studentship advert - University Of Worcester
... aetiologies and prognoses (Paris & Black 2015). However, the two disorders are commonly diagnosed comorbidly. Estimates of the degree of comorbidity vary from as low as 4% (George et al. 2003) to as high as 50% (Wilson et al. 2007) but sample sizes are often very small. This high level of comorbidit ...
... aetiologies and prognoses (Paris & Black 2015). However, the two disorders are commonly diagnosed comorbidly. Estimates of the degree of comorbidity vary from as low as 4% (George et al. 2003) to as high as 50% (Wilson et al. 2007) but sample sizes are often very small. This high level of comorbidit ...
The APA is offering a number of “emerging measures” for... clinical evaluation. These patient assessment measures were developed to be
... Instructions to Clinicians The Severity Measure for Generalized Anxiety Disorder—Child Age 11–17 is a 10-item measure that assesses the severity of generalized anxiety disorder in children and adolescents. The measure was designed to be completed by the child upon receiving a diagnosis of generaliz ...
... Instructions to Clinicians The Severity Measure for Generalized Anxiety Disorder—Child Age 11–17 is a 10-item measure that assesses the severity of generalized anxiety disorder in children and adolescents. The measure was designed to be completed by the child upon receiving a diagnosis of generaliz ...
Traumatic_Brain_Injury
... DSM-IV Criteria A history of many physical complaints before age 30 that occurs over several years and results in seeking treatment Reports of significant social, occupational, or other functional impairment Sxs from 4 separate areas must be experienced (pain, gastrointestinal, sexual, & pseud ...
... DSM-IV Criteria A history of many physical complaints before age 30 that occurs over several years and results in seeking treatment Reports of significant social, occupational, or other functional impairment Sxs from 4 separate areas must be experienced (pain, gastrointestinal, sexual, & pseud ...
Michelle Ayres Occupational Therapist Tracey Barnfield Registered
... To prompt them to drop safety-seeking behaviours, to use helpful skills and strategies To support the client to stop avoiding feared situations To help with a graduated return to regular ...
... To prompt them to drop safety-seeking behaviours, to use helpful skills and strategies To support the client to stop avoiding feared situations To help with a graduated return to regular ...
Important Important Assessment Assessment Important Important
... More than 20% of Hungarians aged 18-24 have used illicit drugs at least once. The spread of so-called designer drugs has also been a current issue. Substance use is more common among people with psychiatric diseases than those of the average population. Long-term substance use can lead to the appear ...
... More than 20% of Hungarians aged 18-24 have used illicit drugs at least once. The spread of so-called designer drugs has also been a current issue. Substance use is more common among people with psychiatric diseases than those of the average population. Long-term substance use can lead to the appear ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder: Perspectives and
... pathology that has its basis in something that is malfunctioning within the person. As is evident conversation has to be deemed to constitute a "medical examination" and the accumulation of certain behaviors and experiences has to meet standards of quantity and time that are deemed sufficient to mer ...
... pathology that has its basis in something that is malfunctioning within the person. As is evident conversation has to be deemed to constitute a "medical examination" and the accumulation of certain behaviors and experiences has to meet standards of quantity and time that are deemed sufficient to mer ...
Chapter 22
... phobia, alcohol dependence, marijuana dependence, and conduct disorder, but not with current simple phobia, overanxious disorder, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity ...
... phobia, alcohol dependence, marijuana dependence, and conduct disorder, but not with current simple phobia, overanxious disorder, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity ...
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder(OCD)
... experienced, at some point during the disturbance, as intrusive and inappropriate and that cause some marked anxiety/stress. ...
... experienced, at some point during the disturbance, as intrusive and inappropriate and that cause some marked anxiety/stress. ...
Psychosis case management-(Dr. Majid Al
... his computer, and has little contact with coworkers or his family. Eight months ago, his performance at work, which was marginal but adequate, began to decline. About this same time, he began to believe that his computer was trying to communicate with him. Several times, he heard a voice that he is ...
... his computer, and has little contact with coworkers or his family. Eight months ago, his performance at work, which was marginal but adequate, began to decline. About this same time, he began to believe that his computer was trying to communicate with him. Several times, he heard a voice that he is ...
Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness in Children and Adolescents
... One complexity is related to timing is the age at which the symptoms began. Kids are more likely to feel irritable and angry than sad or euphoric. Kids are not as able as adults to verbalize feeling states. They know that they feel bad, but they may not be able to be more specific. Children do not h ...
... One complexity is related to timing is the age at which the symptoms began. Kids are more likely to feel irritable and angry than sad or euphoric. Kids are not as able as adults to verbalize feeling states. They know that they feel bad, but they may not be able to be more specific. Children do not h ...
Anxiety Disorder
... 3. maladaptive- harmful; causes suffering 4. unjustifiable- sometimes there’s a good reason ...
... 3. maladaptive- harmful; causes suffering 4. unjustifiable- sometimes there’s a good reason ...
Psychological Disorders - Eric Sweetwood's PTHS Psychology
... • SOMATOFORM DISORDERS are mental disturbances in which psychological problems take a physical (somatic) form, even though no physical cause may be found. Although the symptoms are not caused physically the pain or distress is real, not faked. These differ from Psychosomatic Diseases, genuine physic ...
... • SOMATOFORM DISORDERS are mental disturbances in which psychological problems take a physical (somatic) form, even though no physical cause may be found. Although the symptoms are not caused physically the pain or distress is real, not faked. These differ from Psychosomatic Diseases, genuine physic ...
