Anxiety Disorders Treatment Protocol
... All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health problems in the United States. There are several types of anxiety disorders including obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, social phobia, generalized anxiety di ...
... All Team Members: Patient Self-Management Education & Support Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health problems in the United States. There are several types of anxiety disorders including obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, social phobia, generalized anxiety di ...
Somatoform Disorders - Seattle Children`s Hospital
... • Motor conversion disorders are more common than sensory, and primarily involve the major muscle groups. • Weakness occurs more commonly than dystonia. Common Comorbidities: ...
... • Motor conversion disorders are more common than sensory, and primarily involve the major muscle groups. • Weakness occurs more commonly than dystonia. Common Comorbidities: ...
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
... 2. The preoccupation causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. 3. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g., dissatisfaction with body shape and size in anorexia nervosa.) Jackie Camaren ...
... 2. The preoccupation causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. 3. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g., dissatisfaction with body shape and size in anorexia nervosa.) Jackie Camaren ...
Recognizing and Treating Bipolar Disorder
... of bipolar spectrum disorders.2,6 In the past, bipolar disorder was thought to be relatively rare as compared to unipolar depression. It is well documented that major depression is a common condition, with a lifetime prevalence of 21.3% for females and 12.7% for males in the United States.12 The DSM ...
... of bipolar spectrum disorders.2,6 In the past, bipolar disorder was thought to be relatively rare as compared to unipolar depression. It is well documented that major depression is a common condition, with a lifetime prevalence of 21.3% for females and 12.7% for males in the United States.12 The DSM ...
Anxiety Disorders in the DSM-5 - Mood and Anxiety Disorders Rounds
... 16%–29%.1,2 In addition to provoking substantial disability, anxiety disorders are highly comorbid with other mental and physical disorders, thus complicating the treatment of both types of disorders. This issue of Mood and Anxiety Disorders Rounds highlights changes to the diagnostic category of an ...
... 16%–29%.1,2 In addition to provoking substantial disability, anxiety disorders are highly comorbid with other mental and physical disorders, thus complicating the treatment of both types of disorders. This issue of Mood and Anxiety Disorders Rounds highlights changes to the diagnostic category of an ...
Binge-eAting DisorDer - Practice Fusion Tutorials
... Bipolar and depressive disorders. Increases in appetite and weight gain are included in the criteria for major depressive episode and in the atypical features specifiers for depressive and bipolar disorders. Increased eating in the context of a major depressive episode may or may not be associated w ...
... Bipolar and depressive disorders. Increases in appetite and weight gain are included in the criteria for major depressive episode and in the atypical features specifiers for depressive and bipolar disorders. Increased eating in the context of a major depressive episode may or may not be associated w ...
Abnormal Psychology and Life: An Overview
... diathesis-stress model and provide sections that integrate risk factors to present comprehensive models of various mental disorders. We also provide an appendix of medical conditions with contributing psychological factors that includes a biopsychosocial perspective to explain the interplay of physi ...
... diathesis-stress model and provide sections that integrate risk factors to present comprehensive models of various mental disorders. We also provide an appendix of medical conditions with contributing psychological factors that includes a biopsychosocial perspective to explain the interplay of physi ...
word document
... binge eating or purging behavior (i.e., self-induced vomiting or the misuse of laxatives, diuretics, or enemas). This subtype describes presentations in which weight loss is accomplished primarily through dieting, fasting, and/or excessive exercise. During the last three months, the person has engag ...
... binge eating or purging behavior (i.e., self-induced vomiting or the misuse of laxatives, diuretics, or enemas). This subtype describes presentations in which weight loss is accomplished primarily through dieting, fasting, and/or excessive exercise. During the last three months, the person has engag ...
(007-017) Rafanelli 27-1:(119
... cases they coexist42. A patient’s diminished frustration tolerance and increased mood reactivity while in the hospital are likely due to a sense of demoralization caused by circumstances beyond his control in the hospital. However, his or her more chronic symptoms of anhedonia, social isolation, and ...
... cases they coexist42. A patient’s diminished frustration tolerance and increased mood reactivity while in the hospital are likely due to a sense of demoralization caused by circumstances beyond his control in the hospital. However, his or her more chronic symptoms of anhedonia, social isolation, and ...
