Anorthosite and the lower crust
... emplace grossly at the limit between the upper and lower crusts, where they coalesce to form anorthosite plutons. In the last decade, this model has been improved and partly modified to account for new field-, experimental and geochemical constraints. A major step to confirm the polybaric character ...
... emplace grossly at the limit between the upper and lower crusts, where they coalesce to form anorthosite plutons. In the last decade, this model has been improved and partly modified to account for new field-, experimental and geochemical constraints. A major step to confirm the polybaric character ...
Igneous rocks
... Mineral Composition Ultramafic Rocks – Ultramafic rocks are unusual in that they have low silica contents and very high levels of iron and magnesium. – Some scientists theorize ultramafic rocks are formed by the fractional crystallization of olivine and pyroxene. – Another hypothesis is that ultrama ...
... Mineral Composition Ultramafic Rocks – Ultramafic rocks are unusual in that they have low silica contents and very high levels of iron and magnesium. – Some scientists theorize ultramafic rocks are formed by the fractional crystallization of olivine and pyroxene. – Another hypothesis is that ultrama ...
Origin of Indian Ocean Seamount Province by shallow
... unlikely, because the fractures trend orthogonally with respect to the east–west trend of the Christmas Island chain. Here we combine 40 Ar/39 Ar age, Sr, Nd, Hf and high-precision Pb isotope analyses of volcanic rocks from the province with plate tectonic reconstructions. We find that the seamounts ...
... unlikely, because the fractures trend orthogonally with respect to the east–west trend of the Christmas Island chain. Here we combine 40 Ar/39 Ar age, Sr, Nd, Hf and high-precision Pb isotope analyses of volcanic rocks from the province with plate tectonic reconstructions. We find that the seamounts ...
Geological Society of America Bulletin
... A third segment of ocean floor is presently interacting with continental lithosphere south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec, where Quaternary volcanism is weakly developed within a tectonically complex region that marks the diffuse Cocos-NOAM-Caribbean triple junction. The northern limit of this triple ju ...
... A third segment of ocean floor is presently interacting with continental lithosphere south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec, where Quaternary volcanism is weakly developed within a tectonically complex region that marks the diffuse Cocos-NOAM-Caribbean triple junction. The northern limit of this triple ju ...
The Case for a Hot Archean Climate and its Implications to the
... depths, the flux of CO2 through Archean volcanic arcs likely was higher and deep subduction of carbon may have been hindered. In addition, owing to Earth’s much hotter conditions, the subduction cycles may have also been episodic in nature for most part of the Precambrian …thus making subduction int ...
... depths, the flux of CO2 through Archean volcanic arcs likely was higher and deep subduction of carbon may have been hindered. In addition, owing to Earth’s much hotter conditions, the subduction cycles may have also been episodic in nature for most part of the Precambrian …thus making subduction int ...
Southwest U.S. Region Mountain
... the mantle opening gaps through which hot mantle rocks and magma rose • The North American continental crust, tethered to the Pacific Plate at the San Andreas Fault, was then stretched and thinned on the west end, now stretched about 250 miles, to create the Basin and Range Province • As the west ga ...
... the mantle opening gaps through which hot mantle rocks and magma rose • The North American continental crust, tethered to the Pacific Plate at the San Andreas Fault, was then stretched and thinned on the west end, now stretched about 250 miles, to create the Basin and Range Province • As the west ga ...
Chapter 14 - Mesozoic Geology
... • Subduction of the Farallon plate – beneath the North American plate continued during this time, – resulting in numerous overlapping, – low-angle thrust faults – in which blocks of older strata – were thrust eastward – on top of younger strata ...
... • Subduction of the Farallon plate – beneath the North American plate continued during this time, – resulting in numerous overlapping, – low-angle thrust faults – in which blocks of older strata – were thrust eastward – on top of younger strata ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... • Not all metamorphism occurs under the same conditions, so geologists classify the metamorphic grade, or specific set of conditions under which certain metamorphic rocks form • Metamorphic Facies – groups of metamorphic minerals that form under similar temperature and pressure conditions. • Low-Gra ...
... • Not all metamorphism occurs under the same conditions, so geologists classify the metamorphic grade, or specific set of conditions under which certain metamorphic rocks form • Metamorphic Facies – groups of metamorphic minerals that form under similar temperature and pressure conditions. • Low-Gra ...
Comparison of the Central Metamorphic Belt and Trinity terrane of
... Peacock and Norris, 1989); (2) the Trinity thrust, metamorphic foliation in the Central Metamorphic Belt, and mylonitic foliation at the base of the Trinity terrane are all subparallel (Lipman, 1964; Cannat and Boudier, 1985; Peacock, 1987a); and (3) extensive serpentinization near the base of the T ...
... Peacock and Norris, 1989); (2) the Trinity thrust, metamorphic foliation in the Central Metamorphic Belt, and mylonitic foliation at the base of the Trinity terrane are all subparallel (Lipman, 1964; Cannat and Boudier, 1985; Peacock, 1987a); and (3) extensive serpentinization near the base of the T ...
