TRANSITION ELEMENTS
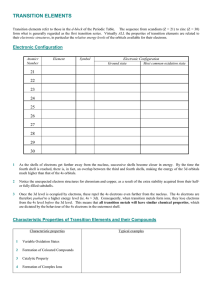
... Transition elements refer to those in the d-block of the Periodic Table. The sequence from scandium (Z = 21) to zinc (Z = 30) form what is generally regarded as the first transition series. Virtually ALL the properties of transition elements are related to their electronic structures, in particular ...
... Transition elements refer to those in the d-block of the Periodic Table. The sequence from scandium (Z = 21) to zinc (Z = 30) form what is generally regarded as the first transition series. Virtually ALL the properties of transition elements are related to their electronic structures, in particular ...
5a. Bonding Chemical Bonds Linkage which holds Types of
... Differences are only found between atoms that actually ______________________________________ ...
... Differences are only found between atoms that actually ______________________________________ ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure
... than one type of element are molecular compounds. • Most molecules are composed of nonmetals. • Chemical formulas that indicate actual number and types of atoms in a molecules are called molecular formulas. Such as H2O, C6H12O6, and C2H4. • Empirical formulas give only the relative number of atoms, ...
... than one type of element are molecular compounds. • Most molecules are composed of nonmetals. • Chemical formulas that indicate actual number and types of atoms in a molecules are called molecular formulas. Such as H2O, C6H12O6, and C2H4. • Empirical formulas give only the relative number of atoms, ...
Atomic number
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in Nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemi ...
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in Nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemi ...
Part A - Chemical Bonding Review PowerPoint Presentation
... • Covalent bond: formed when atoms share electrons. • Metallic bond: ions of metals are surrounded by sea of electrons that bind all ions together. ...
... • Covalent bond: formed when atoms share electrons. • Metallic bond: ions of metals are surrounded by sea of electrons that bind all ions together. ...
Atomic Theory - Somerset Academy
... was that the atom would have a weak positive charge. • Rutherford tested this idea by firing positively charged particles at gold foil. • He expected particles to pass through. • His results surprised him. ...
... was that the atom would have a weak positive charge. • Rutherford tested this idea by firing positively charged particles at gold foil. • He expected particles to pass through. • His results surprised him. ...
Atoms are not the smallest thing
... Describe the three particles in the atom Define atomic number and mass number Describe isotopes Write symbols for elements Determine the numbers of particles in any atom from the element symbol ...
... Describe the three particles in the atom Define atomic number and mass number Describe isotopes Write symbols for elements Determine the numbers of particles in any atom from the element symbol ...
atomic structure i
... People have difficulty with the size of an atom. It's so infinitesimally small that we neglect it. But if we could expand an atom's size to fit our visible world, we would find it impossible to ignore. If the nucleus of an atom were the size of a grape, the electrons would be about one mile away! Or ...
... People have difficulty with the size of an atom. It's so infinitesimally small that we neglect it. But if we could expand an atom's size to fit our visible world, we would find it impossible to ignore. If the nucleus of an atom were the size of a grape, the electrons would be about one mile away! Or ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Then (4)proposed, in his law of ...
... that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Then (4)proposed, in his law of ...
lecture 7
... The simplest element is hydrogen (H); its atoms contain one proton in the nucleus. The next simplest element is helium (He); its atoms contain two protons in the nucleus. The most massive element that exists naturally in any significant quantities is uranium (U) (we’ll hear a lot about uranium throu ...
... The simplest element is hydrogen (H); its atoms contain one proton in the nucleus. The next simplest element is helium (He); its atoms contain two protons in the nucleus. The most massive element that exists naturally in any significant quantities is uranium (U) (we’ll hear a lot about uranium throu ...
File - Mc Guckin Science
... random orbits. • Scientists cannot predict where they will be at any given moment. • Electrons travel so fast, they appear to form a “cloud” around the nucleus. ...
... random orbits. • Scientists cannot predict where they will be at any given moment. • Electrons travel so fast, they appear to form a “cloud” around the nucleus. ...
