chapter 13
... c. behavioral (include the terms “self-defeating,” “paradox,” “avoidance learning,” and “anxiety reduction hypothesis”) d. cognitive 20. Define what is meant by the term “psychosis.” 21. Define “delusion.” 22. Define “hallucination” and name the most common type. 23. Describe the emotion, communicat ...
... c. behavioral (include the terms “self-defeating,” “paradox,” “avoidance learning,” and “anxiety reduction hypothesis”) d. cognitive 20. Define what is meant by the term “psychosis.” 21. Define “delusion.” 22. Define “hallucination” and name the most common type. 23. Describe the emotion, communicat ...
Brain development
... The clinical presentation of trauma-related symptoms can evolve. In the typical evaluation process, the evaluating clinical team or clinician rarely has the benefit of complete history about the origin and evolution of symptoms. Histories are frequently based upon one caregiver’s recollection and as ...
... The clinical presentation of trauma-related symptoms can evolve. In the typical evaluation process, the evaluating clinical team or clinician rarely has the benefit of complete history about the origin and evolution of symptoms. Histories are frequently based upon one caregiver’s recollection and as ...
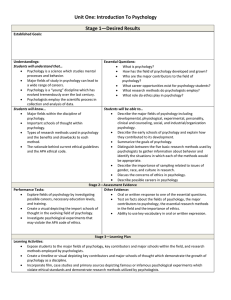
Introduction to Psychology
... a “harmful dysfunction” in which behavior is judged to be: atypical--not ...
... a “harmful dysfunction” in which behavior is judged to be: atypical--not ...
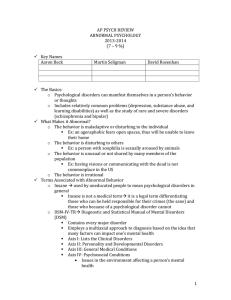
Abnormal Psychology
... •Marked by crying, fitful sleep, tension, anger, and irritability •Brief and not too severe Postpartum Depression: Moderately severe depression that begins within three months following childbirth •Marked by mood swings, despondency, feelings of inadequacy, and an inability to cope with the new baby ...
... •Marked by crying, fitful sleep, tension, anger, and irritability •Brief and not too severe Postpartum Depression: Moderately severe depression that begins within three months following childbirth •Marked by mood swings, despondency, feelings of inadequacy, and an inability to cope with the new baby ...
Mass Psychogenic Illness
... Disorder Treatment Psychoanalysis -- try to give therapy to the main personality who "knows" the others ...
... Disorder Treatment Psychoanalysis -- try to give therapy to the main personality who "knows" the others ...
Chapter 5: Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – Such feelings and experiences dominate and interfere with life functioning – Primary problem involves depersonalization and derealization • Facts and Statistics – Comorbidity with anxiety and mood disorders is extremely high – Onset is typically around age 16 – Usually runs a lifelong chronic cour ...
... – Such feelings and experiences dominate and interfere with life functioning – Primary problem involves depersonalization and derealization • Facts and Statistics – Comorbidity with anxiety and mood disorders is extremely high – Onset is typically around age 16 – Usually runs a lifelong chronic cour ...
Dissociative Diso
... objects in their visual field, as well as those reporting paralysis of the legs might get up and run somewhere in an emergency and are astounded they were able to do this. -This can account for some who are miraculously “cured” during religious ceremonies. ...
... objects in their visual field, as well as those reporting paralysis of the legs might get up and run somewhere in an emergency and are astounded they were able to do this. -This can account for some who are miraculously “cured” during religious ceremonies. ...
Roadmap for Diagnosis
... P. The best predictor of future behavior is past behavior (p.47) Q. More symptoms of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis (p.47) R. Typical feature of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis; in the presence of nontypical features, look for alternatives (p.47) S. Previou ...
... P. The best predictor of future behavior is past behavior (p.47) Q. More symptoms of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis (p.47) R. Typical feature of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis; in the presence of nontypical features, look for alternatives (p.47) S. Previou ...