02 Psychology of personality. Modern theories of personality
... Similar chronic relapsing condition as the somatization disorder. Patients report worse health than do those with chronic medical condition and their report of specific symptoms if they meet the severity criteria is sufficient and need not to be considered legitimate by the clinician. Treatment stra ...
... Similar chronic relapsing condition as the somatization disorder. Patients report worse health than do those with chronic medical condition and their report of specific symptoms if they meet the severity criteria is sufficient and need not to be considered legitimate by the clinician. Treatment stra ...
Unit 3: Mental Illness and Disorders
... Borderline PD was so called because it was thought to lie on the ‘borderline’ between neurotic (anxiety) disorders and psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. ...
... Borderline PD was so called because it was thought to lie on the ‘borderline’ between neurotic (anxiety) disorders and psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. ...
Mood disorders
... Mood disorders Mood disorders are clinical conditions, conditions, in most cases recurrent and chronic diseases of which the essential feature is a disturbance of mood. mood. Mood: Mood: persistent emotional states that affect how an individual acts, acts, think and perceivel his or her environment ...
... Mood disorders Mood disorders are clinical conditions, conditions, in most cases recurrent and chronic diseases of which the essential feature is a disturbance of mood. mood. Mood: Mood: persistent emotional states that affect how an individual acts, acts, think and perceivel his or her environment ...
Working with the complex relationships between addictions and
... Diagnosis The possible relationships between addictions and psychiatric symptoms or disorders are the following: (according to McDowell & Spitz, 1999): ...
... Diagnosis The possible relationships between addictions and psychiatric symptoms or disorders are the following: (according to McDowell & Spitz, 1999): ...
All You Wanted to Know About Medications But Were Afraid
... • Usually these children are difficult to treat and there is considerable controversy about the criteria as they are referred to as “rapid cyclers and often have mood lability, mood swings, affective storms, irritability and aggressiveness, periodic agitation, explosiveness and severe temper tantru ...
... • Usually these children are difficult to treat and there is considerable controversy about the criteria as they are referred to as “rapid cyclers and often have mood lability, mood swings, affective storms, irritability and aggressiveness, periodic agitation, explosiveness and severe temper tantru ...
Achieving Permanency For Children Diagnosed With Reactive
... This is a common psychiatric mood disorder representing 2 to 3 percent of the general population. It is a genetic, inherited, familial disorder that ultimately results in biochemical imbalances within one’s central nervous system. It manifests in manic (or hypomanic, a lesser form of manic) and/or d ...
... This is a common psychiatric mood disorder representing 2 to 3 percent of the general population. It is a genetic, inherited, familial disorder that ultimately results in biochemical imbalances within one’s central nervous system. It manifests in manic (or hypomanic, a lesser form of manic) and/or d ...
ADHD - Pearson - Clinical Assessment
... start using other people’s things without asking or receiving permission; for adolescents and adults, may intrude into or take over what others are doing). ...
... start using other people’s things without asking or receiving permission; for adolescents and adults, may intrude into or take over what others are doing). ...
SS10 - Psychology
... 49. Defendants who are actively hallucinating and experiencing delusions during the time of their trials are most likely to be: A) judged not guilty of the crime by reason of insanity. B) judged not guilty of the crime due to incompetence. C) committed for treatment until they improve enough to be r ...
... 49. Defendants who are actively hallucinating and experiencing delusions during the time of their trials are most likely to be: A) judged not guilty of the crime by reason of insanity. B) judged not guilty of the crime due to incompetence. C) committed for treatment until they improve enough to be r ...
SS10 - Psychology
... 49. Defendants who are actively hallucinating and experiencing delusions during the time of their trials are most likely to be: A) judged not guilty of the crime by reason of insanity. B) judged not guilty of the crime due to incompetence. C) committed for treatment until they improve enough to be r ...
... 49. Defendants who are actively hallucinating and experiencing delusions during the time of their trials are most likely to be: A) judged not guilty of the crime by reason of insanity. B) judged not guilty of the crime due to incompetence. C) committed for treatment until they improve enough to be r ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, and Dissociative Disorders Homework
... 7. Suppose a person makes an appointment with a doctor once a month to check for cancer, even though her tests are always negative. Which somatoform behavior does this behavior suggest? _______________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... 7. Suppose a person makes an appointment with a doctor once a month to check for cancer, even though her tests are always negative. Which somatoform behavior does this behavior suggest? _______________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
Disorders First Apparent in Childhood
... 3. Parent is rewarded for giving in 4. Parents likelihood of giving in is increased * If this pattern is typical, it is a risk factor. It also tends to escalate over time ...
... 3. Parent is rewarded for giving in 4. Parents likelihood of giving in is increased * If this pattern is typical, it is a risk factor. It also tends to escalate over time ...
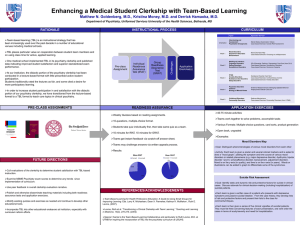
Enhancing a Medical Student Clerkship with Team
... Goal: Identify static and dynamic risk and protective factors for suicide in clinical cases. Discuss rationale for clinical decision-making (including hospitalization) of suicidal patients. Each team is given a written case of a patient who presents with depressive symptoms and passive suicidal id ...
