ATM 316 - Balanced flow
... The geostrophic wind (Vg ) is the combination of pressure gradient (PGF) and Coriolis forces that creates a straight-line wind, parallel to the isobars. In this context, if air is seen to curve, in order to follow curved isobars, then another force must be acting – such as the centripetal force. The ...
... The geostrophic wind (Vg ) is the combination of pressure gradient (PGF) and Coriolis forces that creates a straight-line wind, parallel to the isobars. In this context, if air is seen to curve, in order to follow curved isobars, then another force must be acting – such as the centripetal force. The ...
1 Multi-Step Equations with Like Terms
... There are two like terms: the x and the −2x (don’t forget that the negative sign applies to everything in the parentheses). So we need to get those terms together. The associative and distributive properties let us rewrite the equation as x + 5 − 2x + 3 = 6, and then the commutative property lets us ...
... There are two like terms: the x and the −2x (don’t forget that the negative sign applies to everything in the parentheses). So we need to get those terms together. The associative and distributive properties let us rewrite the equation as x + 5 − 2x + 3 = 6, and then the commutative property lets us ...
Sec Math Implementing the 4
... 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically 6. Attend to precision 7. Look for and make use of structure 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning ...
... 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically 6. Attend to precision 7. Look for and make use of structure 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning ...
Chapter 5 Pressure Variation in Flowing Fluids
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
Mathematics Essential Curriculum
... A.REI.B.3 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Note: Students have solved multi-step linear equations in Grade 8. Pretest this standard and review as needed. Create equations that describe numbers or relationships. A.C ...
... A.REI.B.3 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Note: Students have solved multi-step linear equations in Grade 8. Pretest this standard and review as needed. Create equations that describe numbers or relationships. A.C ...
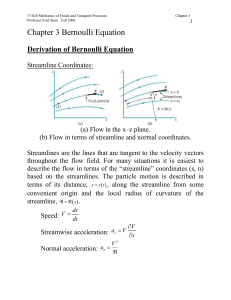
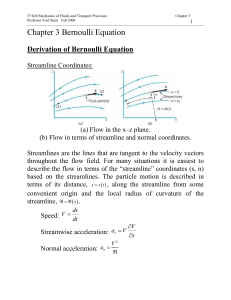
Chapter 3 Bernoulli Equation
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
ConcepTest Question
... a. The mass flow into the control volume is equal to the mass flow out of the control volume b. The rate of change of the amount of mass in the control volume is balanced by the net rate at which mass flows out through the control surface c. The accumulation of mass in the control volume is balanced ...
... a. The mass flow into the control volume is equal to the mass flow out of the control volume b. The rate of change of the amount of mass in the control volume is balanced by the net rate at which mass flows out through the control surface c. The accumulation of mass in the control volume is balanced ...
CHAPTER 05
... 17.The energy equation involves stored energy, heat transfer, and what else? A.velocity B.pressure C.work 18.What represents all of the ways in which energy is exchanged between the control volume contents and surrounding because of temperature difference? YOUR ANSWER: The heat transfer rate 19.Work ...
... 17.The energy equation involves stored energy, heat transfer, and what else? A.velocity B.pressure C.work 18.What represents all of the ways in which energy is exchanged between the control volume contents and surrounding because of temperature difference? YOUR ANSWER: The heat transfer rate 19.Work ...
Abstracts
... The Dynamics of Liquid Movement Inside the Nozzle During the Bubble Departures for Low Air Volume Flow Rate The main aim of investigation was to analyze the influence of liquid movement inside the nozzle on the dynamics of bubble departure. Dynamics of such process decides about the periodic and ape ...
... The Dynamics of Liquid Movement Inside the Nozzle During the Bubble Departures for Low Air Volume Flow Rate The main aim of investigation was to analyze the influence of liquid movement inside the nozzle on the dynamics of bubble departure. Dynamics of such process decides about the periodic and ape ...
Demonstration 1: Fluid Properties, Viscosity
... upon the temperature of the fluid and is characterized by a property called the dynamic viscosity [Ns/m2]. This property provides a measure of how much the fluid resists the shearing motion. A large value of is characteristic of a fluid with large resistance to shearing motions relative to the ...
... upon the temperature of the fluid and is characterized by a property called the dynamic viscosity [Ns/m2]. This property provides a measure of how much the fluid resists the shearing motion. A large value of is characteristic of a fluid with large resistance to shearing motions relative to the ...
6.1 Solving Equations by Using Inverse Operations ` • : "undo" or
... Investigate: Try the Balance Puzzle. When solving linear €;quat!ons, think of the equaliion a:, a with the sign as li;>-: iT-iddle c r When an operation is done to one side of a r equation, it must be done to the other in order to keeo ba!&iv:e The idea is to isolate on the other side. ...
... Investigate: Try the Balance Puzzle. When solving linear €;quat!ons, think of the equaliion a:, a with the sign as li;>-: iT-iddle c r When an operation is done to one side of a r equation, it must be done to the other in order to keeo ba!&iv:e The idea is to isolate on the other side. ...
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.