Programme - Richmond Foundation
... younger than 12 years. Even though Separation Anxiety Disorder may emerge during adolescence and adulthood the typical age of onset is during childhood. If left untreated or mismanaged, difficulties in adulthood will develop. Moreover, it may lead to school refusal which will therefore effect a chil ...
... younger than 12 years. Even though Separation Anxiety Disorder may emerge during adolescence and adulthood the typical age of onset is during childhood. If left untreated or mismanaged, difficulties in adulthood will develop. Moreover, it may lead to school refusal which will therefore effect a chil ...
Generalized anxiety disorder
... (GABA) agonist benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam, diazepam, and lorazepam, ( mainly for Somatic symptoms). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have been considered first-line pharmacological treatment. Buspirone - for Psychic symptoms (beneficial effects may take 2-4wks). is simila ...
... (GABA) agonist benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam, diazepam, and lorazepam, ( mainly for Somatic symptoms). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have been considered first-line pharmacological treatment. Buspirone - for Psychic symptoms (beneficial effects may take 2-4wks). is simila ...
chapter 15 power point - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – 4th ed. (DSM ...
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – 4th ed. (DSM ...
Chronic Condition Coding Awareness: Bipolar
... shifts in mood, energy, activity levels, and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks1. People who have bipolar disorder can have periods in which they feel overly happy and energized and other periods of feeling very sad, hopeless, and sluggish. In between those periods, they usually feel normal. ...
... shifts in mood, energy, activity levels, and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks1. People who have bipolar disorder can have periods in which they feel overly happy and energized and other periods of feeling very sad, hopeless, and sluggish. In between those periods, they usually feel normal. ...
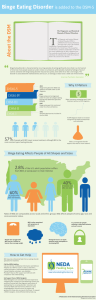
changes to diagnostic criteria for eating disorders from dsm-iv
... otherwise specified” category may actually have Binge-Eating Disorder. Binge-Eating Disorder being listed now as a disorder of its own, has huge clinical implications in terms of accessing treatment for people who may have previously suffered from a condition that might have been considered to be "g ...
... otherwise specified” category may actually have Binge-Eating Disorder. Binge-Eating Disorder being listed now as a disorder of its own, has huge clinical implications in terms of accessing treatment for people who may have previously suffered from a condition that might have been considered to be "g ...
Memory - Union County College
... • The power of diagnostic labels. • Confusion of serious mental disorders with normal problems. • The illusion of objectivity and universality. ...
... • The power of diagnostic labels. • Confusion of serious mental disorders with normal problems. • The illusion of objectivity and universality. ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder - Melanie Pena
... Who Came Up With It? • DID is said to date back to Paleolithic times in cave paintings where shamans would change into animals or take in other spirits. ...
... Who Came Up With It? • DID is said to date back to Paleolithic times in cave paintings where shamans would change into animals or take in other spirits. ...
Chapter Outline - Cengage Learning
... Pervasive developmental disorders. Pervasive developmental disorders are severe disturbances affecting language, social relations, and emotions, distortions that would be abnormal at any developmental stage. Prevalence of autistic disorder is about 2 per 10,000 children; the other pervasive developm ...
... Pervasive developmental disorders. Pervasive developmental disorders are severe disturbances affecting language, social relations, and emotions, distortions that would be abnormal at any developmental stage. Prevalence of autistic disorder is about 2 per 10,000 children; the other pervasive developm ...
early onset bipolar disorder
... criteria are met nearly every day for a least a one week period. ...
... criteria are met nearly every day for a least a one week period. ...
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
Co-Occurring Disorders
... Cross Addiction The APA Glossary, 8th Ed. 2003 defines crossdependence: “ A drug’s ability to suppress physical manifestations of substance dependence produced by another drug and to maintain the physically dependent state. It provides the rationale for the treatment of dependence on one substance, ...
... Cross Addiction The APA Glossary, 8th Ed. 2003 defines crossdependence: “ A drug’s ability to suppress physical manifestations of substance dependence produced by another drug and to maintain the physically dependent state. It provides the rationale for the treatment of dependence on one substance, ...
Unit 12 Practice-No Answers
... depressive episode. experience depressive symptoms at their most extreme levels of severity. begin to rebound from their depression. transition from a manic phase to a depressive phase. ...
... depressive episode. experience depressive symptoms at their most extreme levels of severity. begin to rebound from their depression. transition from a manic phase to a depressive phase. ...
CH 13 study guide
... 7. The DSM-5 categorizes and subdivides disorders according to general types of symptoms, severity, course, and other phenomena. What are anxiety disorders? 1. Anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, specific phobia and social phobia, and panic disorder. Obsessive-compulsive disorder ...
... 7. The DSM-5 categorizes and subdivides disorders according to general types of symptoms, severity, course, and other phenomena. What are anxiety disorders? 1. Anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, specific phobia and social phobia, and panic disorder. Obsessive-compulsive disorder ...
2.2 What are Mood Disorders? - Counselling and Psychotherapy in
... Cyclothymic Disorder: at least 2 years of numerous periods of Hypomanic symptoms that do not meet criteria for a manic episode and numerous periods of depressive symptoms that do not meet criteria for a Major Depressive Episode. Bipolar Disorder Not Otherwise Specified: Bipolar features that do not ...
