The treatment and management of bipolar disorder
... Taking ongoing medication (even when the person is well) can prevent bipolar relapse, reduce hospitalizations and suicide risk. Medications can also reduce symptoms if the person experiences a bipolar episode.1,2 Some bipolar episodes are more severe than others. While many people can be treated at ...
... Taking ongoing medication (even when the person is well) can prevent bipolar relapse, reduce hospitalizations and suicide risk. Medications can also reduce symptoms if the person experiences a bipolar episode.1,2 Some bipolar episodes are more severe than others. While many people can be treated at ...
Full Text
... marked anxiety, burst of anger was also described in patients with BD. Cyclothimic disorder represent more chronic and less severe clinical form of bipolar disorder with periods of hypomanic symptoms alternating with periods of mild or moderate depression. Lifetime prevalence of bipolar disorder typ ...
... marked anxiety, burst of anger was also described in patients with BD. Cyclothimic disorder represent more chronic and less severe clinical form of bipolar disorder with periods of hypomanic symptoms alternating with periods of mild or moderate depression. Lifetime prevalence of bipolar disorder typ ...
Chapter 11 Summary
... Anxiety can be described as an immediate reaction (known as the fight/flight response) to perceived danger or threat. The physical system, cognitive system, and behavioral system are the three interrelated response systems in which symptoms of anxiety are expressed. Some anxiety experiences during c ...
... Anxiety can be described as an immediate reaction (known as the fight/flight response) to perceived danger or threat. The physical system, cognitive system, and behavioral system are the three interrelated response systems in which symptoms of anxiety are expressed. Some anxiety experiences during c ...
ESSU Technical Assistance Resources
... affecting children and adolescents, impacting anywhere from 2% to 27% of children and adolescents (Costello, Egger & Angold, 2005). Children with internalizing disorders such as depression and anxiety are often overlooked, and symptoms and impairments are often not addressed. The negative effects of ...
... affecting children and adolescents, impacting anywhere from 2% to 27% of children and adolescents (Costello, Egger & Angold, 2005). Children with internalizing disorders such as depression and anxiety are often overlooked, and symptoms and impairments are often not addressed. The negative effects of ...
Chapter 16: Psychological Disorders
... given a particular diagnostic label. These more precise diagnostic criteria reduce the chances that the same patient will be classified as schizophrenic by one doctor and manic depressive by another. Because researchers often rely on diagnostic labels to study underlying factors that may cause disor ...
... given a particular diagnostic label. These more precise diagnostic criteria reduce the chances that the same patient will be classified as schizophrenic by one doctor and manic depressive by another. Because researchers often rely on diagnostic labels to study underlying factors that may cause disor ...
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Curr Opin Psychiatry
... difficulties in establishing enduring relationships since early in life, when using such a term. Such a comprehensive assessment will also help demarcate the problems from other pathology, such as bipolar disorder. These results and the fact that adolescent irritability is an independent predictor o ...
... difficulties in establishing enduring relationships since early in life, when using such a term. Such a comprehensive assessment will also help demarcate the problems from other pathology, such as bipolar disorder. These results and the fact that adolescent irritability is an independent predictor o ...
Durand and Barlow Chapter 6: Mood Disorders and Suicide
... – Disturbed physical functioning – Anhedonia – Loss of pleasure/interest in usual activities ...
... – Disturbed physical functioning – Anhedonia – Loss of pleasure/interest in usual activities ...
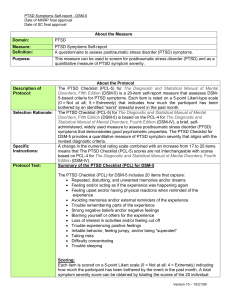
DSM-IV-TR criteria for PTSD
... The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders provides standard criteria and common language for the classification of mental disorders. It is published by the American Psychiatric Association. The fifth revision (DSM-5) is scheduled to release in May 2013: This will include changes to t ...
... The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders provides standard criteria and common language for the classification of mental disorders. It is published by the American Psychiatric Association. The fifth revision (DSM-5) is scheduled to release in May 2013: This will include changes to t ...
