Psi Chi/ PSA - Michigan State University
... rationality of the motivation. b. An act or acts performed in response to such an impulse. ...
... rationality of the motivation. b. An act or acts performed in response to such an impulse. ...
Obsessive–compulsive disorder
... The cognitive–behavioral model suggests that compulsive behaviour is carried out to remove anxiety-provoking intrusive thoughts. Unfortunately this only brings about temporary relief as the thought reemerges. Each time the behaviour occurs it is negatively reinforced (see Reinforcement) by the relie ...
... The cognitive–behavioral model suggests that compulsive behaviour is carried out to remove anxiety-provoking intrusive thoughts. Unfortunately this only brings about temporary relief as the thought reemerges. Each time the behaviour occurs it is negatively reinforced (see Reinforcement) by the relie ...
DSM-5: Assessment and Treatment of PTSD
... F. Duration of the disturbance (Criteria B, C, D, and E) is more than 1 month. G. The disturbance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. H. The disturbance is not attributable to physiological effects of a substance (e.g ...
... F. Duration of the disturbance (Criteria B, C, D, and E) is more than 1 month. G. The disturbance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. H. The disturbance is not attributable to physiological effects of a substance (e.g ...
Complex Trauma Exposure and Symptoms in Urban Traumatized
... that individuals diagnosed with PTSD were 8 times more likely to have three or more additional diagnoses than individuals with other psychiatric illness. Chronicity and co-occurrence as they relate to trauma appear to be particularly salient, as evidence indicates that they may have a direct, dose-d ...
... that individuals diagnosed with PTSD were 8 times more likely to have three or more additional diagnoses than individuals with other psychiatric illness. Chronicity and co-occurrence as they relate to trauma appear to be particularly salient, as evidence indicates that they may have a direct, dose-d ...
Boyle MP 2014 - Adler Graduate School
... prescribed, character traits often mimic the behaviors that raise red flags to mental health professionals. These traits have usually been present throughout the duration of their lives. Negative patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving seem natural to these individuals. Individuals who meet the ...
... prescribed, character traits often mimic the behaviors that raise red flags to mental health professionals. These traits have usually been present throughout the duration of their lives. Negative patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving seem natural to these individuals. Individuals who meet the ...
1 CHAPTER 7 SCHIZOPHRENIA Schizophrenia a serious mental
... delusions and formal thought disorder. This is like diagnosing heart disease only at the time of myocardial infarction. Recently, schizophrenia has been conceptualized in four phases. 1) Risk phase – this mainly includes genetic, intrauterine (infection) and obstetric risks, although other risks may ...
... delusions and formal thought disorder. This is like diagnosing heart disease only at the time of myocardial infarction. Recently, schizophrenia has been conceptualized in four phases. 1) Risk phase – this mainly includes genetic, intrauterine (infection) and obstetric risks, although other risks may ...
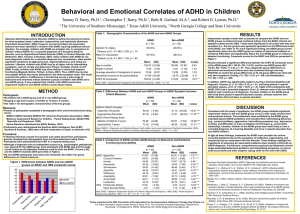
N - The University of Southern Mississippi
... for three symptom areas: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity (American Psychiatric Association, 2000). However, several correlates and associated features have been identified in children with ADHD requiring additional clinical attention. For example, children with ADHD are at higher risk, i ...
... for three symptom areas: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity (American Psychiatric Association, 2000). However, several correlates and associated features have been identified in children with ADHD requiring additional clinical attention. For example, children with ADHD are at higher risk, i ...
A Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: How to alleviate her suffering Accurate diagnosis, tailored
... tension, depressed mood, and somatic complaints such as breast tenderness and bloating—often are mild to moderate and cause minimal distress.1 However, approximately 3% to 9% of women experience moderate to severe premenstrual mood symptoms that meet criteria for premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMD ...
... tension, depressed mood, and somatic complaints such as breast tenderness and bloating—often are mild to moderate and cause minimal distress.1 However, approximately 3% to 9% of women experience moderate to severe premenstrual mood symptoms that meet criteria for premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMD ...
Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Effective Case
... happens more days that not; and lasts for at least 6 months (American Psychiatric Association, 2013). Individuals with GAD feel like their thoughts are spinning out of control and become preoccupied with fears of imminent disaster, making it hard to concentrate and resulting in a strong emotional re ...
