IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008, p-ISSN:2319-7676.
... the season, indicating that the orchid is controlling the uptake of nutrients by the fungus preventing parasitism. In terrestrial orchids having annual cycle where a period of growth is followed by loss of leaves and roots, the orchid is maintained below ground generally as tuber, pseudobulb or rhiz ...
... the season, indicating that the orchid is controlling the uptake of nutrients by the fungus preventing parasitism. In terrestrial orchids having annual cycle where a period of growth is followed by loss of leaves and roots, the orchid is maintained below ground generally as tuber, pseudobulb or rhiz ...
Rice Plant- and Leaf Hoppers
... Mites also known as acarina belong to phylum Arachnida, to which spiders also belong. These are minute organisms that can rarely be seen with naked eyes. Mites cause heavy damage in crops especially ...
... Mites also known as acarina belong to phylum Arachnida, to which spiders also belong. These are minute organisms that can rarely be seen with naked eyes. Mites cause heavy damage in crops especially ...
The Silurian Period \(443
... • It developed a massive root system that would have been useful for structural support and the uptake of nutrients and water; root system depths in excess of 1 m have been reported for this tree. • It developed broad leaves, that improved sunlight capture. As a perennial plant it probably shed its ...
... • It developed a massive root system that would have been useful for structural support and the uptake of nutrients and water; root system depths in excess of 1 m have been reported for this tree. • It developed broad leaves, that improved sunlight capture. As a perennial plant it probably shed its ...
PLANTAIN FHIA-21
... Panama disease fungus, but it is susceptible to both Radopholus similis and Pratylenchus coffeae, the two most important nematodes. ...
... Panama disease fungus, but it is susceptible to both Radopholus similis and Pratylenchus coffeae, the two most important nematodes. ...
ANTAGONISTIC INTERACTION AGAINST PLANT INSECTS
... Rodolia cardinalis, the vedalia beetle, was imported to Australia in the 19th century, successfully controlling cottony cushion scale. ...
... Rodolia cardinalis, the vedalia beetle, was imported to Australia in the 19th century, successfully controlling cottony cushion scale. ...
2016 Tree Sale Flier 2016 v1.pub
... One of the earliest flowering plants in Spring for pollinators. Red and yellow flowers on plants to 2 feet tall, tolerates a wide variety of soils and sun, from shade to full sun. Deer resistant. Self sows small black ...
... One of the earliest flowering plants in Spring for pollinators. Red and yellow flowers on plants to 2 feet tall, tolerates a wide variety of soils and sun, from shade to full sun. Deer resistant. Self sows small black ...
genomebiology.com
... hypothesized that PEP1 might be the A. alpina homolog of FLC, and demonstrated that this is indeed the case. What is interesting is that vernalization only transiently results in PEP1 repression in A. alpina; this is in contrast to the situation in Arabidopsis, in which vernalization can result in ...
... hypothesized that PEP1 might be the A. alpina homolog of FLC, and demonstrated that this is indeed the case. What is interesting is that vernalization only transiently results in PEP1 repression in A. alpina; this is in contrast to the situation in Arabidopsis, in which vernalization can result in ...
Viburnum Suspensum
... flourishes in areas with mild winters. Its foliage is leathery and coarse, with broad oval leaves. Viburnum Suspensum grow densely and regularly reach between ten and twelve feet in both height and spread. Viburnum Suspensum bloom from early spring through late summer. Their flowers are small, and t ...
... flourishes in areas with mild winters. Its foliage is leathery and coarse, with broad oval leaves. Viburnum Suspensum grow densely and regularly reach between ten and twelve feet in both height and spread. Viburnum Suspensum bloom from early spring through late summer. Their flowers are small, and t ...
False Solomon`s Seal (Smilacina racemosa) False Solomon`s Seal
... Solomon’s Seal in that the tiny, creamy white, fragrant flowers form a cluster at the end of the curving stem rather than drooping beneath the stem. The flowers have six sepals. The leaves of the two plants look somewhat similar. False Solomon’s Seal leaves are alternate along the stem, oval, parall ...
... Solomon’s Seal in that the tiny, creamy white, fragrant flowers form a cluster at the end of the curving stem rather than drooping beneath the stem. The flowers have six sepals. The leaves of the two plants look somewhat similar. False Solomon’s Seal leaves are alternate along the stem, oval, parall ...
