Emotion Regulation as a Transdiagnostic Process in
... each day for 5 consecutive days (702 goals). For each goal, participants rated the extent to which they: 1) considered it important, 2) experienced goal-interfering emotions, 3) used regulation strategies to manage such emotions, and 4) were able to achieve it. Goal importance was not associated wit ...
... each day for 5 consecutive days (702 goals). For each goal, participants rated the extent to which they: 1) considered it important, 2) experienced goal-interfering emotions, 3) used regulation strategies to manage such emotions, and 4) were able to achieve it. Goal importance was not associated wit ...
Hypochondriasis and Health Anxiety
... is lower and it subsides early, andinother es during exposur relation to the actual degree of threat (if any threat is extreme leaving otherg,hand, even more quickly. avoidance strategi With repeated practice, the nce, checkin feared situations no longer asking for reassura 6. Do not use subtle even ...
... is lower and it subsides early, andinother es during exposur relation to the actual degree of threat (if any threat is extreme leaving otherg,hand, even more quickly. avoidance strategi With repeated practice, the nce, checkin feared situations no longer asking for reassura 6. Do not use subtle even ...
Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder
... To briefly identify the differences between an Axis I and Axis II disorder.( I.E. Between the symptoms that one suffers from compared to who the individual has become developmentally.) To identify the signs and symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder To identify the prevalence and course of this ...
... To briefly identify the differences between an Axis I and Axis II disorder.( I.E. Between the symptoms that one suffers from compared to who the individual has become developmentally.) To identify the signs and symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder To identify the prevalence and course of this ...
Abnormal Behaviors
... behavior and, using traditional learning procedures, to teach new, more appropriate, and more adaptive responses. For example, a behavioral analysis of a case of child abuse might suggest that a father abuses his children because he learned the abusive behavior from his father and must now learn mo ...
... behavior and, using traditional learning procedures, to teach new, more appropriate, and more adaptive responses. For example, a behavioral analysis of a case of child abuse might suggest that a father abuses his children because he learned the abusive behavior from his father and must now learn mo ...
Co-occurring Disorders The Mix of Meds and Therapy
... • Anxiety about being in places or situations from which escape might be difficult (or embarrassing) in the event of a panic attack • The situations are avoided or are endured with marked distress • Anxiety or phobic avoidance is not better accounted for by another mental disorder ...
... • Anxiety about being in places or situations from which escape might be difficult (or embarrassing) in the event of a panic attack • The situations are avoided or are endured with marked distress • Anxiety or phobic avoidance is not better accounted for by another mental disorder ...
2003년 1학기 이상심리학 Abnormal Psychology V.M. Durand & …
... exposure to unfamiliar people or possible scrutiny by others, with the fear that one will be embarrassed or humiliated. ...
... exposure to unfamiliar people or possible scrutiny by others, with the fear that one will be embarrassed or humiliated. ...
Anxiety disorder specificity of anxiety sensitivity in a community
... Anxiety sensitivity (AS) is an individual difference variable characterized by a fear of anxietyrelated sensations arising from beliefs that these sensations have harmful consequences (Reiss, 1991). AS is conceptualized as being comprised of three inter-correlated lower-order components that load on ...
... Anxiety sensitivity (AS) is an individual difference variable characterized by a fear of anxietyrelated sensations arising from beliefs that these sensations have harmful consequences (Reiss, 1991). AS is conceptualized as being comprised of three inter-correlated lower-order components that load on ...
Somatoform disorders
... afraid others will think them vain or they may feel too embarrassed to do so. ...
... afraid others will think them vain or they may feel too embarrassed to do so. ...
Mental Disorders and Suicide
... A mental disorder is an illness that affects the mind and prevents a person from being productive, adjusting to life situations, or getting along with others. Most mental disorders are characterized by abnormal thoughts, feelings, or behaviors that make people uncomfortable with themselves or at odd ...
... A mental disorder is an illness that affects the mind and prevents a person from being productive, adjusting to life situations, or getting along with others. Most mental disorders are characterized by abnormal thoughts, feelings, or behaviors that make people uncomfortable with themselves or at odd ...
Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology
... • Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder in which the anxiety suddenly escalates at times into a terrifying panic attack, a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. ...
... • Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder in which the anxiety suddenly escalates at times into a terrifying panic attack, a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. ...
Psychiatry and Medicine
... directly ( Parkinson’s disease, stroke, infections, endocrine disorders & malignancy). • Illness factors ( pain, threat to life, course, duration & disability). • Treatment factors ( side effects, uncertainty of outcome & self-care demands ). • Patients factors ( psychological vulnerability, social ...
... directly ( Parkinson’s disease, stroke, infections, endocrine disorders & malignancy). • Illness factors ( pain, threat to life, course, duration & disability). • Treatment factors ( side effects, uncertainty of outcome & self-care demands ). • Patients factors ( psychological vulnerability, social ...