Best Practices for adolescent girls with conversion disorder
... with 6% of new outpatient referrals having functional conversion symptoms, the same as for multiple sclerosis and for all movement disorders combined (Nicholson and Kanaan, 2009). Co-morbidity with other disorders such as depression and anxiety is quite common and these diagnoses should take precede ...
... with 6% of new outpatient referrals having functional conversion symptoms, the same as for multiple sclerosis and for all movement disorders combined (Nicholson and Kanaan, 2009). Co-morbidity with other disorders such as depression and anxiety is quite common and these diagnoses should take precede ...
OHSU Presentation Template
... http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2847794/ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2902192/ ...
... http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2847794/ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2902192/ ...
Introduction To DSM-5- Part II
... disorders due to a general medical condition and substance-induced anxiety disorder – Reflect recognition that substances, medication and medical conditions can present with symptoms similar to primary OC and related disorders such as pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS) * Codes ar ...
... disorders due to a general medical condition and substance-induced anxiety disorder – Reflect recognition that substances, medication and medical conditions can present with symptoms similar to primary OC and related disorders such as pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS) * Codes ar ...
Abnormal Psychology - The Great Pretender: The Art of Passing
... Enduring pattern of inner experience or behavior that deviates from expectations of culture, manifested in two or more of the following: -- cognition (perception of self, others) -- affectivity (intensity, range of emotions) -- interpersonal functioning -- impulse control ...
... Enduring pattern of inner experience or behavior that deviates from expectations of culture, manifested in two or more of the following: -- cognition (perception of self, others) -- affectivity (intensity, range of emotions) -- interpersonal functioning -- impulse control ...
Introduction to Working with the Asian Patient in Primary Care
... E. The episode is not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning, or to necessitate hospitalization, and there are no psychotic features. F. The symptoms are not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication, or other ...
... E. The episode is not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning, or to necessitate hospitalization, and there are no psychotic features. F. The symptoms are not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication, or other ...
Strategies for Ameliorating Secondary Trauma in Mental
... -Persistent re-experiencing of the event -Persistent avoidance or emotional numbing - Persistent symptoms of increase emotional arousal Duration of more than one month (otherwise acute Stress Disorder); Causes significant distress or impairment in functioning ...
... -Persistent re-experiencing of the event -Persistent avoidance or emotional numbing - Persistent symptoms of increase emotional arousal Duration of more than one month (otherwise acute Stress Disorder); Causes significant distress or impairment in functioning ...
Psychological Disorders
... Mental health professionals may refer to the DSM V. The DSM V is a book that describes the specific symptoms and diagnostic guidelines for different psychological disorders. 1. The first edition of DSM was published in 1952. The DSM V is the 2013 update to the American Psychiatric Association's cl ...
... Mental health professionals may refer to the DSM V. The DSM V is a book that describes the specific symptoms and diagnostic guidelines for different psychological disorders. 1. The first edition of DSM was published in 1952. The DSM V is the 2013 update to the American Psychiatric Association's cl ...
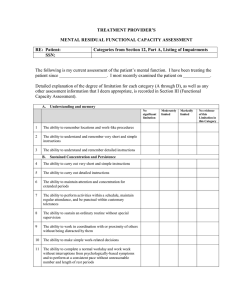
TREATMENT PROVIDER`S MENTAL RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL
... f. Sensation (e.g., diminished or heightened) ...
... f. Sensation (e.g., diminished or heightened) ...
When worrying gets out of control
... But people who brood on their problems and develop other symptoms that diminish the quality of life are those who develop debilitating anxiety disorders and should seek professional help. Anxiety and depression are the two most common mental disorders, Kumar said. Most of his patients suffer from o ...
... But people who brood on their problems and develop other symptoms that diminish the quality of life are those who develop debilitating anxiety disorders and should seek professional help. Anxiety and depression are the two most common mental disorders, Kumar said. Most of his patients suffer from o ...
Schizoaffective Disorder
... Diagnostic criteria according to DSM-V A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive or manic) concurrent with Criterion A of schizophrenia B. Delusions or hallucinations for 2 or more weeks in the absence of a major mood episode (depressive or ma ...
... Diagnostic criteria according to DSM-V A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive or manic) concurrent with Criterion A of schizophrenia B. Delusions or hallucinations for 2 or more weeks in the absence of a major mood episode (depressive or ma ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... mimic disease or injury (paralysis, blindness, illness, or chronic pain, for example) for which there is no identifiable physical cause. In such cases it is assumed that psychological factors underlie the symptoms. – Dissociative disorder (Nevid Pgs. 394, 396-397 Coon, Pgs. 500-501): Temporary amnes ...
... mimic disease or injury (paralysis, blindness, illness, or chronic pain, for example) for which there is no identifiable physical cause. In such cases it is assumed that psychological factors underlie the symptoms. – Dissociative disorder (Nevid Pgs. 394, 396-397 Coon, Pgs. 500-501): Temporary amnes ...
Mental Health In Australia
... What distinguishes fear from anxiety? Fear is a state of immediate alarm in response to a serious, known threat to one’s well-being Anxiety is a state of alarm in response to a vague sense of threat or danger Both have the same physiological features – increase in respiration, perspiration, musc ...
... What distinguishes fear from anxiety? Fear is a state of immediate alarm in response to a serious, known threat to one’s well-being Anxiety is a state of alarm in response to a vague sense of threat or danger Both have the same physiological features – increase in respiration, perspiration, musc ...