... Cyclothymic Disorder: at least 2 years of numerous periods of Hypomanic symptoms that do not meet criteria for a manic episode and numerous periods of depressive symptoms that do not meet criteria for a Major Depressive Episode. Bipolar Disorder Not Otherwise Specified: Bipolar features that do not ...
ed-day-bh-olson-blocker-kennedy-1-25-17
... when patients are in their early 20s, but completed suicide is most common after age 30 and usually occurs in patients who fail to recover after many attempts at treatment. In contrast, suicidal actions such as impulsive overdoses or superficial cutting, most often seen in younger patients, do not u ...
... when patients are in their early 20s, but completed suicide is most common after age 30 and usually occurs in patients who fail to recover after many attempts at treatment. In contrast, suicidal actions such as impulsive overdoses or superficial cutting, most often seen in younger patients, do not u ...
Mood Disorders in Children & Adolescents
... • Prevalence up to 8.3% in early adolescence. • Rates in females increase at age 13-14; greater than 2:1 when compared with males at late adolescence. • 1 in 4 adolescents have experienced a depressive episode by age 18. Wichstrom, 1999; Kessler et al., 1996 ...
... • Prevalence up to 8.3% in early adolescence. • Rates in females increase at age 13-14; greater than 2:1 when compared with males at late adolescence. • 1 in 4 adolescents have experienced a depressive episode by age 18. Wichstrom, 1999; Kessler et al., 1996 ...
Chapter 6 Abnormal mental state and maladaptive behavior
... and precisely what is inherited. 2.6 Psychological/Cognitive factors Attributions are inferences we draw about causes of events, others’ behavior, own behavior. Hopelessness Theory of Depression: People who are depressed tend to make. Internal, stable, global attributions for negative experiences an ...
... and precisely what is inherited. 2.6 Psychological/Cognitive factors Attributions are inferences we draw about causes of events, others’ behavior, own behavior. Hopelessness Theory of Depression: People who are depressed tend to make. Internal, stable, global attributions for negative experiences an ...
Mental Illness for Individuals with IDD
... *Schizophrenia is characterized by disorganized thinking, emotional disturbance, and/or impaired perceptions of reality. *Must consider developmental level – belief in fantasy ...
... *Schizophrenia is characterized by disorganized thinking, emotional disturbance, and/or impaired perceptions of reality. *Must consider developmental level – belief in fantasy ...
Mental and Emotional Health
... Anxiety disorders may first become apparent during the teen years or young adulthood. anxiety disorder A disorder in which intense anxiety or fear keeps a person from functioning normally ...
... Anxiety disorders may first become apparent during the teen years or young adulthood. anxiety disorder A disorder in which intense anxiety or fear keeps a person from functioning normally ...
Binge-eating Disorder - University of Alberta
... The demographics of PTSD: BR and SR Why do some people develop PTSD? The nature of the trauma The nature of the person The nature of subsequent experience Implications for treatment: Social support, exposure and stress-induced analgesia The crisis in “Crisis-Counselling” ...
... The demographics of PTSD: BR and SR Why do some people develop PTSD? The nature of the trauma The nature of the person The nature of subsequent experience Implications for treatment: Social support, exposure and stress-induced analgesia The crisis in “Crisis-Counselling” ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Detachment from the trauma and negative reinforcement seem critical Behavioral view focuses on similarity to malingering The incidence of conversion disorder has declined, suggesting a role for social factors ...
... Detachment from the trauma and negative reinforcement seem critical Behavioral view focuses on similarity to malingering The incidence of conversion disorder has declined, suggesting a role for social factors ...
Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12)
... 1. What are the most notable features of behavioral treatment? 2. What is systematic desensitization therapy? What is an anxiety hierarchy, and how is it used in systematic desensitization therapy? 3. How does dismantling contribute to scientific critique of systematic desensitization? 4. What does ...
... 1. What are the most notable features of behavioral treatment? 2. What is systematic desensitization therapy? What is an anxiety hierarchy, and how is it used in systematic desensitization therapy? 3. How does dismantling contribute to scientific critique of systematic desensitization? 4. What does ...
MH 3.1 Personality Disorders, Schizophrenia, Bipolar
... During our teenage years we are struggling with identity, how to gain control over, and express our emotions. Moods of adolescents commonly swing from feeling vulnerable to dependent to knowing that they are the smartest on in their family. (remember? I do!) ...
... During our teenage years we are struggling with identity, how to gain control over, and express our emotions. Moods of adolescents commonly swing from feeling vulnerable to dependent to knowing that they are the smartest on in their family. (remember? I do!) ...
Illness Summaries from DSM 5
... Illness Anxiety Disorder (Hypochondriasis) - Individuals with this disorder (often called “hypochondriacs” by those who know them) are preoccupied with the belief or fear that they have a serious medical condition. Their belief or fear is triggered by their own misinterpretation of their physical sy ...
... Illness Anxiety Disorder (Hypochondriasis) - Individuals with this disorder (often called “hypochondriacs” by those who know them) are preoccupied with the belief or fear that they have a serious medical condition. Their belief or fear is triggered by their own misinterpretation of their physical sy ...
Learners with Emotional or Behavioral Disorders
... childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood. • One-third of adults with OCD develop symptoms as children, and research indicates that OCD might run in families. ...
... childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood. • One-third of adults with OCD develop symptoms as children, and research indicates that OCD might run in families. ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.