... happens more days that not; and lasts for at least 6 months (American Psychiatric Association, 2013). Individuals with GAD feel like their thoughts are spinning out of control and become preoccupied with fears of imminent disaster, making it hard to concentrate and resulting in a strong emotional re ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... and clinical experience in the field of BDs. There was no funding from any source for the development of the guidelines and the activities of the workgroup. All the members of the workgroup were psychiatrists who are in active clinical practice and were selected according to their expertise and with ...
... and clinical experience in the field of BDs. There was no funding from any source for the development of the guidelines and the activities of the workgroup. All the members of the workgroup were psychiatrists who are in active clinical practice and were selected according to their expertise and with ...
Comorbid Depressive and Anxiety Disorders in 509 Individuals With
... groups. In addition to attenuated psychotic symptoms, subjects at high risk for psychosis usually present with other clinical concerns. High levels of negative symptoms, significant impairments in academic performance and occupational functioning, and difficulties with interpersonal relationships as ...
... groups. In addition to attenuated psychotic symptoms, subjects at high risk for psychosis usually present with other clinical concerns. High levels of negative symptoms, significant impairments in academic performance and occupational functioning, and difficulties with interpersonal relationships as ...
management of difficult cases: healing the
... somatic difficulties, (occasionally) with more severe problems like Depersonalization, Nightmares & sleep disorders, Eating disorders, Apparent psychotic symptoms, Identity problems, Suicidality or self-injury, Recovery from substance abuse, and Recovery from child abuse. B. They have a history of t ...
... somatic difficulties, (occasionally) with more severe problems like Depersonalization, Nightmares & sleep disorders, Eating disorders, Apparent psychotic symptoms, Identity problems, Suicidality or self-injury, Recovery from substance abuse, and Recovery from child abuse. B. They have a history of t ...
Mood Disorders
... From a strict diagnostic point of view, our discussion of mood disorders might now be complete. However, there is growing recognition that many or even most patients seen in clinical practice may have a mood disorder that is not well described by the categories outlined above. Formally, they would b ...
... From a strict diagnostic point of view, our discussion of mood disorders might now be complete. However, there is growing recognition that many or even most patients seen in clinical practice may have a mood disorder that is not well described by the categories outlined above. Formally, they would b ...
About Anxiety Attacks - UCLA Center for Mental Health in Schools
... to outside professionals. It calls for practices that • reduce environmental and personal stressors (e.g., making environmental changes and offering personal accommodations to reduce stressors) • enhance the motivation and capacity of school staff to reduce anxiety provoking situations and provide r ...
... to outside professionals. It calls for practices that • reduce environmental and personal stressors (e.g., making environmental changes and offering personal accommodations to reduce stressors) • enhance the motivation and capacity of school staff to reduce anxiety provoking situations and provide r ...
persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)
... young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that treatment begins. If a patient has even mild symptoms of depression during a remission this is a strong predictor that a major depressive episode will recur. With appropriate treatment, 70-80% of individuals ...
... young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that treatment begins. If a patient has even mild symptoms of depression during a remission this is a strong predictor that a major depressive episode will recur. With appropriate treatment, 70-80% of individuals ...
Personality Disorders
... However, these disorders often do not come to a clinician’s attention until years later, after a series of difficulties have forced clients into treatment or after they have become motivated to change a life of constant, emotional turmoil. Also, by definition, personality disorders are relatively st ...
... However, these disorders often do not come to a clinician’s attention until years later, after a series of difficulties have forced clients into treatment or after they have become motivated to change a life of constant, emotional turmoil. Also, by definition, personality disorders are relatively st ...
EEG Neurofeedback for Treating Psychiatric Disorders
... In a survey, 36 children, ages 6 years to 17 years, receiving EEG neurofeedback as a treatment for attention-deficit disorder (ADD)/ADHD were evaluated for changes in both subjective and objective clinical parameters (Alhambra et al., 1995). After 20 sessions, subjective improvement based on parenta ...
... In a survey, 36 children, ages 6 years to 17 years, receiving EEG neurofeedback as a treatment for attention-deficit disorder (ADD)/ADHD were evaluated for changes in both subjective and objective clinical parameters (Alhambra et al., 1995). After 20 sessions, subjective improvement based on parenta ...