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 11: Processes: Herbivory 2. Basic
... • 3) Increased mortality - repeated defoliation by herbivores can kill plants or make them more susceptible to death but they can defend – e.g. Fig 8.4 Begon, 3rd ed., and module death in Fig. 9.4) ...
... • 3) Increased mortality - repeated defoliation by herbivores can kill plants or make them more susceptible to death but they can defend – e.g. Fig 8.4 Begon, 3rd ed., and module death in Fig. 9.4) ...
Gardeners Exchange Group Favorite Plant List ACANTHUS
... Cut flower stalks back to ground after flowering unless reseeding is desired. To plant from seed, sow seeds in a cold frame in mid-to-late spring and plant in ground in mid-season for blooms the next year; or lift clumps after flowering and plant new rosettes. May need to be staked if plant does not ...
... Cut flower stalks back to ground after flowering unless reseeding is desired. To plant from seed, sow seeds in a cold frame in mid-to-late spring and plant in ground in mid-season for blooms the next year; or lift clumps after flowering and plant new rosettes. May need to be staked if plant does not ...
Popsicle Series - Proven Winners
... first year getting established and will not be floriferous, but the bud count should increase each year. Do not cut plants all the way back in the fall since the lower part of the stem often carries next year’s buds. Buds will also come from underground like herbaceous peonies. ...
... first year getting established and will not be floriferous, but the bud count should increase each year. Do not cut plants all the way back in the fall since the lower part of the stem often carries next year’s buds. Buds will also come from underground like herbaceous peonies. ...
present1
... it poses and what is being done about it, after all, we don’t want a planet looking like this… ...
... it poses and what is being done about it, after all, we don’t want a planet looking like this… ...
06_chapter 2
... containers such as clay pots have several cuts and holes to facilitate adequate aeration and proper drainage are routinely used. In the recent times, plastic containers are gaining importance due to their less weight, easy to transport, free from deposition of algae or salts on their sides and longe ...
... containers such as clay pots have several cuts and holes to facilitate adequate aeration and proper drainage are routinely used. In the recent times, plastic containers are gaining importance due to their less weight, easy to transport, free from deposition of algae or salts on their sides and longe ...
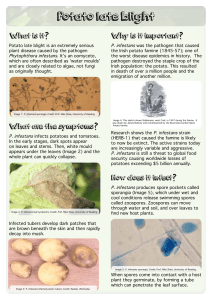
Potato Late Blight Information Sheet
... In ideal conditions, P. infestans can complete its life cycle in just five days. Sporangia start to form when temperatures are above 10°C and humidity is over 75% for more than two days. Rain washes spores from infected leaves into the soil; where they infect potato tubers. Wind can help spread spor ...
... In ideal conditions, P. infestans can complete its life cycle in just five days. Sporangia start to form when temperatures are above 10°C and humidity is over 75% for more than two days. Rain washes spores from infected leaves into the soil; where they infect potato tubers. Wind can help spread spor ...
Nutrition in Plants 1
... their food. How do they survive and from where do they derive nutrition? Like humans and animals such plants depend on the food produced by other plants. They use the heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Look at Fig. 1.5. Do you see yellow tubular structures twining around the stem and branches of a tre ...
... their food. How do they survive and from where do they derive nutrition? Like humans and animals such plants depend on the food produced by other plants. They use the heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Look at Fig. 1.5. Do you see yellow tubular structures twining around the stem and branches of a tre ...
Brazilian Elodea Cordgrass/Spartina Knotweeds Asian Clam
... clog stream channels. More than 30 days ...
... clog stream channels. More than 30 days ...
"Nymphaeales". - UConn - University of Connecticut
... Water lilies dominate most water gardens and ornamental ponds. Horticulturally, the most important genus is Nymphaea (Figure 1), containing nearly 250 cultivars, whose fragrant, showy blossoms range from white to numerous shades of green, orange, red, blue and purple. Most cultivars are hardy. About ...
... Water lilies dominate most water gardens and ornamental ponds. Horticulturally, the most important genus is Nymphaea (Figure 1), containing nearly 250 cultivars, whose fragrant, showy blossoms range from white to numerous shades of green, orange, red, blue and purple. Most cultivars are hardy. About ...