ADHD Presentation Slides - NCTM Birmingham, AL, 2005
... have other mental disorders. Over half of the children diagnosed with ADHD carry the disorder into adulthood. A large number of adults who were never diagnosed as a child show clear symptoms of ADHD. AMA’s Special Council Report showed little evidence of widespread over-diagnosis of ADHD or over-pre ...
... have other mental disorders. Over half of the children diagnosed with ADHD carry the disorder into adulthood. A large number of adults who were never diagnosed as a child show clear symptoms of ADHD. AMA’s Special Council Report showed little evidence of widespread over-diagnosis of ADHD or over-pre ...
ADHD Presentation - NCTM Anaheim, CA, 2005
... have other mental disorders. Over half of the children diagnosed with ADHD carry the disorder into adulthood. A large number of adults who were never diagnosed as a child show clear symptoms of ADHD. AMA’s Special Council Report showed little evidence of widespread over-diagnosis of ADHD or over-pre ...
... have other mental disorders. Over half of the children diagnosed with ADHD carry the disorder into adulthood. A large number of adults who were never diagnosed as a child show clear symptoms of ADHD. AMA’s Special Council Report showed little evidence of widespread over-diagnosis of ADHD or over-pre ...
A Case Report - ALEX IGLESIAS, Ph.D.
... decision was reached to treat him symptomatically and if necessary, proceed to uncovering methods. The etiology of this case consisted of features of panic disorder which created an optimal environment for phobic conditions to develop. The patient then created the avoidance from I-95 as a defense. T ...
... decision was reached to treat him symptomatically and if necessary, proceed to uncovering methods. The etiology of this case consisted of features of panic disorder which created an optimal environment for phobic conditions to develop. The patient then created the avoidance from I-95 as a defense. T ...
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... tension, or sleep disturbance. Patients must meet all 6 diagnostic criteria. What physical examination findings indicate possible generalized anxiety disorder? A patient with GAD can appear restless, irritable, or fatigued. In primary care settings, patients with GAD may also have medically unexplai ...
... tension, or sleep disturbance. Patients must meet all 6 diagnostic criteria. What physical examination findings indicate possible generalized anxiety disorder? A patient with GAD can appear restless, irritable, or fatigued. In primary care settings, patients with GAD may also have medically unexplai ...
The Black Mask of Humanity: Racial/Ethnic Discrimination and Post
... instances of discrimination are as frequent as reported; but the devastating emotional responses to the racist acts are unsettling. The range and intensity of emotional responses varies from mild to overwhelming, and the duration of such responses varies from days to months or years. With a fair deg ...
... instances of discrimination are as frequent as reported; but the devastating emotional responses to the racist acts are unsettling. The range and intensity of emotional responses varies from mild to overwhelming, and the duration of such responses varies from days to months or years. With a fair deg ...
ADHD: Our Advancing Knowledge and Implications for the
... Hyperactive Child Syndrome (1960’s) ADD ...
... Hyperactive Child Syndrome (1960’s) ADD ...
Treating Anxiety and OCD: Past, Present and Future
... Question for DSM V • Is OCD part of Anxiety disorder ? • If it is separate then what disorders should be included ? • What may be the system that we could use to diagnose those disorders ? • OCD in other psychiatric disorders- Is there a case for “schizo-obsessive” ...
... Question for DSM V • Is OCD part of Anxiety disorder ? • If it is separate then what disorders should be included ? • What may be the system that we could use to diagnose those disorders ? • OCD in other psychiatric disorders- Is there a case for “schizo-obsessive” ...
Aggression as a Symptom of Mood
... pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) is unknown but available evidence suggests that it may be as high or possibly even higher than in the general population. Clinic-based studies suggest that depression is the most common psychiatric disorder in PDD, with rates between 30-37% (Ghaziuddin, Ghaziu ...
... pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) is unknown but available evidence suggests that it may be as high or possibly even higher than in the general population. Clinic-based studies suggest that depression is the most common psychiatric disorder in PDD, with rates between 30-37% (Ghaziuddin, Ghaziu ...
Evidence Summary: Diagnosing Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) in Adolescence:
... professionals that PDs cannot be diagnosed until adult life and that they are ‘untreatable’. This belief is especially common among clinicians in relation to borderline personality disorder (BPD), the most common and severe PD in clinical practice (4). ...