Depressive disorders include disruptive mood
... young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that treatment begins. If a patient has even mild symptoms of depression during a remission this is a strong predictor that a major depressive episode will recur. With appropriate treatment, 70-80% of individuals ...
... young age; multiple episodes of depression, and; the length of time after symptom onset that treatment begins. If a patient has even mild symptoms of depression during a remission this is a strong predictor that a major depressive episode will recur. With appropriate treatment, 70-80% of individuals ...
Conversion Disorder - Europe`s Journal of Psychology
... & Barrett, 2004; Piper, Lillevik, & Kritzer, 2008; Rofé, 2008), which constitutes the "cornerstone on which the whole structure of psychoanalysis rests" (Freud, 1914, p. 16). Many others question the soundness of "Freudian unconscious", the second pillar of the psychoanalytic theory of neuroses and ...
... & Barrett, 2004; Piper, Lillevik, & Kritzer, 2008; Rofé, 2008), which constitutes the "cornerstone on which the whole structure of psychoanalysis rests" (Freud, 1914, p. 16). Many others question the soundness of "Freudian unconscious", the second pillar of the psychoanalytic theory of neuroses and ...
Bipolar_Child_2009 - Research Repository UCD
... disorder is the classic prototype of the condition historically known as manic-depression. In DSM IV TR cyclothymia and BDNOS are also listed as bipolar conditions. In children and adolescents, cyclothymia is diagnosed when, over a period of at least a year, there are many hypomanic episodes alterna ...
... disorder is the classic prototype of the condition historically known as manic-depression. In DSM IV TR cyclothymia and BDNOS are also listed as bipolar conditions. In children and adolescents, cyclothymia is diagnosed when, over a period of at least a year, there are many hypomanic episodes alterna ...
MRI in Autism Discordant Siblings
... Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)- Pervasive pattern of negativistic, defiant, disobedient, and hostile behaviors toward authority figures Conduct Disorder (CD)- Repetitive pattern of violating the basic rights of others/ major age-appropriate social norms or rules are violated Mood disorders (dep ...
... Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)- Pervasive pattern of negativistic, defiant, disobedient, and hostile behaviors toward authority figures Conduct Disorder (CD)- Repetitive pattern of violating the basic rights of others/ major age-appropriate social norms or rules are violated Mood disorders (dep ...
Dissociative Experience and Cultural Neuroscience
... Though many of the college students who scored high on the DES came close to meeting the criteria for DSM-IV dissociative disorders, it is notable that they failed to meet the distress criterion (Ross et al. 1990). This criterion states that individuals must experience ‘‘clinically significant distr ...
... Though many of the college students who scored high on the DES came close to meeting the criteria for DSM-IV dissociative disorders, it is notable that they failed to meet the distress criterion (Ross et al. 1990). This criterion states that individuals must experience ‘‘clinically significant distr ...
Chakras
... suddenly becomes weak. If the patient continues to think about their problem while, at the same time, thinking about a previous time: 1, 2, 3, … etc. years ago, the muscle suddenly becomes strong again at the time before the trauma occurred: ...
... suddenly becomes weak. If the patient continues to think about their problem while, at the same time, thinking about a previous time: 1, 2, 3, … etc. years ago, the muscle suddenly becomes strong again at the time before the trauma occurred: ...
MissHExp4ocd
... - But research results relating to serotonin are varied – sometimes symptoms have been made worse. There is a great deal of contradictory research. - Drugs seem to show only partial alleviation of the symptoms so the process is not fully understood. The exact function of neurotransmitters in the dev ...
... - But research results relating to serotonin are varied – sometimes symptoms have been made worse. There is a great deal of contradictory research. - Drugs seem to show only partial alleviation of the symptoms so the process is not fully understood. The exact function of neurotransmitters in the dev ...
Alcohol Misuse - Dr Philip Morris
... An ‘anti-craving’ drug Supportive evidence base of clinical trials for mid-term use (up to 12 months) Reduces relapse to heavy drinking and reduces alcohol consumption Can be used in ‘controlled drinking’ models Most effective when high levels of craving, positive family history, and in patients wit ...
... An ‘anti-craving’ drug Supportive evidence base of clinical trials for mid-term use (up to 12 months) Reduces relapse to heavy drinking and reduces alcohol consumption Can be used in ‘controlled drinking’ models Most effective when high levels of craving, positive family history, and in patients wit ...