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY 6 criteria for determining "normal
... or caring that their behavior is harmful/hurtful to others display little if any anxiety about future discomforts or punishments 2 groups (1 APD boys, other maladjusted boys with adolescent adjustment diagnosis) hooked up to galvanic skin conductance/response (GSR) apparatus (measures electrical co ...
... or caring that their behavior is harmful/hurtful to others display little if any anxiety about future discomforts or punishments 2 groups (1 APD boys, other maladjusted boys with adolescent adjustment diagnosis) hooked up to galvanic skin conductance/response (GSR) apparatus (measures electrical co ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Dr. Robert Hare describes his EEG studies and later SPECT (single photon emission computerized tomography) studies on language processing by psychopathic persons, and reflects on what these results ...
... Dr. Robert Hare describes his EEG studies and later SPECT (single photon emission computerized tomography) studies on language processing by psychopathic persons, and reflects on what these results ...
Depressive & Anxiety disorders
... • Target dose of SSRIs in IBS appears is in the range found to be efficacious in the treatment of depression. • SSRI trials should be at least 8–12 weeks in duration of IBS. ...
... • Target dose of SSRIs in IBS appears is in the range found to be efficacious in the treatment of depression. • SSRI trials should be at least 8–12 weeks in duration of IBS. ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Cognitive Theories – Cognitive theories hold that certain styles of thinking, over-interpreting harmless situations as threatening, for example, make some people more vulnerable to anxiety disorders. Personality – The personality trait of neuroticism has been linked to anxiety disorders, and stress ...
... Cognitive Theories – Cognitive theories hold that certain styles of thinking, over-interpreting harmless situations as threatening, for example, make some people more vulnerable to anxiety disorders. Personality – The personality trait of neuroticism has been linked to anxiety disorders, and stress ...
Psychological Disorders
... promotes anxiety and panic attacks; social phobias may occur because of an obsessive fear of social embarrassment or negative judgments – psychodynamic: anxiety disorders are the result of an unconscious conflict or fear; desire to avoid a previously abrasive experience can generate ritualistic beha ...
... promotes anxiety and panic attacks; social phobias may occur because of an obsessive fear of social embarrassment or negative judgments – psychodynamic: anxiety disorders are the result of an unconscious conflict or fear; desire to avoid a previously abrasive experience can generate ritualistic beha ...
CHAPTER 18
... occurs in response to a perceived danger. Types of disorders are defined in the DSMIV. 1. Phobic Disorder – most common anxiety disorder; refers to a persistent, excessive or irrational fear of a particular object or situation. It must interfere with a person’s normal life. 2. Panic Disorders - char ...
... occurs in response to a perceived danger. Types of disorders are defined in the DSMIV. 1. Phobic Disorder – most common anxiety disorder; refers to a persistent, excessive or irrational fear of a particular object or situation. It must interfere with a person’s normal life. 2. Panic Disorders - char ...
Conversion Disorder in Young People
... The symptom or deficit, after appropriate investigation, cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or as a culturally lt ll sanctioned ti d behavior b h i or experience. i The symptom or deficit causes clinically significant distress or impairment i ...
... The symptom or deficit, after appropriate investigation, cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition, the direct effects of a substance, or as a culturally lt ll sanctioned ti d behavior b h i or experience. i The symptom or deficit causes clinically significant distress or impairment i ...
What is Dissociation? - University of Delaware
... Depersonalization Disorder Dissociative Amnesia Dissociative Fugue Dissociative Trance Disorder** Dissociative Identity Disorder ...
... Depersonalization Disorder Dissociative Amnesia Dissociative Fugue Dissociative Trance Disorder** Dissociative Identity Disorder ...
phychological disorders
... St John’s Wort There is considerable public interest in claims that extracts from the herb Hypericum perforatum, commonly known as St. John’s wort, may be an effective treatment for depression. Although St. John’s wort is widely prescribed in Europe, clinical research in the USA is incomplete. ...
... St John’s Wort There is considerable public interest in claims that extracts from the herb Hypericum perforatum, commonly known as St. John’s wort, may be an effective treatment for depression. Although St. John’s wort is widely prescribed in Europe, clinical research in the USA is incomplete. ...
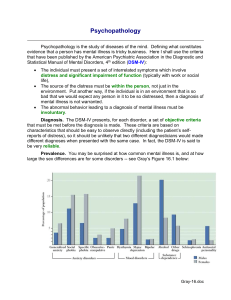
Psychopathology
... Drugs that enhance the action of serotonin alone or of norepinephrine alone can be equally effective in the same individuals, despite the fact that serotonin and norepinephrine are involved in different brain areas with different functions. Environmental Factors. Persons who have recently suffered ...
... Drugs that enhance the action of serotonin alone or of norepinephrine alone can be equally effective in the same individuals, despite the fact that serotonin and norepinephrine are involved in different brain areas with different functions. Environmental Factors. Persons who have recently suffered ...