Mental health disorders
... adoptive relatives of these 66 adoptees, including both parents and siblings. The relatives were then separated into four groups: group 1 — biological relatives of adoptees with schizophrenia; group 2 — adoptive relatives of adoptees with schizophrenia; group 3 — biological relatives of adoptees wit ...
... adoptive relatives of these 66 adoptees, including both parents and siblings. The relatives were then separated into four groups: group 1 — biological relatives of adoptees with schizophrenia; group 2 — adoptive relatives of adoptees with schizophrenia; group 3 — biological relatives of adoptees wit ...
Dissociative Self-mutilation: A Case Report of Dissociative Amnesia
... between them. However, she feared that she would be abandoned by her father if she mutilated herself. The wish to merge with and separate from her father created a more difficult dilemma, from which she escaped by dissociative amnesia. She repressed unacceptable memories of self-mutilation to an unc ...
... between them. However, she feared that she would be abandoned by her father if she mutilated herself. The wish to merge with and separate from her father created a more difficult dilemma, from which she escaped by dissociative amnesia. She repressed unacceptable memories of self-mutilation to an unc ...
Problem Gambling and Mental Health Recovery
... 6. After losing money gambling, often returns another day to get even (“chasing one’s losses”) 7. Lies to conceal the extent of involvement with gambling 8. Has jeopardized or lost a significant relationship, job, or educational or career opportunity because of gambling 9. Relies on others to provid ...
... 6. After losing money gambling, often returns another day to get even (“chasing one’s losses”) 7. Lies to conceal the extent of involvement with gambling 8. Has jeopardized or lost a significant relationship, job, or educational or career opportunity because of gambling 9. Relies on others to provid ...
Schizophrenia - SAGE Journals
... 20th century, the literature on psychotic disorders was dominated by a brain-versus-mind distinction that fueled many futile debates about whether schizophrenia was a biological or a psychological disorder. In fact, prior to the 1970s, the field of psychiatry distinguished between organic and functi ...
... 20th century, the literature on psychotic disorders was dominated by a brain-versus-mind distinction that fueled many futile debates about whether schizophrenia was a biological or a psychological disorder. In fact, prior to the 1970s, the field of psychiatry distinguished between organic and functi ...
Narcissistic Personality Disorder: Progress in Recognition and Treatment
... absence of depression, lack of communication, self-esteem dysregulation, and life events that decrease self-esteem. The diagnostic focus on patients’ external characteristics and interpersonal behavior tends to dismiss the importance of their internal distress and painful experiences of self-esteem ...
... absence of depression, lack of communication, self-esteem dysregulation, and life events that decrease self-esteem. The diagnostic focus on patients’ external characteristics and interpersonal behavior tends to dismiss the importance of their internal distress and painful experiences of self-esteem ...
The relationship between prior psychiatric disorder
... have found an association between CFS/ME and personality factors such as emotional instability (Kato et al. 2006) and Cluster C personality traits (Henderson & Tannock, 2004) suggesting this is an area that requires further investigation. The increased level of family psychiatric illness among indiv ...
... have found an association between CFS/ME and personality factors such as emotional instability (Kato et al. 2006) and Cluster C personality traits (Henderson & Tannock, 2004) suggesting this is an area that requires further investigation. The increased level of family psychiatric illness among indiv ...
A multi-site single blind clinical study to compare
... prevalence of post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in people with psychotic disorders ranges from 12% to 29% [2,3]. This can be considered high compared to estimated prevalence rates in the general population, which range from 0.4% to 3.5% [4-6]. In a meta-analytical study evidence was found that m ...
... prevalence of post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in people with psychotic disorders ranges from 12% to 29% [2,3]. This can be considered high compared to estimated prevalence rates in the general population, which range from 0.4% to 3.5% [4-6]. In a meta-analytical study evidence was found that m ...
psychometric properties of the depression - Site BU
... each diagnostic group (range of as = 0.88-0.96). As noted above, 20 patients were re-administered the DASS 2 weeks following their initial intake evaluation. These patients had the following principal diagnoses: panic disorder (n = 7), G A D (n = 4), major depression (n = 4), social phobia (n = 2), ...