... professionals that PDs cannot be diagnosed until adult life and that they are ‘untreatable’. This belief is especially common among clinicians in relation to borderline personality disorder (BPD), the most common and severe PD in clinical practice (4). ...
Tilburg University Mental disorders as complex networks Nuijten
... – simple counts of how many symptoms a person displays – not everyone with the same diagnosis has the same symptoms. For instance, according to the DSM-5 (American Psychiatric Association 2013) MD is diagnosed using nine symptoms that function as diagnostic criteria: depressed mood, diminished inter ...
... – simple counts of how many symptoms a person displays – not everyone with the same diagnosis has the same symptoms. For instance, according to the DSM-5 (American Psychiatric Association 2013) MD is diagnosed using nine symptoms that function as diagnostic criteria: depressed mood, diminished inter ...
Chapter 16: Psychological Disorders
... given a particular diagnostic label. These more precise diagnostic criteria reduce the chances that the same patient will be classified as schizophrenic by one doctor and manic depressive by another. Because researchers often rely on diagnostic labels to study underlying factors that may cause disor ...
... given a particular diagnostic label. These more precise diagnostic criteria reduce the chances that the same patient will be classified as schizophrenic by one doctor and manic depressive by another. Because researchers often rely on diagnostic labels to study underlying factors that may cause disor ...
Psychological Disorders - Miami East Local Schools
... given a particular diagnostic label. These more precise diagnostic criteria reduce the chances that the same patient will be classified as schizophrenic by one doctor and manic depressive by another. Because researchers often rely on diagnostic labels to study underlying factors that may cause disor ...
... given a particular diagnostic label. These more precise diagnostic criteria reduce the chances that the same patient will be classified as schizophrenic by one doctor and manic depressive by another. Because researchers often rely on diagnostic labels to study underlying factors that may cause disor ...
(Disorders). - Paul Trapnell
... Disorder shows up in how a person thinks, feels, gets along with others, and the ability to control own actions ...
... Disorder shows up in how a person thinks, feels, gets along with others, and the ability to control own actions ...
Birthplace
... bothered by an identified “worst” stressful event in the past month. The PTSD Checklist (PCL-5) for The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) is based on the PCL-4 for The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV), a brief, ...
... bothered by an identified “worst” stressful event in the past month. The PTSD Checklist (PCL-5) for The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) is based on the PCL-4 for The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV), a brief, ...
OSC_Psychology_TestBank_Ch15_Psychological_Disorders
... mood, excessive talkativeness, irritability, increased activity levels, and other symptoms C. in which an individual has a tendency to repetitively and passively dwell on one’s depressed symptoms, their meanings, and their consequences *D. that applies to women who experience an episode of major dep ...
... mood, excessive talkativeness, irritability, increased activity levels, and other symptoms C. in which an individual has a tendency to repetitively and passively dwell on one’s depressed symptoms, their meanings, and their consequences *D. that applies to women who experience an episode of major dep ...
1. Medical Condition ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY
... the symptoms of which can persist through adolescence into adulthood and become lifelong.1-3 This has been confirmed in long-term follow-up studies which have demonstrated the persistence of symptoms in many adults diagnosed with ADHD in childhood.4–8 A meta-analysis of follow-up ADHD studies report ...
... the symptoms of which can persist through adolescence into adulthood and become lifelong.1-3 This has been confirmed in long-term follow-up studies which have demonstrated the persistence of symptoms in many adults diagnosed with ADHD in childhood.4–8 A meta-analysis of follow-up ADHD studies report ...
Mental disorders as complex networks
... – simple counts of how many symptoms a person displays – not everyone with the same diagnosis has the same symptoms. For instance, according to the DSM-5 (American Psychiatric Association 2013) MD is diagnosed using nine symptoms that function as diagnostic criteria: depressed mood, diminished inter ...
... – simple counts of how many symptoms a person displays – not everyone with the same diagnosis has the same symptoms. For instance, according to the DSM-5 (American Psychiatric Association 2013) MD is diagnosed using nine symptoms that function as diagnostic criteria: depressed mood, diminished inter ...