Masses of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
2003
... Using the information in the table, classify the substances (A, B, C, D) as either metallic, ionic, covalent network or covalent molecular structures. OUTCOME – P 14 (2 marks) ...
... Using the information in the table, classify the substances (A, B, C, D) as either metallic, ionic, covalent network or covalent molecular structures. OUTCOME – P 14 (2 marks) ...
Chapter 2
... Protons and neutrons make up the almost the entire mass of each atom and are located in the nucleus. In our model of the atom, the electrons are arranged in orbits or shells around the nucleus and equal the number of protons in a neutral atom. However, because they may be a long way from the nucleus ...
... Protons and neutrons make up the almost the entire mass of each atom and are located in the nucleus. In our model of the atom, the electrons are arranged in orbits or shells around the nucleus and equal the number of protons in a neutral atom. However, because they may be a long way from the nucleus ...
Name Parts of an Atom Worksheet Date_______ Substances that
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
E:\My Documents\snc1p\atomic structure.wpd
... If the number of protons in the nucleus increases by one as you from one element to the next in the periodic table, why does the relative atomic mass not increase by one as you go from one element to the next in the periodic table? This was a very important question. Since the relative atomic mass d ...
... If the number of protons in the nucleus increases by one as you from one element to the next in the periodic table, why does the relative atomic mass not increase by one as you go from one element to the next in the periodic table? This was a very important question. Since the relative atomic mass d ...
Chemistry EOC Review
... 104. How are the pressure and volume of a gas related? 105. A gas is originally at a volume of 6 mL and a pressure of 1 atm. If the pressure is increased to 2 atm, what is the new volume of the gas? 106. State Charles’s Law (*Remember that temperature in Charles’s Law must be in Kelvin) 107. Oxygen ...
... 104. How are the pressure and volume of a gas related? 105. A gas is originally at a volume of 6 mL and a pressure of 1 atm. If the pressure is increased to 2 atm, what is the new volume of the gas? 106. State Charles’s Law (*Remember that temperature in Charles’s Law must be in Kelvin) 107. Oxygen ...
Ch#4 Atoms and Elements
... • Atoms can form ions by gaining or losing electrons. Metals tend to lose one or more electrons to form positive ions called cations and are named by using the name of the parent atom. Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form negative ions called anions and are named by using the root of the ato ...
... • Atoms can form ions by gaining or losing electrons. Metals tend to lose one or more electrons to form positive ions called cations and are named by using the name of the parent atom. Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form negative ions called anions and are named by using the root of the ato ...
Unit 2 matter - Kowenscience.com
... • All physical and chemical properties are classified as being either extensive or intensive. Extensive Property ...
... • All physical and chemical properties are classified as being either extensive or intensive. Extensive Property ...
Energy and Matter
... Warm up: Why is a chemical change different than a physical change? Temperature is a measure of kinetic energy Measured by thermometers Farenheit, Celcius, and Kelvin Scales C=5/9(F-32) F=(9/5C)+32 K=C+273 C=K-273 Absolute zero: where an atom has no more kinetic energy. Impossible to attain. ...
... Warm up: Why is a chemical change different than a physical change? Temperature is a measure of kinetic energy Measured by thermometers Farenheit, Celcius, and Kelvin Scales C=5/9(F-32) F=(9/5C)+32 K=C+273 C=K-273 Absolute zero: where an atom has no more kinetic energy. Impossible to attain. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... a. Dalton’s theory explained the laws of conservation of matter and constant composition. (How?) b. Dalton predicted the law of multiple proportions - two elements can form more than one compound by combining in different ratios. (This was later confirmed.) H2O and H2O2; CO and CO2 2.2 The Discovery ...
... a. Dalton’s theory explained the laws of conservation of matter and constant composition. (How?) b. Dalton predicted the law of multiple proportions - two elements can form more than one compound by combining in different ratios. (This was later confirmed.) H2O and H2O2; CO and CO2 2.2 The Discovery ...