Continental Growth and Recycling in Convergent Orogens with
... The growth and evolution of continental crust through geological time is the result of a balance between the magmatic extraction of juvenile material from the mantle and the return of continental material to the mantle via sediment subduction, subduction erosion, and delamination. Continental growth ...
... The growth and evolution of continental crust through geological time is the result of a balance between the magmatic extraction of juvenile material from the mantle and the return of continental material to the mantle via sediment subduction, subduction erosion, and delamination. Continental growth ...
The Identification of Common Rocks
... earth where a number of quite large crystals grow, then is moved nearer to the surface where it is cooled rapidly. The resulting rock has some large, well-formed crystals sitting within a fine-grained matrix; it is called a porphyry. The large crystals are called phenocrysts. A large number of igneo ...
... earth where a number of quite large crystals grow, then is moved nearer to the surface where it is cooled rapidly. The resulting rock has some large, well-formed crystals sitting within a fine-grained matrix; it is called a porphyry. The large crystals are called phenocrysts. A large number of igneo ...
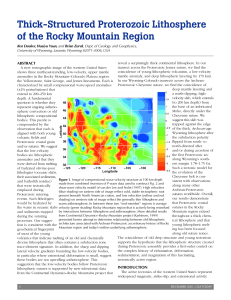
Thick-Structured Proterozoic Lithosphere of the Rocky Mountain
... suggest this slab was bodies. This puzzle is trapped against the edge compounded by the of the thick, Archean-age observation that each is Wyoming lithosphere after aligned with both young the subduction polarity volcanic fields and flipped from south- to Proterozoic crustal grain north-directed aft ...
... suggest this slab was bodies. This puzzle is trapped against the edge compounded by the of the thick, Archean-age observation that each is Wyoming lithosphere after aligned with both young the subduction polarity volcanic fields and flipped from south- to Proterozoic crustal grain north-directed aft ...
New Tectonic Map of Georgia (Explanatory Note)
... regional structures, that means the study of Late Alpine and present deformation of the Earth’s crust and investigation of the formation mechanisms of different tectonic structures. Such researches on the territory of Georgia have been carried out over a long period of time [2, 19, 29-34]. A problem ...
... regional structures, that means the study of Late Alpine and present deformation of the Earth’s crust and investigation of the formation mechanisms of different tectonic structures. Such researches on the territory of Georgia have been carried out over a long period of time [2, 19, 29-34]. A problem ...
Granitoids
... A few broad generalizations: 1) Most granitoids of significant volume occur in areas where the continental crust has been thickened by orogeny, either continental arc subduction or collision of sialic masses. Many granites, however, may postdate the thickening event by tens of millions of years. Ima ...
... A few broad generalizations: 1) Most granitoids of significant volume occur in areas where the continental crust has been thickened by orogeny, either continental arc subduction or collision of sialic masses. Many granites, however, may postdate the thickening event by tens of millions of years. Ima ...
Strain accumulation across the Eastern California Shear Zone at
... Figure 2. Map of the GPS arraysacrossthe EasternCalifornia ShearZone (solid triangles)and aroundYucca Mountain (solid circles). The velocity relative to the fixed interior of North America for each monument is shown by an arrow. The 95% confidenceellipse is shownat the tip of the arrow. The location ...
... Figure 2. Map of the GPS arraysacrossthe EasternCalifornia ShearZone (solid triangles)and aroundYucca Mountain (solid circles). The velocity relative to the fixed interior of North America for each monument is shown by an arrow. The 95% confidenceellipse is shownat the tip of the arrow. The location ...
Origin of Mesoproterozoic A-type granites in Laurentia
... Mesoproterozoic A-type or “anorogenic” granites of ∼ 1.4 Ga age was emplaced within composite, heterogeneous Proterozoic crust. Zircons are an ideal mineral to constrain the granite petrogenetic history because they are repositories of both age (U–Pb geochronology) and tracer (Lu–Hf isotopic) inform ...
... Mesoproterozoic A-type or “anorogenic” granites of ∼ 1.4 Ga age was emplaced within composite, heterogeneous Proterozoic crust. Zircons are an ideal mineral to constrain the granite petrogenetic history because they are repositories of both age (U–Pb geochronology) and tracer (Lu–Hf isotopic) inform ...
29. Sr-, Nd-, AND Pb-ISOTOPIC COMPOSITION OF VOLCANIC
... The Lower and Middle Series volcanic rocks at Site 917 show clear indications of contamination of the magmas with continental crust (Larsen, Saunders, Clift, et al., 1994; Fitton et al., this volume). Variation of incompatible-element ratios with SiO2 content cannot be explained by differentiation o ...
... The Lower and Middle Series volcanic rocks at Site 917 show clear indications of contamination of the magmas with continental crust (Larsen, Saunders, Clift, et al., 1994; Fitton et al., this volume). Variation of incompatible-element ratios with SiO2 content cannot be explained by differentiation o ...
Chapter 7 - Heritage Collegiate
... ions to move through the rocks more easily. These ions may cause the minerals in the rock to recrystallize into more stable crystals or to change into completely different minerals. Changes in Texture Caused by Metamorphism The degree of metamorphism (how much the parent rock is changed) can be dete ...