Autism and epilepsy: a comprehensive medical approach 2014
... disability, symptomatic vs. unknown cause, and history of regression 35-65% of patients with Autism have EEG abnormalities Epilepsy in autism confers increased mortality ...
... disability, symptomatic vs. unknown cause, and history of regression 35-65% of patients with Autism have EEG abnormalities Epilepsy in autism confers increased mortality ...
The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders
... disorders (with onset more than 2 weeks after substance use) may occur, but should be coded as F1x.75. Psychoactive substance-induced psychotic disorders may present with varying patterns of symptoms. These variations will be influenced by the type of substance involved and the personality of the us ...
... disorders (with onset more than 2 weeks after substance use) may occur, but should be coded as F1x.75. Psychoactive substance-induced psychotic disorders may present with varying patterns of symptoms. These variations will be influenced by the type of substance involved and the personality of the us ...
Addictions
... • try to protect others from the harmful consequences • try to control other people of their behavior • feel responsible for what • do not meet their other people say or do own needs • seek the approval • avoid living their own of others lives by concentrating on • have difficulty having fun other p ...
... • try to protect others from the harmful consequences • try to control other people of their behavior • feel responsible for what • do not meet their other people say or do own needs • seek the approval • avoid living their own of others lives by concentrating on • have difficulty having fun other p ...
pptx - 2.86 MBMDD Definitions and diagnosis
... April 2016 (2) WHO. ICD-10 Classification .1993. Available from: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/GRNBOOK.pdf. Accessed April 2016 . (3). American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. 4th edition: American Psychiatric Association. 1994:866; ...
... April 2016 (2) WHO. ICD-10 Classification .1993. Available from: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/GRNBOOK.pdf. Accessed April 2016 . (3). American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. 4th edition: American Psychiatric Association. 1994:866; ...
Linköping University Post Print Implementation of Internet-based preventive
... effective than the same intervention without a coach in terms of clinical outcomes, drop-out and economic costs. Moreover, we will investigate which level of support by a coach is more effective compared to other levels of support. Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, a total of 500 subject ...
... effective than the same intervention without a coach in terms of clinical outcomes, drop-out and economic costs. Moreover, we will investigate which level of support by a coach is more effective compared to other levels of support. Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, a total of 500 subject ...
Treatment of Young Children with Separation Anxiety
... • Person has been exposed to traumatic event; outside the realm of typical human experience; the person’s response involved fear, helplessness, or horror • In children, this may be expressed by disorganized or agitated behavior • The traumatic event is re-experienced, through thoughts or dreams, the ...
... • Person has been exposed to traumatic event; outside the realm of typical human experience; the person’s response involved fear, helplessness, or horror • In children, this may be expressed by disorganized or agitated behavior • The traumatic event is re-experienced, through thoughts or dreams, the ...
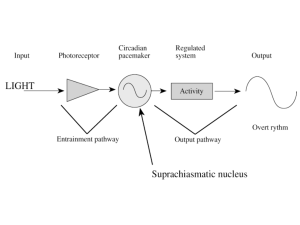
Learning and Sleep - University of Illinois Archives
... rhythmicity is seasonal affective disorder (listed as bipolar 1 disorder, bipolar II disorder or major depressive disorder, recurrent, “with seasonal pattern”), a cyclothymic (depressive) disorder that tends to occur in the fall or winter as daylength shortens. Seasonal affective disorder often goes ...
... rhythmicity is seasonal affective disorder (listed as bipolar 1 disorder, bipolar II disorder or major depressive disorder, recurrent, “with seasonal pattern”), a cyclothymic (depressive) disorder that tends to occur in the fall or winter as daylength shortens. Seasonal affective disorder often goes ...
Treatment-resistant anxiety disorders
... issue lead to dimensional or symptomatic or to spectrum approach that leads to other set of problems such as overgeneralization. For example, a widely accepted obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) spectrum includes a very diverse group of disorders ranging from autism to kleptomania.31 One of the iss ...
... issue lead to dimensional or symptomatic or to spectrum approach that leads to other set of problems such as overgeneralization. For example, a widely accepted obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) spectrum includes a very diverse group of disorders ranging from autism to kleptomania.31 One of the iss ...
22 Assessment & Anxiety Disorders
... behaviors, or events contribute For example, Dennis Rader was to developing mental disorders. a shy and polite child who preferred to spend time alone. As a boy, he recalls watching his grandparents strangle chickens at their farm, and by the time he reached high school, he was strangling cats and d ...
