The CBQ and the Core Phenotype - Juvenile Bipolar Research
... subgroups on parent-reported severe self-injury and severe injury to others and on frequency of parentreported suicidal threats. High fear-of-harm was strongly associated with parent-reported severe selfinjury and severe injury to others. For injurious acts directed at others they found a nearly-eig ...
... subgroups on parent-reported severe self-injury and severe injury to others and on frequency of parentreported suicidal threats. High fear-of-harm was strongly associated with parent-reported severe selfinjury and severe injury to others. For injurious acts directed at others they found a nearly-eig ...
Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 6th edition
... • During and immediately after trauma, many people become highly anxious and depressed – For some, feelings persist well after the trauma • These people may be experiencing: – Acute stress disorder – Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) ...
... • During and immediately after trauma, many people become highly anxious and depressed – For some, feelings persist well after the trauma • These people may be experiencing: – Acute stress disorder – Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) ...
Between 1 and 2% of adults have avoidant personality disorder
... difficult to distinguish one from another The frequent lack of agreement between clinicians and diagnosticians has raised concerns about the validity and reliability of these categories It is important to note that diagnoses of personality disorder can easily be ...
... difficult to distinguish one from another The frequent lack of agreement between clinicians and diagnosticians has raised concerns about the validity and reliability of these categories It is important to note that diagnoses of personality disorder can easily be ...
Folie a Deux Versus Genetically Driven Delusional Disorder: Case
... was diagnosed as suffering from paranoid schizophrenia. In 1988, she was first brought to our department for treatment. T.U. showed paranoid ideas, and was extremely suspicious, irritated, anxious, and depressed. Within 2 weeks, she became logorrheic and reported some of her delusional beliefs: her ...
... was diagnosed as suffering from paranoid schizophrenia. In 1988, she was first brought to our department for treatment. T.U. showed paranoid ideas, and was extremely suspicious, irritated, anxious, and depressed. Within 2 weeks, she became logorrheic and reported some of her delusional beliefs: her ...
Diagnosis in the Assessment Process
... disorders are now required by federal and state laws (e.g., PL94-142, Individuals with Disabilities Education Act [IDEA]) and a diagnosis is generally necessary if professionals are to identify students with such disorders. Today, teachers, school counselors, school psychologists, child study team m ...
... disorders are now required by federal and state laws (e.g., PL94-142, Individuals with Disabilities Education Act [IDEA]) and a diagnosis is generally necessary if professionals are to identify students with such disorders. Today, teachers, school counselors, school psychologists, child study team m ...
conference proceedings - Columbia University School of Social Work
... The first Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (posthumously named DSM-I) was, of course, primarily a nomenclature, rather than the comprehensive manual that we have today. It grew out of a need for a uniform naming system for the disorders for which the field of psychiatry was responsible. Prior to it ...
... The first Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (posthumously named DSM-I) was, of course, primarily a nomenclature, rather than the comprehensive manual that we have today. It grew out of a need for a uniform naming system for the disorders for which the field of psychiatry was responsible. Prior to it ...
Is hypochondriasis an anxiety disorder?
... significant others about bodily sensations which have been appropriately evaluated and judged to be benign. As a result of these emotional, cognitive and behavioural manifestations, hypochondriasis is often disruptive to social, occupational and family functioning, and its associated economic costs ...
... significant others about bodily sensations which have been appropriately evaluated and judged to be benign. As a result of these emotional, cognitive and behavioural manifestations, hypochondriasis is often disruptive to social, occupational and family functioning, and its associated economic costs ...
Binge-eAting DisorDer - Practice Fusion Tutorials
... Some individuals describe a dissociative quality during, or following, the binge-eating episodes. The impairment in control associated with binge eating may not be absolute; for example, an individual may continue binge eating while the telephone is ringing but will cease if a roommate or spouse une ...
... Some individuals describe a dissociative quality during, or following, the binge-eating episodes. The impairment in control associated with binge eating may not be absolute; for example, an individual may continue binge eating while the telephone is ringing but will cease if a roommate or spouse une ...
