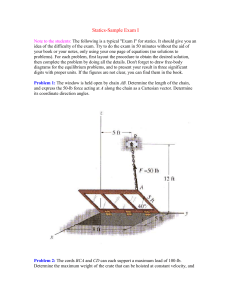
Chapter 5 Physics 205 Solution of Home Work Problems
... well (0 ≤ x ≤ L) and in the region beyond (x > L) that satisfy the appropriate boundary conditions at x = 0 and x = ∞. Enforce the proper matching conditions at x = L to find an equation for the allowed energies of this system. Are there conditions for which no solution is possible? Explain. ...
... well (0 ≤ x ≤ L) and in the region beyond (x > L) that satisfy the appropriate boundary conditions at x = 0 and x = ∞. Enforce the proper matching conditions at x = L to find an equation for the allowed energies of this system. Are there conditions for which no solution is possible? Explain. ...
MATH-UA 123 Calculus III Part1
... (a) Find the unit normal vector as a function of t. (b) Find the curvature as a function of t. (c) Find the unit binormal vector at t = 0. 4. (10 points) Answer “true” or “false.” No justification is needed. No work needs to be shown for this problem. (a) If there is a direction u such that Du f (x∗ ...
... (a) Find the unit normal vector as a function of t. (b) Find the curvature as a function of t. (c) Find the unit binormal vector at t = 0. 4. (10 points) Answer “true” or “false.” No justification is needed. No work needs to be shown for this problem. (a) If there is a direction u such that Du f (x∗ ...
Bilevel programming, pricing problems and Stackelberg games
... A bilevel optimization problem consists in an optimization problem in which some of the constraints specify that a subset of variables must be an optimal solution to another optimization problem. This paradigm is particularly appropriate to model competition between agents, a leader and a follower, ...
... A bilevel optimization problem consists in an optimization problem in which some of the constraints specify that a subset of variables must be an optimal solution to another optimization problem. This paradigm is particularly appropriate to model competition between agents, a leader and a follower, ...
Data Representation Methods
... • The class includes thousands of real-world problems. • Highly unlikely that any NP-hard problem can be solved by a polynomial time algorithm. ...
... • The class includes thousands of real-world problems. • Highly unlikely that any NP-hard problem can be solved by a polynomial time algorithm. ...
Multiple-criteria decision analysis

Multiple-criteria decision-making or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly considers multiple criteria in decision-making environments. Whether in our daily lives or in professional settings, there are typically multiple conflicting criteria that need to be evaluated in making decisions. Cost or price is usually one of the main criteria. Some measure of quality is typically another criterion that is in conflict with the cost. In purchasing a car, cost, comfort, safety, and fuel economy may be some of the main criteria we consider. It is unusual that the cheapest car is the most comfortable and the safest one. In portfolio management, we are interested in getting high returns but at the same time reducing our risks. Again, the stocks that have the potential of bringing high returns typically also carry high risks of losing money. In a service industry, customer satisfaction and the cost of providing service are two conflicting criteria that would be useful to consider.In our daily lives, we usually weigh multiple criteria implicitly and we may be comfortable with the consequences of such decisions that are made based on only intuition. On the other hand, when stakes are high, it is important to properly structure the problem and explicitly evaluate multiple criteria. In making the decision of whether to build a nuclear power plant or not, and where to build it, there are not only very complex issues involving multiple criteria, but there are also multiple parties who are deeply affected from the consequences.Structuring complex problems well and considering multiple criteria explicitly leads to more informed and better decisions. There have been important advances in this field since the start of the modern multiple-criteria decision-making discipline in the early 1960s. A variety of approaches and methods, many implemented by specialized decision-making software, have been developed for their application in an array of disciplines, ranging from politics and business to the environment and energy.








![x ∈ T, t ∈ [0, T], / / 1 - tanh(x](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014977084_1-7bf26f3ddf496dc5f9f135747c88ccb1-300x300.png)