... ions to move through the rocks more easily. These ions may cause the minerals in the rock to recrystallize into more stable crystals or to change into completely different minerals. Changes in Texture Caused by Metamorphism The degree of metamorphism (how much the parent rock is changed) can be dete ...
Map Reading and Earthquake/Volcano Plotting Activity
... The next slide shows a picture of a map with earthquake and volcano data plotted, it has a little more data than you plotted. ...
... The next slide shows a picture of a map with earthquake and volcano data plotted, it has a little more data than you plotted. ...
Convergent-Boundary Mountains
... The Appalachian Mountains–A Case Study • The geology of the Appalachian mountain range, which is located in the eastern United States, has been the subject of many studies. • Geologists have divided the Appalachian Mountain Belt into several distinct regions, including the Valley and Ridge, the Blue ...
... The Appalachian Mountains–A Case Study • The geology of the Appalachian mountain range, which is located in the eastern United States, has been the subject of many studies. • Geologists have divided the Appalachian Mountain Belt into several distinct regions, including the Valley and Ridge, the Blue ...
Do faults trigger folding in the lithosphere
... that both processes may develop concurrently, so that faulting may serve as a mechanism of folding in the brittle domain. We support this hypothesis by direct numerical modeling. The results are compared with the data on three most prominent and well-known cases of the oceanic and continental foldin ...
... that both processes may develop concurrently, so that faulting may serve as a mechanism of folding in the brittle domain. We support this hypothesis by direct numerical modeling. The results are compared with the data on three most prominent and well-known cases of the oceanic and continental foldin ...
Why the Philippine Sea Plate Moves as It Does
... We covered this topic by starting out with a cross-section of a archetype convergent zone, starting with the downgoing plate that is flexed at the outer bulge, the trench (and those turgid turbidites), the accretionary prism (and its thrusts and melange character), the forearc basin, the volcanic ar ...
... We covered this topic by starting out with a cross-section of a archetype convergent zone, starting with the downgoing plate that is flexed at the outer bulge, the trench (and those turgid turbidites), the accretionary prism (and its thrusts and melange character), the forearc basin, the volcanic ar ...
Homework of 9/19
... A batholith is the largest kind of pluton. It is an intrusive igneous body of irregular shape that cuts across the layering or other fabric of the rock into which it intrudes. The largest batholith in North America, approximately 1500 km long, is the Coast Range batholith of British Columbia and ...
... A batholith is the largest kind of pluton. It is an intrusive igneous body of irregular shape that cuts across the layering or other fabric of the rock into which it intrudes. The largest batholith in North America, approximately 1500 km long, is the Coast Range batholith of British Columbia and ...
Rapid tectonic exhumation, detachment faulting and orogenic
... Tourmakeady Volcanic Groups. The modern dip of the tectonic fabric within the Clew Bay Complex and its overlying relationship with the South Mayo Trough can, however, be understood if it is recognized that the entire region has been tilted and overturned following exhumation, as a result of the D3 d ...
... Tourmakeady Volcanic Groups. The modern dip of the tectonic fabric within the Clew Bay Complex and its overlying relationship with the South Mayo Trough can, however, be understood if it is recognized that the entire region has been tilted and overturned following exhumation, as a result of the D3 d ...
Great Lakes tectonic zone
The Great Lakes tectonic zone is bounded by South Dakota at its tip and heads northeast to south of Duluth, Minnesota, then heads east through northern Wisconsin, Marquette, Michigan, and then trends more northeasterly to skim the northern-most shores of lakes Michigan and Huron before ending in the Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, area.During the Late Archean Era the Algoman orogeny added landmass to the Superior province by volcanic activity and continental collision along a boundary that stretches from present-day South Dakota, U.S., into the Lake Huron region near Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.This crustal boundary is the Great Lakes tectonic zone. It is 1,400 km (870 mi) long, and separates the older Archean gneissic terrane to the south from younger Late Archean greenstone-granite terrane to the north.The zone is characterized by active compression during the Algoman orogeny (about 2,700 million years ago), a pulling-apart (extensional) tectonics (2,450 to 2,100 million years ago), a second compression during the Penokean orogeny (1,900 to 1,850 million years ago), a second extension during Middle Proterozoic time (1,600 million years ago) and minor reactivation during Phanerozoic time (the past 500 million years).Collision began along the Great Lakes tectonic zone (GLTZ) with the Algoman mountain-building event and continued for tens of millions of years. During the formation of the GLTZ, the gneissic Minnesota River Valley subprovince was thrust up onto the Superior province's edge as it consumed the Superior province's oceanic crust. Fragmentation of the Kenorland supercontinent began 2,450 million years ago and was completed by 2,100 million years ago. The Wyoming province is the continental landmass that is hypothesized to have rifted away from the southern Superior province portion of Kenorland, before moving rapidly west and docking with the Laurentia supercontinent 1,850 to 1,715 million years ago. Sedimentation from the GLTZ-rifting environment continued into the Penokean orogeny, which is the next major tectonic event in the Great Lakes region. Several earthquakes have been documented in Minnesota, Michigan's Upper Peninsula and Sudbury in the last 120 years along the GLTZ.