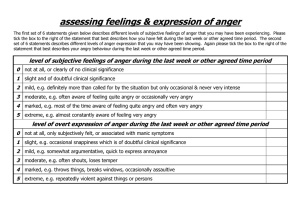
Anger Assessment Questionnaire
... BACKGROUND: This study sought to evaluate the degree of anger and aggression experienced by psychiatric outpatients and to determine whether anger is as prominent an emotional state in these patients as are depression and anxiety. We also sought to determine which Axis I and Axis II disorders were a ...
... BACKGROUND: This study sought to evaluate the degree of anger and aggression experienced by psychiatric outpatients and to determine whether anger is as prominent an emotional state in these patients as are depression and anxiety. We also sought to determine which Axis I and Axis II disorders were a ...
Deconstructing the DSM-5 By Jason H. King The DSM
... To diagnose a substance abuse disorder in the DSM-IV-TR, individuals only needed to present with one criterion, whereas to diagnose a substance-related disorder in the DSM-5, individuals must present with a minimum of two criteria. And to avoid overdiagnosing substance abuse solely on legal involve ...
... To diagnose a substance abuse disorder in the DSM-IV-TR, individuals only needed to present with one criterion, whereas to diagnose a substance-related disorder in the DSM-5, individuals must present with a minimum of two criteria. And to avoid overdiagnosing substance abuse solely on legal involve ...
Definitions and Diagnosis of Schizophrenia
... • E: The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (eg, a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition • F: If there is a history of autism spectrum disorder or a communication disorder of childhood onset, the additional diagnosis of schizophrenia is ma ...
... • E: The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (eg, a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition • F: If there is a history of autism spectrum disorder or a communication disorder of childhood onset, the additional diagnosis of schizophrenia is ma ...
Is it Trauma or Fantasy-based? Comparing Dissociative Identity
... of Dorahy et al.[25,26]. Therefore, we provide descriptions of the dissociative personality states of patients and simulating controls who participated in our study. These reported differences coincide with theoretical differences[27]. Descriptions of neutral personality states (NPS) and trauma-rela ...
... of Dorahy et al.[25,26]. Therefore, we provide descriptions of the dissociative personality states of patients and simulating controls who participated in our study. These reported differences coincide with theoretical differences[27]. Descriptions of neutral personality states (NPS) and trauma-rela ...
Recovering from Violent Crime - Canadian Resource Centre for
... Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is often times a diagnosis that follows ASD. It is more often diagnosed in people who have experienced or witnessed incidents of very violent crimes or are victims of war. The symptoms are similar to those present in ASD except fo ...
... Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is often times a diagnosis that follows ASD. It is more often diagnosed in people who have experienced or witnessed incidents of very violent crimes or are victims of war. The symptoms are similar to those present in ASD except fo ...
Mood (affective) disorders (F30-F39)
... The patient is currently depressed, as in severe depressive episode with psychotic symptoms (F32.3), and has had at least one authenticated hypomanic, manic, or mixed affective episode in the past. F31.6 Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mixed The patient has had at least one authenticated ...
... The patient is currently depressed, as in severe depressive episode with psychotic symptoms (F32.3), and has had at least one authenticated hypomanic, manic, or mixed affective episode in the past. F31.6 Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mixed The patient has had at least one authenticated ...
Psychological and Neurobehavioral Comparisons of Children with
... and because of the historical confusion over the validity of HFA and Asperger’s Disorder as separate diagnostic entities. It is estimated that 75% of individuals diagnosed with Autistic Disorder will have IQ’s below 70, and up to 50% of them are mute or severely lacking in communication skills (Penn ...
... and because of the historical confusion over the validity of HFA and Asperger’s Disorder as separate diagnostic entities. It is estimated that 75% of individuals diagnosed with Autistic Disorder will have IQ’s below 70, and up to 50% of them are mute or severely lacking in communication skills (Penn ...
- Positive Emotion and Psychopathology Lab
... across disorders. Three candidate transdiagnostic processes involved in emotion regulation – rumination, worry, and automatic negative thoughts – were examined in euthymic bipolar I disorder (n ¼ 21) and insomnia (n ¼ 19), and a non-clinical control group (n ¼ 20). Rumination and worry were endorsed ...
