Exploring 9e
... Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to stigmatize people? ...
... Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to stigmatize people? ...
Chapter 16 – Psychological Disorders
... striking earlier (late teens). It may reflect today’s young adults’ greater willingness to disclose depression, as well as our tendency to forget many negative experiences over time. Objective 14: If one identical twin has MDD, 50% chance the other twin has it too. Bipolar – 70% chance. Adopted pe ...
... striking earlier (late teens). It may reflect today’s young adults’ greater willingness to disclose depression, as well as our tendency to forget many negative experiences over time. Objective 14: If one identical twin has MDD, 50% chance the other twin has it too. Bipolar – 70% chance. Adopted pe ...
Personality disorders - Faribault Area Learning Center
... • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close relationships often precede depression • With each new generation, depression is striking earlier and affecting more people ...
... • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close relationships often precede depression • With each new generation, depression is striking earlier and affecting more people ...
Dissociative Disorders
... One or more episodes of inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature, that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
... One or more episodes of inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature, that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
File
... Because personality disorders describe long-standing and enduring patterns of behavior, they are most often diagnosed in adulthood. It is uncommon for them to be diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, because a child or teen is under constant development, personality changes and maturation. However, ...
... Because personality disorders describe long-standing and enduring patterns of behavior, they are most often diagnosed in adulthood. It is uncommon for them to be diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, because a child or teen is under constant development, personality changes and maturation. However, ...
Lawyers and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
... post-traumatic stress disorder experienced by their clients. In the therapy world, we call this vicarious traumatization. It is understood that professionals who work with people needing their help begin to experience the same emotions and even some of the same symptoms as their clients. Judges are ...
... post-traumatic stress disorder experienced by their clients. In the therapy world, we call this vicarious traumatization. It is understood that professionals who work with people needing their help begin to experience the same emotions and even some of the same symptoms as their clients. Judges are ...
13A-Psychdisorder-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
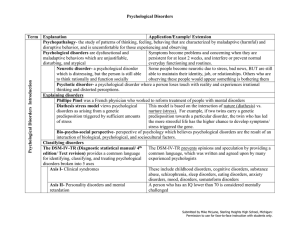
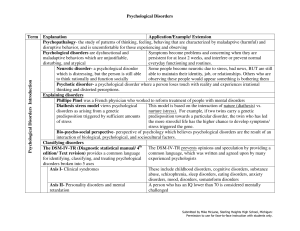
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
SOMATOFORM DISORDERS
... Psychological distress: anxiety, depression Common suicidal threats Medical history is circumstantial, vague, imprecise, inconsistent, disorganized ...
... Psychological distress: anxiety, depression Common suicidal threats Medical history is circumstantial, vague, imprecise, inconsistent, disorganized ...
Mental Disorders
... Nick is on crutches and has to go to the 4th floor for his doctors appointment. He looks at the elevator and begins to sweat. He tells his family he is going to crutch up 4 flights of stairs because he refuses to ride in the elevator. Mr. Pagani hands his class a worksheet and tells them to complete ...
... Nick is on crutches and has to go to the 4th floor for his doctors appointment. He looks at the elevator and begins to sweat. He tells his family he is going to crutch up 4 flights of stairs because he refuses to ride in the elevator. Mr. Pagani hands his class a worksheet and tells them to complete ...
Psychological Disord..
... “Each of the mental disorders is conceptualized as: A clinically significant (=abnormal) behavioural or psychological syndrome or pattern that – Occurs in a person and that is associated with present distress (a painful symptom) – Or disability (impairment in one or more important areas of functioni ...
... “Each of the mental disorders is conceptualized as: A clinically significant (=abnormal) behavioural or psychological syndrome or pattern that – Occurs in a person and that is associated with present distress (a painful symptom) – Or disability (impairment in one or more important areas of functioni ...
Psychotherapy For Bipolar Disorder
... Current point prevalence 18+ (NIMH) = 2.6% Median age of onset: ...
... Current point prevalence 18+ (NIMH) = 2.6% Median age of onset: ...