... behaviors, or events contribute For example, Dennis Rader was to developing mental disorders. a shy and polite child who preferred to spend time alone. As a boy, he recalls watching his grandparents strangle chickens at their farm, and by the time he reached high school, he was strangling cats and d ...
PRIEBEFactorsInfluencing2010POSTP - QMRO Home
... identify factors associated with subjective quality of life in different diagnostic groups whilst controlling for confounding factors, within-subject clustering of paired measurements and heterogeneity across studies using xtmixed and gllamm in Stata 1046, 47. In this three-level model, paired measu ...
... identify factors associated with subjective quality of life in different diagnostic groups whilst controlling for confounding factors, within-subject clustering of paired measurements and heterogeneity across studies using xtmixed and gllamm in Stata 1046, 47. In this three-level model, paired measu ...
Structural Relationships Among Dimensions of the DSM
... and depression symptoms operate on a continuum, analyses at the diagnostic level rely largely on data that do not reflect the dimensional nature of these features.' Categorization of dimensional variables usually forfeits meaningful information by artificially (and often erroneously) collapsing vari ...
... and depression symptoms operate on a continuum, analyses at the diagnostic level rely largely on data that do not reflect the dimensional nature of these features.' Categorization of dimensional variables usually forfeits meaningful information by artificially (and often erroneously) collapsing vari ...
Bolton CAMHS Referral Criteria
... We would expect that any previous intervention especially if carried out by the referrer is summarised in terms of engagement, motivation, content and outcome. We would value a statement regarding the child, young person and family’s expectation of CAMHS referral. Where a young person is deemed to h ...
... We would expect that any previous intervention especially if carried out by the referrer is summarised in terms of engagement, motivation, content and outcome. We would value a statement regarding the child, young person and family’s expectation of CAMHS referral. Where a young person is deemed to h ...
Eating disorders, anxiety and depression
... does not meet all the criteria for a specific eating disorder. For example, a person may show all of the psychological signs of anorexia but not yet be considered underweight for their height. This does not mean that the person has a less serious eating disorder; all disorders in this category are ...
... does not meet all the criteria for a specific eating disorder. For example, a person may show all of the psychological signs of anorexia but not yet be considered underweight for their height. This does not mean that the person has a less serious eating disorder; all disorders in this category are ...
PDF version
... Tourette Syndrome is a much rarer, but more severe tic disorder, where patients may make noises, such as barking a word or sound, and movements, such as repetitive flinching or eye blinking, on an almost daily basis for years. ...
... Tourette Syndrome is a much rarer, but more severe tic disorder, where patients may make noises, such as barking a word or sound, and movements, such as repetitive flinching or eye blinking, on an almost daily basis for years. ...
Chapter 2
... health professionals often work closely with psychiatrists and consult with them when a client needs medication. Another difference is that clinical psychologists are trained ...
... health professionals often work closely with psychiatrists and consult with them when a client needs medication. Another difference is that clinical psychologists are trained ...
Is there a significant interaction between life adversity and the brain
... The main limitations of this review are the publication bias, some missing data and the heterogeneity of the studies made it difficult to directly compare them. Discussion To our knowledge this is the first systematic review of this topic. It has shown that this area of research should be pursued fu ...
... The main limitations of this review are the publication bias, some missing data and the heterogeneity of the studies made it difficult to directly compare them. Discussion To our knowledge this is the first systematic review of this topic. It has shown that this area of research should be pursued fu ...
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum disorder is a mental disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be ""not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups"". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively ""severe"" mental disorders through to relatively ""mild and nonclinical deficits"".In some cases, a spectrum approach joins together conditions that were previously considered separately. A notable example of this trend is the autism spectrum, where conditions on this spectrum may now all be referred to as autism spectrum disorders. In other cases, what was treated as a single disorder comes to be seen (or seen once again) as comprising a range of types, a notable example being the bipolar spectrum. A spectrum approach may also expand the type or the severity of issues which are included, which may lessen the gap with other diagnoses or with what is considered ""normal"". Proponents of this approach argue that it is in line with evidence of gradations in the type or severity of symptoms in the general population, and helps reduce the stigma associated with a diagnosis. Critics, however, argue that it can take attention and resources away from the most serious conditions associated with the most disability, or on the other hand could unduly medicalize problems which are simply challenges people face in life.