... across disorders. Three candidate transdiagnostic processes involved in emotion regulation – rumination, worry, and automatic negative thoughts – were examined in euthymic bipolar I disorder (n ¼ 21) and insomnia (n ¼ 19), and a non-clinical control group (n ¼ 20). Rumination and worry were endorsed ...
Definition from DSM-5 ®—Understanding Mental Disorders What is
... that meets criteria for hoarding disorder because the lack of clutter is due to a thirdparty intervention. Hoarding disorder contrasts with normative collecting behavior, which is organized and systematic, even if in some cases the actual amount of possessions may be similar to the amount accumulate ...
... that meets criteria for hoarding disorder because the lack of clutter is due to a thirdparty intervention. Hoarding disorder contrasts with normative collecting behavior, which is organized and systematic, even if in some cases the actual amount of possessions may be similar to the amount accumulate ...
The Prosecutor`s Guide to Mental Health Disorders
... Disorders, however, are very rare. Further, the victim is likely to be under the active care of a mental health professional, who will be the best judge of her ability to testify competently. When the victim’s treating mental health professional determines that she is able to testify, the prosecutor ...
... Disorders, however, are very rare. Further, the victim is likely to be under the active care of a mental health professional, who will be the best judge of her ability to testify competently. When the victim’s treating mental health professional determines that she is able to testify, the prosecutor ...
Behavioural addictions and the transition from DSM-IV-TR to DSM-5
... ‘Substance-related and Addictive Disorders’ 4. Pathophysiological models for drug addiction were therefore considered to be relevant to GD and affected patients, who may benefit from therapeutic approaches used to treat SUDs 21. There is strong evidence suggesting that similar predispositions (gen ...
... ‘Substance-related and Addictive Disorders’ 4. Pathophysiological models for drug addiction were therefore considered to be relevant to GD and affected patients, who may benefit from therapeutic approaches used to treat SUDs 21. There is strong evidence suggesting that similar predispositions (gen ...
Disorders and Therapies Powerpoint
... suffer torture and violence, they are also often forced to commit atrocities against others. Not surprisingly, These children suffer from a very high rate of posttraumatic stress disorder (Bayer &others, 2007; Kohrt & others, 2008). One survey of former child soldiers in refugee camps in Uganda foun ...
... suffer torture and violence, they are also often forced to commit atrocities against others. Not surprisingly, These children suffer from a very high rate of posttraumatic stress disorder (Bayer &others, 2007; Kohrt & others, 2008). One survey of former child soldiers in refugee camps in Uganda foun ...
Dimensions and Latent Classes of Episodic Mania-Like Argyris Stringaris Daniel Stahl
... early bipolar presentations (Wozniak et al. 1995). However, subsequent studies have not found evidence to support such a view (Leibenluft 2011; Potegal, et al. 2009; Stringaris et al. 2010a). In light of the current state of evidence, this study anchors its examination of mania-like symptoms on the ...
... early bipolar presentations (Wozniak et al. 1995). However, subsequent studies have not found evidence to support such a view (Leibenluft 2011; Potegal, et al. 2009; Stringaris et al. 2010a). In light of the current state of evidence, this study anchors its examination of mania-like symptoms on the ...
ICD-10: F60-62 Personality Disorders (F62.0
... Personality disorders are therefore subdivided according to clusters of traits that correspond to the most frequent or conspicuous behavioural manifestations. The subtypes so described are widely recognized as major forms of personality deviation. In making a diagnosis of personality disorder, the c ...
... Personality disorders are therefore subdivided according to clusters of traits that correspond to the most frequent or conspicuous behavioural manifestations. The subtypes so described are widely recognized as major forms of personality deviation. In making a diagnosis of personality disorder, the c ...
Chapter 8 - IPFW.edu
... • World has become unreal World appears strange, peculiar, foreign, dream-like Objects appear at times strangely diminished in size, at times flat Incapable of experiencing emotions Feeling as if they were dead, lifeless, mere automatons © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... • World has become unreal World appears strange, peculiar, foreign, dream-like Objects appear at times strangely diminished in size, at times flat Incapable of experiencing emotions Feeling as if they were dead, lifeless, mere automatons © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...