... each diagnostic group (range of as = 0.88-0.96). As noted above, 20 patients were re-administered the DASS 2 weeks following their initial intake evaluation. These patients had the following principal diagnoses: panic disorder (n = 7), G A D (n = 4), major depression (n = 4), social phobia (n = 2), ...
Quick Reference Guide
... without difficulty. Nevertheless, the extent of depression may not be clear without a thorough and systematic history, mental state examination and risk assessment. Patients with acute severe mental illnesses usually require admission to hospital for a short period of time or referral to a specialis ...
... without difficulty. Nevertheless, the extent of depression may not be clear without a thorough and systematic history, mental state examination and risk assessment. Patients with acute severe mental illnesses usually require admission to hospital for a short period of time or referral to a specialis ...
Bipolar Disorder CPM - Intermountain Healthcare
... and more comorbidities (including substance abuse). Use of antidepressants is also associated with increased incidence of mixed episodes.HIR1, GOL1, PRI, SHA • Frequency of episodes. Cycling varies from an average of 1 cycle every 3 years to the severe variation called rapid cycling. Rapid cycling ...
... and more comorbidities (including substance abuse). Use of antidepressants is also associated with increased incidence of mixed episodes.HIR1, GOL1, PRI, SHA • Frequency of episodes. Cycling varies from an average of 1 cycle every 3 years to the severe variation called rapid cycling. Rapid cycling ...
Learning and Sleep - University of Illinois Archives
... Seasonal affective disorder often goes into full remission (or a change from depression to mania or hypomania) as daylength increases in the spring. This is often diagnosed when there are regular seasonally-occuring depressive episodes (at least twice) and no other periods of depression. This disord ...
... Seasonal affective disorder often goes into full remission (or a change from depression to mania or hypomania) as daylength increases in the spring. This is often diagnosed when there are regular seasonally-occuring depressive episodes (at least twice) and no other periods of depression. This disord ...
National Eating Disorders Awareness Month
... These include the following beliefs: O Being slender is idealized in society, O One should fear being fat, and O A person’s weight and shape greatly influence their overall identity as cited in ...
... These include the following beliefs: O Being slender is idealized in society, O One should fear being fat, and O A person’s weight and shape greatly influence their overall identity as cited in ...
National Eating Disorder Awareness Week (PPT)
... These include the following beliefs: O Being slender is idealized in society, O One should fear being fat, and O A person’s weight and shape greatly influence their overall identity as cited in ...
... These include the following beliefs: O Being slender is idealized in society, O One should fear being fat, and O A person’s weight and shape greatly influence their overall identity as cited in ...
National Eating Disorders Awareness Month
... These include the following beliefs: O Being slender is idealized in society, O One should fear being fat, and O A person’s weight and shape greatly influence their overall identity as cited in ...
... These include the following beliefs: O Being slender is idealized in society, O One should fear being fat, and O A person’s weight and shape greatly influence their overall identity as cited in ...
Here
... in her life, as well as her assessment of her feelings, desires, beliefs, values, behaviors, and goals, may transform her sense of self. Considering her psychological states merely a function of unbalanced brain chemistry divorced from the environmental, social, and cultural context may lead her to ...
... in her life, as well as her assessment of her feelings, desires, beliefs, values, behaviors, and goals, may transform her sense of self. Considering her psychological states merely a function of unbalanced brain chemistry divorced from the environmental, social, and cultural context may lead her to ...
Dissociative Disorders
... The memory gap usually concerns a traumatic or stressful event in the person’s life. The memory impairment is reversible; it sometimes resolves spontaneously, but it can also be reversed by hypnosis. The memory gap can be localized to a specific period of time, or it can be selective, whereby the pe ...
... The memory gap usually concerns a traumatic or stressful event in the person’s life. The memory impairment is reversible; it sometimes resolves spontaneously, but it can also be reversed by hypnosis. The memory gap can be localized to a specific period of time, or it can be selective, whereby the pe ...
PPT: Presentation Slides - Intermountain Physician
... reported for a diagnosis of postpartum depression. Though the description of ICD-10 code mentions the term “puerperal psychosis,” a more severe form of postpartum illness, it can still be used to report postpartum depression. ...
