepare the soil before planting by deeply incorporating organic matter to loosen and ensure good drainage. Potatoes like a slightly acidic soil, so decreasing the pH with sulfur might help de-crease the chances of disease. Plant the potatoes, eye side up, about 6” deep, 2-3’ apart. Do this 3-4 week ...
... Prepare the soil before planting by deeply incorporating organic matter to loosen and ensure good drainage. Potatoes like a slightly acidic soil, so decreasing the pH with sulfur might help de-crease the chances of disease. Plant the potatoes, eye side up, about 6” deep, 2-3’ apart. Do this 3-4 week ...
Folklore claims of some ethnomedicinal plants used by Bhil Tribes of
... studies and documents provide important for understanding the complex heritage of tribal communities and their association with environment and nature. It is also observe that were uses roots of 7, seeds of 5 species, barks, Inflorescence, leaves, rhizomes, fruits of 2 species each and whole plant o ...
... studies and documents provide important for understanding the complex heritage of tribal communities and their association with environment and nature. It is also observe that were uses roots of 7, seeds of 5 species, barks, Inflorescence, leaves, rhizomes, fruits of 2 species each and whole plant o ...
Poison Hemlock
... ditches and waste areas. It also invades native plant communities in riparian woodlands, open floodplains and along stream banks. ...
... ditches and waste areas. It also invades native plant communities in riparian woodlands, open floodplains and along stream banks. ...
Printable List - Virginia Highlands Community College
... Semi-sun succulent, great indoor plant Semi-sun succulent, great indoor plant High light, air-filtering houseplant High light, air-filtering houseplant, outside to 32F Release oxygen at night, semi-sun houseplant Release oxygen at night, semi-sun houseplant Beautiful blooms, shade-loving forest cact ...
... Semi-sun succulent, great indoor plant Semi-sun succulent, great indoor plant High light, air-filtering houseplant High light, air-filtering houseplant, outside to 32F Release oxygen at night, semi-sun houseplant Release oxygen at night, semi-sun houseplant Beautiful blooms, shade-loving forest cact ...
Plant morphology

Plant morphology or phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants. This is usually considered distinct from plant anatomy, which is the study of the internal structure of plants, especially at the microscopic level. Plant morphology is useful in the visual identification of plants.