Chapter 48: Populations and Communities
... • No two organisms can occupy the same niche in the same place at the same time • When two species compete, both find themselves under pressure from natural selection to change in ways that decrease their competition • Ties ecology and evolution together ...
... • No two organisms can occupy the same niche in the same place at the same time • When two species compete, both find themselves under pressure from natural selection to change in ways that decrease their competition • Ties ecology and evolution together ...
Growing Lomandra from seed
... grass sward which will compete with Lomandra. To ensure dense coverage of Lomandra, especially in actively eroding areas, plant at 0.5-1m centres in an offset, zig-zag pattern with rows 1m apart. The clumps will quickly expand and form dense mats. It is important to mark the Lomandras with a stake a ...
... grass sward which will compete with Lomandra. To ensure dense coverage of Lomandra, especially in actively eroding areas, plant at 0.5-1m centres in an offset, zig-zag pattern with rows 1m apart. The clumps will quickly expand and form dense mats. It is important to mark the Lomandras with a stake a ...
Eelgrass and oysters - Bayville
... Wild celery has long, flat, ribbon-like leaves that can grow to about 5 feet long. The leaves have a light green stripe running down the center and grow in a cluster from the base of the plant which is white. Wild celery is important to the ecosystem of the Chesapeake Bay for a number of reasons. It ...
... Wild celery has long, flat, ribbon-like leaves that can grow to about 5 feet long. The leaves have a light green stripe running down the center and grow in a cluster from the base of the plant which is white. Wild celery is important to the ecosystem of the Chesapeake Bay for a number of reasons. It ...
native garden - Palm Beach State College
... Why Native? Established native plants are typically easier to maintain, and usually require less irrigation, fertilization and pesticides than exotics. Most native plants ‘know their neighborhood’ very well, developing resistance to disease and pests common for their location. Many birds, butterflie ...
... Why Native? Established native plants are typically easier to maintain, and usually require less irrigation, fertilization and pesticides than exotics. Most native plants ‘know their neighborhood’ very well, developing resistance to disease and pests common for their location. Many birds, butterflie ...
native plant list - Portland Water District
... Small white clusters of flowers bloom in late spring and are followed by fall fruits which are attractive to birds. Prefers full sun to part shade. Zones 2-7. Common Witchhazel (Hamamelis virginiana) Grows 10 to 15 feet high with an equal spread. Prefers moist, acidic soil and grows best with full s ...
... Small white clusters of flowers bloom in late spring and are followed by fall fruits which are attractive to birds. Prefers full sun to part shade. Zones 2-7. Common Witchhazel (Hamamelis virginiana) Grows 10 to 15 feet high with an equal spread. Prefers moist, acidic soil and grows best with full s ...
C. Growth rate
... –Density-dependent factors operate most strongly when a population is A. large and dense. B. large but sparse. C. small and sparse. D. small, but growing. ...
... –Density-dependent factors operate most strongly when a population is A. large and dense. B. large but sparse. C. small and sparse. D. small, but growing. ...
Perovskia atriplicifolia

Perovskia atriplicifolia (/pəˈrɒvskiə ætrɪplɪsɪˈfoʊliə/), commonly called Russian sage, is a flowering herbaceous perennial plant and subshrub. Although not a member of Salvia, the genus of other plants commonly called sage, it is closely related to them. It has an upright habit, typically reaching 0.5–1.2 m (1 ft 8 in–3 ft 11 in) tall, with square stems and gray-green leaves that yield a distinctive odor when crushed, but it is best known for its flowers. Its flowering season extends from mid-summer to as late as October, with blue to violet blossoms arranged into showy, branched panicles.Native to the steppes and hills of southwestern and central Asia, it was introduced to cultivation by Vasily Perovsky in the 19th century. Successful over a wide range of climate and soil conditions, it has since become popular and widely planted. Several cultivars have been developed, differing primarily in leaf shape and overall height; 'Blue Spire' is the most common. This variation has been widely used in gardens and landscaping. P. atriplicifolia was the Perennial Plant Association's 1995 Plant of the Year, and the 'Blue Spire' cultivar received the Award of Garden Merit from the Royal Horticultural Society.The species has a long history of use in traditional medicine in its native range, where it is employed as a treatment for a variety of ailments. This has led to the investigation of its phytochemistry. Its flowers can be eaten in salads or crushed for dyemaking, and the plant has been considered for potential use in the phytoremediation of contaminated soil.