... reported for a diagnosis of postpartum depression. Though the description of ICD-10 code mentions the term “puerperal psychosis,” a more severe form of postpartum illness, it can still be used to report postpartum depression. ...
Addictions
... • Mood disorders A mental disorder involving moods that are extreme is a mood disorder, sometimes called an affective disorder. – Clinical depression is characterized by longlasting feelings of hopelessness, sadness, or helplessness. – General symptoms include deep sadness, apathy, fatigue, agitatio ...
... • Mood disorders A mental disorder involving moods that are extreme is a mood disorder, sometimes called an affective disorder. – Clinical depression is characterized by longlasting feelings of hopelessness, sadness, or helplessness. – General symptoms include deep sadness, apathy, fatigue, agitatio ...
Testing the `Extreme Female Brain` Theory of Psychosis in Adults
... At the time of interview, all participants who were directly interviewed were free from overt symptoms of psychosis and were considered by their clinicians or referring individuals to be mentally healthy. In the case of individuals unable to be interviewed directly, status of current symptoms was no ...
... At the time of interview, all participants who were directly interviewed were free from overt symptoms of psychosis and were considered by their clinicians or referring individuals to be mentally healthy. In the case of individuals unable to be interviewed directly, status of current symptoms was no ...
Sleep & Psychiatr 2011 (Koranyi Lecture) 2011_compressed
... features; apnea can produce secondary depression. Serious sleep apnea can cause sufficient impairment to suggest dementia; severe snoring in a “demented” patient could be a treatable illness. Apnea or PLMD can cause sleep deprivation which can cause relapse of mania or depression. ...
... features; apnea can produce secondary depression. Serious sleep apnea can cause sufficient impairment to suggest dementia; severe snoring in a “demented” patient could be a treatable illness. Apnea or PLMD can cause sleep deprivation which can cause relapse of mania or depression. ...
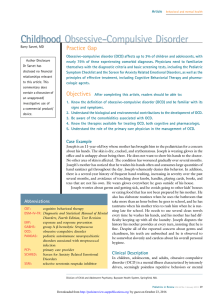
Childhood Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
... activity usually recognize them to be irrational; however, children tend to be less insightful. Whether or not there is insight, the compulsive behavior and obsessive thoughts seem irresistible and necessary. There is a wide spectrum of severity and disability associated with childhood OCD, includin ...
... activity usually recognize them to be irrational; however, children tend to be less insightful. Whether or not there is insight, the compulsive behavior and obsessive thoughts seem irresistible and necessary. There is a wide spectrum of severity and disability associated with childhood OCD, includin ...
A multi-site single blind clinical study to compare the effects of
... prevalence of post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in people with psychotic disorders ranges from 12% to 29% [2,3]. This can be considered high compared to estimated prevalence rates in the general population, which range from 0.4% to 3.5% [4-6]. In a meta-analytical study evidence was found that m ...
... prevalence of post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in people with psychotic disorders ranges from 12% to 29% [2,3]. This can be considered high compared to estimated prevalence rates in the general population, which range from 0.4% to 3.5% [4-6]. In a meta-analytical study evidence was found that m ...
Psychopathology2e_c06_PPT
... Marked fear or anxiety of situations from which escape might be difficult or in which help might be unavailable in the event of panic symptoms Agoraphobia diagnosis requires fear of at least two: • Public transportation, open spaces, enclosed places, standing in line or being in a crowd, or bein ...
... Marked fear or anxiety of situations from which escape might be difficult or in which help might be unavailable in the event of panic symptoms Agoraphobia diagnosis requires fear of at least two: • Public transportation, open spaces, enclosed places, standing in line or being in a crowd, or bein ...
View Full Page PDF
... as a somatoform disorder in DSM-IV, many now view it as more closely related to OCD, due to its obsessive–compulsive symptoms and positive response to similar therapy and drug treatments. It appears to differ in several important respects however. Only 30% of people with OCD have an additional diagn ...
... as a somatoform disorder in DSM-IV, many now view it as more closely related to OCD, due to its obsessive–compulsive symptoms and positive response to similar therapy and drug treatments. It appears to differ in several important respects however. Only 30% of people with OCD have an additional diagn ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.