Forced Convection
... Assuming no‐slip condition at the wall, the velocity of the fluid layer at the wall is zero. The motionless layer slows down the particles of the neighboring fluid layers as a result of friction between the two adjacent layers. The presence of the plate is felt up to some distance ...
... Assuming no‐slip condition at the wall, the velocity of the fluid layer at the wall is zero. The motionless layer slows down the particles of the neighboring fluid layers as a result of friction between the two adjacent layers. The presence of the plate is felt up to some distance ...
Factor by Using the Distributive Property
... Factoring by Grouping Factoring by grouping is used to factor polynomials that do not hall the same GCF. This is primarily used to factor polynomials with four terms. Example 2: Factoring Using Grouping Factor each expression. a.) ...
... Factoring by Grouping Factoring by grouping is used to factor polynomials that do not hall the same GCF. This is primarily used to factor polynomials with four terms. Example 2: Factoring Using Grouping Factor each expression. a.) ...
Interactions between freestream turbulence and boundary layers
... Rodi (1991) corresponds to that of our example, and the results in the early stages of the interaction are very similar to these theoretical results. Both the DNS and experiments demonstrate the sharp difference between the form and magnitude of the fluctuations in the zones {U} and {M}, and both sh ...
... Rodi (1991) corresponds to that of our example, and the results in the early stages of the interaction are very similar to these theoretical results. Both the DNS and experiments demonstrate the sharp difference between the form and magnitude of the fluctuations in the zones {U} and {M}, and both sh ...
slides - NIMML
... – Throwing dice in a simulation is easier than integrating stochastic [partial, delay] differential equations ...
... – Throwing dice in a simulation is easier than integrating stochastic [partial, delay] differential equations ...
Delay Differential Equations
... The DDEs are coded in a straightforward way using a global variable state which is sign(y1 (t)). Parameters would be defined in the main program for parameter studies. We could write Z(1) here instead of Z(1,1). function yp = ddes(t,y,Z) ...
... The DDEs are coded in a straightforward way using a global variable state which is sign(y1 (t)). Parameters would be defined in the main program for parameter studies. We could write Z(1) here instead of Z(1,1). function yp = ddes(t,y,Z) ...
Request for the Revision of WIPO Standard ST.80 (annex 1)
... (i) That Act is a modern instrument and as such generally induces the publication of new kinds of data not foreseen by the 1934 and 1960 Acts; (ii) It is the result of a large consensus that (contrary to the more one dimensional 1934 and 1960 Acts), the 1999 Act tries to accommodate the specific nee ...
... (i) That Act is a modern instrument and as such generally induces the publication of new kinds of data not foreseen by the 1934 and 1960 Acts; (ii) It is the result of a large consensus that (contrary to the more one dimensional 1934 and 1960 Acts), the 1999 Act tries to accommodate the specific nee ...
Math 2214, Fall 2014, Form A
... 8. An aquarium containing 20 gallons of water is connected to a pump which drives water through a filter and then pumps it back into the aquarium. The filter removes 90% of the pollutants passing through it. Water in the aquarium is pumped out at a rate of 0.2 gallons per minute through the filter ...
... 8. An aquarium containing 20 gallons of water is connected to a pump which drives water through a filter and then pumps it back into the aquarium. The filter removes 90% of the pollutants passing through it. Water in the aquarium is pumped out at a rate of 0.2 gallons per minute through the filter ...
Fluid Mechanics Primer
... the influence of a constant force δFx. • The oil next to the block sticks to the block and moves at velocity δu. The surface beneath the oil is stationary and the oil there sticks to that surface and has velocity zero. • No-slip boundary condition--The condition of zero velocity at a boundary is k ...
... the influence of a constant force δFx. • The oil next to the block sticks to the block and moves at velocity δu. The surface beneath the oil is stationary and the oil there sticks to that surface and has velocity zero. • No-slip boundary condition--The condition of zero velocity at a boundary is k ...
Bernoulli`s equation
... side, ur = 0 and u2θ > 0, so from Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure there is lower than at the stagnation points but it must have the same symmetry as the flow. Notice that, from Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure does not depend on the direction of the flow, but on its speed kuk only. However, the r ...
... side, ur = 0 and u2θ > 0, so from Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure there is lower than at the stagnation points but it must have the same symmetry as the flow. Notice that, from Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure does not depend on the direction of the flow, but on its speed kuk only. However, the r ...
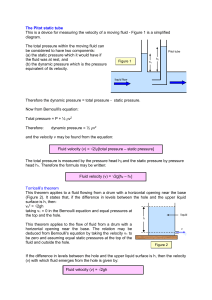
Pitot and Toricelli
... Fluid velocity (v) = √2/[total pressure – static pressure] The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a ...
... Fluid velocity (v) = √2/[total pressure – static pressure] The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a ...
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.