... Goal: Identify static and dynamic risk and protective factors for suicide in clinical cases. Discuss rationale for clinical decision-making (including hospitalization) of suicidal patients. Each team is given a written case of a patient who presents with depressive symptoms and passive suicidal id ...
Psychological Disorders
... • What is the DSM-IV? Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: the book to classify mental disorders • In 2012- updated version = DSM V ...
... • What is the DSM-IV? Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: the book to classify mental disorders • In 2012- updated version = DSM V ...
Just click here.
... the absence of purging. The advantage of the EDNOS category was that people could receive an eating disorder diagnosis without meeting the relatively narrow criteria for anorexia or bulimia. The disadvantage was that people with very different symptoms got lumped into the same category, which made a ...
... the absence of purging. The advantage of the EDNOS category was that people could receive an eating disorder diagnosis without meeting the relatively narrow criteria for anorexia or bulimia. The disadvantage was that people with very different symptoms got lumped into the same category, which made a ...
Psychiatric Essentials 31 August 2012 Presented By
... Need for evaluation of combined therapies, eg ...
... Need for evaluation of combined therapies, eg ...
The Anxiety Disorders Some Practical Questions & Answers
... Acknowledge the patient. Introduce yourself. Inform the patient about the Duration of tests or treatment. Explain what is going to happen next. Thank the patient for the opportunity to serve. ...
... Acknowledge the patient. Introduce yourself. Inform the patient about the Duration of tests or treatment. Explain what is going to happen next. Thank the patient for the opportunity to serve. ...
CAUTIONS - Florida Alcohol and Drug Abuse Association
... The DSM-5 (May, 2013) Changes from DSM-IV Use of the term “addiction” No longer diagnoses of “abuse” or “dependence” “Substance Use Disorders” (DSM-IV) > “Substance Use and Addictive Disorders” (DSM-5) The seven criteria from the DSM-IV for dependence and the four for abuse are collapsed in ...
... The DSM-5 (May, 2013) Changes from DSM-IV Use of the term “addiction” No longer diagnoses of “abuse” or “dependence” “Substance Use Disorders” (DSM-IV) > “Substance Use and Addictive Disorders” (DSM-5) The seven criteria from the DSM-IV for dependence and the four for abuse are collapsed in ...
Psychological Disorders
... – More women than men – Irrational fear of being embarrassed, judged or critically evaluated by others – Realize that their fear is excessive but they still approach social situations with tremendous anxiety ...
... – More women than men – Irrational fear of being embarrassed, judged or critically evaluated by others – Realize that their fear is excessive but they still approach social situations with tremendous anxiety ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... million people suffer from this disorder. Women are 2-4 times more likely to be diagnosed with Borderline Personality Disorder than men, and the highest risks of BPD are found between the ages of 19 and 34. Some of the warning signs to look for to see if your child/children fit the pattern of BPD ar ...
... million people suffer from this disorder. Women are 2-4 times more likely to be diagnosed with Borderline Personality Disorder than men, and the highest risks of BPD are found between the ages of 19 and 34. Some of the warning signs to look for to see if your child/children fit the pattern of BPD ar ...
Uppers, Downers and All Arounders
... – Heavy use of alcohol, sedative-hypnotics or withdrawal from stimulant drugs can aggravate depression – Brain predisposed to schizophrenia can develop it – Psychotic episode can be triggered by psychedelics ...
... – Heavy use of alcohol, sedative-hypnotics or withdrawal from stimulant drugs can aggravate depression – Brain predisposed to schizophrenia can develop it – Psychotic episode can be triggered by psychedelics ...
Psychological Disorders - Trinity School District
... • In addition, mental disorders are the leading cause of disability in the U.S. and Canada for ages 15-44. • Nearly half (45 percent) of those with any mental disorder meet criteria for 2 or more disorders, with severity strongly related to comorbidity. • Most common disorders were anxiety, phobias, ...
... • In addition, mental disorders are the leading cause of disability in the U.S. and Canada for ages 15-44. • Nearly half (45 percent) of those with any mental disorder meet criteria for 2 or more disorders, with severity strongly related to comorbidity. • Most common disorders were anxiety, phobias, ...
Kinds of Anxiety Issues I Work With Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... humiliation (social phobia). Feeling socially clumsy, having trouble with small talk in social situations, and letting fear of embarrassment or humiliation cause avoidance of triggering situations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder - Can manifest from mild to severe including obsessive thoughts and repe ...
... humiliation (social phobia). Feeling socially clumsy, having trouble with small talk in social situations, and letting fear of embarrassment or humiliation cause avoidance of triggering situations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder - Can manifest from mild to severe including obsessive thoughts and repe ...
Bipolar Disorder an Overview
... shown to be effective in preventing relapses of manic, or in the one case, depressive episodes. The first known and "gold standard" mood stabilizer is lithium, while almost as widely used is sodium valproate, also used as an anticonvulsant. Depending on the severity of the case, anti-convulsants may ...
... shown to be effective in preventing relapses of manic, or in the one case, depressive episodes. The first known and "gold standard" mood stabilizer is lithium, while almost as widely used is sodium valproate, also used as an anticonvulsant. Depending on the severity of the case, anti-convulsants may ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.