DSM 5 AND DISRUPTIVE MOOD DYSREGULATION DISORDER Gail Fernandez, M.D.
... • In the NIMH sample, the mean age at study entry is 11.7 years, but parents report a mean age at onset nearly 7 years earlier. • The mean Children’s Global Assessment Scale (CGAS) score was 45.8 (SD=6.9), compared with a mean score of 46.5 (SD=12.4) for 107 youths with bipolar disorder recruited ov ...
... • In the NIMH sample, the mean age at study entry is 11.7 years, but parents report a mean age at onset nearly 7 years earlier. • The mean Children’s Global Assessment Scale (CGAS) score was 45.8 (SD=6.9), compared with a mean score of 46.5 (SD=12.4) for 107 youths with bipolar disorder recruited ov ...
Pediatric Mental Health - Idaho School Counselors
... motor tics for greater than one year Chronic vocal tic disorder: one or more vocal tics for greater than one year Transient tic disorder: one or more tics for greater than 4 weeks but less than 12 months Tic disorder NOS (not other wise ...
... motor tics for greater than one year Chronic vocal tic disorder: one or more vocal tics for greater than one year Transient tic disorder: one or more tics for greater than 4 weeks but less than 12 months Tic disorder NOS (not other wise ...
Session 5-Psychiatric disorders_Signs and Types
... Flight of ideas: Stream of accelerated thoughts with abrupt changes between topics and no central ...
... Flight of ideas: Stream of accelerated thoughts with abrupt changes between topics and no central ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... • Bipolar I disorder– involves episodes of mania or mixed episodes that include symptoms of both mania and depression – Diagnosis of a manic episode requires the presence of elevated or irritable mood + 3 additional symptoms ...
... • Bipolar I disorder– involves episodes of mania or mixed episodes that include symptoms of both mania and depression – Diagnosis of a manic episode requires the presence of elevated or irritable mood + 3 additional symptoms ...
Abnormal Psychology
... of people who suffer from psychological disorders Behavior and or thoughts From depression, substance abuse, learning difficulties to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder ...
... of people who suffer from psychological disorders Behavior and or thoughts From depression, substance abuse, learning difficulties to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder ...
Position Statement 55 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in
... siblings of people affected by ADHD have a two to eight fold increased risk of having the condition compared with the relatives of unaffected controls [7]. Environmental factors such as maternal smoking and exposure to lead and certain pesticides make an additional small contribution to the disorder ...
... siblings of people affected by ADHD have a two to eight fold increased risk of having the condition compared with the relatives of unaffected controls [7]. Environmental factors such as maternal smoking and exposure to lead and certain pesticides make an additional small contribution to the disorder ...
Chapter 13 - Bakersfield College
... investigators want to develop a theory of depression that will suggest ways to treat it. Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1998) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes 2. Common causes of depression ...
... investigators want to develop a theory of depression that will suggest ways to treat it. Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1998) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes 2. Common causes of depression ...
Childhood Anxiety Disorders List
... injury or the death of a parent), had mental health problems before the event, and who lack a strong support network. Violence at home also increases a child’s risk of developing PTSD after a traumatic event. ...
... injury or the death of a parent), had mental health problems before the event, and who lack a strong support network. Violence at home also increases a child’s risk of developing PTSD after a traumatic event. ...
Somatoform and Dissociative
... These disorders run in families, but it is not clear whether this is due to genetics or modeling. Different theories claim different origins for this disorder Treatment Psychodynamic treatment involves helping people identify feelings and thoughts behind the symptoms and find more adaptive ways of c ...
... These disorders run in families, but it is not clear whether this is due to genetics or modeling. Different theories claim different origins for this disorder Treatment Psychodynamic treatment involves helping people identify feelings and thoughts behind the symptoms and find more adaptive ways of c ...
Asperger disorder
... Lack of sharing enjoyment, interests, or achievements with other people Lack of social or emotional reciprocity ...
... Lack of sharing enjoyment, interests, or achievements with other people Lack of social or emotional reciprocity ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.