Democritus
... RULE 2: Atoms radiate energy when an electron jumps from a higher-energy orbit to a lower-energy orbit. Also, an atom absorbs energy when an electron gets boosted from a low-energy orbit to a high-energy orbit. ...
... RULE 2: Atoms radiate energy when an electron jumps from a higher-energy orbit to a lower-energy orbit. Also, an atom absorbs energy when an electron gets boosted from a low-energy orbit to a high-energy orbit. ...
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1
... 13. Because each element has a different number of protons and electrons, they’re “n” values differ from each other. Each element thus produces its own emission spectra which allows scientists to identify elements. 14. Coulomb’s law says that oppositely charged objects attract. Electrons should “fal ...
... 13. Because each element has a different number of protons and electrons, they’re “n” values differ from each other. Each element thus produces its own emission spectra which allows scientists to identify elements. 14. Coulomb’s law says that oppositely charged objects attract. Electrons should “fal ...
MIDTERM REVIEW UNIT 1: Mass/Measurement
... 9. Each chemistry teacher provides 6 test tubes to each lab group. In each class there are 12 lab groups, and the teacher has four classes. There are a total of 5 chemistry teachers. ...
... 9. Each chemistry teacher provides 6 test tubes to each lab group. In each class there are 12 lab groups, and the teacher has four classes. There are a total of 5 chemistry teachers. ...
1. The Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny
... A. All elements are composed of atoms. B. All atoms of the same element have the same mass. C. Atoms contain subatomic particles. D. A compound contains atoms of more ...
... A. All elements are composed of atoms. B. All atoms of the same element have the same mass. C. Atoms contain subatomic particles. D. A compound contains atoms of more ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... ◦ electrons are the only particles in Plum Pudding atoms ◦ the atom is mostly empty space ◦ cannot have a bunch of negatively charged particles near each other as they would repel the structure of the atom contains many negatively charged electrons these electrons are held in the atom by their attra ...
... ◦ electrons are the only particles in Plum Pudding atoms ◦ the atom is mostly empty space ◦ cannot have a bunch of negatively charged particles near each other as they would repel the structure of the atom contains many negatively charged electrons these electrons are held in the atom by their attra ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... ◦ electrons are the only particles in Plum Pudding atoms ◦ the atom is mostly empty space ◦ cannot have a bunch of negatively charged particles near each other as they would repel the structure of the atom contains many negatively charged electrons these electrons are held in the atom by their attra ...
... ◦ electrons are the only particles in Plum Pudding atoms ◦ the atom is mostly empty space ◦ cannot have a bunch of negatively charged particles near each other as they would repel the structure of the atom contains many negatively charged electrons these electrons are held in the atom by their attra ...
Haley CHM2045 Final Review
... 2. A 1.0 L mixture of He, Ar, and Ne has a total pressure of 654 mmHg at 298 K. If the partial pressure of He is 378 mmHg and the partial pressure of Ne is 112 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of Ar? 3. Lithium reacts with nitrogen gas in the following reaction, 6Li + N2 —> 2Li3N What mass of lith ...
... 2. A 1.0 L mixture of He, Ar, and Ne has a total pressure of 654 mmHg at 298 K. If the partial pressure of He is 378 mmHg and the partial pressure of Ne is 112 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of Ar? 3. Lithium reacts with nitrogen gas in the following reaction, 6Li + N2 —> 2Li3N What mass of lith ...
Atoms
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form che ...
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form che ...
chapter_2_2007
... Reactants-substances that are changed, usually on the left side of the equation. Products-new chemical substances formed, usually on the right side of the equation. ...
... Reactants-substances that are changed, usually on the left side of the equation. Products-new chemical substances formed, usually on the right side of the equation. ...
Document
... 1. Write ELEMENT SYMBOLS for each element in the compound. 2. Use each PREFIX to write the number of each atom as a SUBSCRIPT next to the symbol (omit the subscript 1). ...
... 1. Write ELEMENT SYMBOLS for each element in the compound. 2. Use each PREFIX to write the number of each atom as a SUBSCRIPT next to the symbol (omit the subscript 1). ...
Academic Chemistry Final Exam Review
... 0.454 atm at a temperature of -15oC and a volume of 3.48L. If conditions are changes to those of STP, what will be the new volume of the sample? ...
... 0.454 atm at a temperature of -15oC and a volume of 3.48L. If conditions are changes to those of STP, what will be the new volume of the sample? ...
Oxidation and Reduction
... beautiful green patina as it ages. Metals rust or corrode in the presence of air and water. Minerals (ionic compounds) found in ore can be decomposed with the use of electricity to produce pure metals and nonmetals. All of these reactions are examples of oxidation and reduction, otherwise known as r ...
... beautiful green patina as it ages. Metals rust or corrode in the presence of air and water. Minerals (ionic compounds) found in ore can be decomposed with the use of electricity to produce pure metals and nonmetals. All of these reactions are examples of oxidation and reduction, otherwise known as r ...
Atomic - Chemistry R: 4(AE) 5(A,C)
... •Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits, or energy levels. • An atom has energy levels. Electrons can only exist in these energy levels, not in between. •When an atom is in the ground state, the electrons exist in the energy levels closest to the nucleus. •GROUND STATE: the lowest e ...
... •Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits, or energy levels. • An atom has energy levels. Electrons can only exist in these energy levels, not in between. •When an atom is in the ground state, the electrons exist in the energy levels closest to the nucleus. •GROUND STATE: the lowest e ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, SYMBOLS, FORULAS 7
... Symbols are written with one, two, or three letters. The first letter is always capitalized. Each element has a different symbol ...
... Symbols are written with one, two, or three letters. The first letter is always capitalized. Each element has a different symbol ...
Chemistry Final Exam Practice Test
... d) exceptions to the law of definite proportions e) solids at room temperature ...
... d) exceptions to the law of definite proportions e) solids at room temperature ...
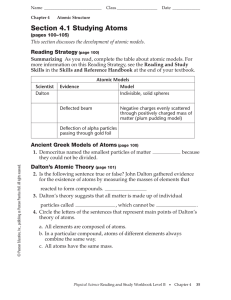
Section 4.1 Studying Atoms
... 6. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) charge because they were attracted to a positive ...
... 6. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) charge because they were attracted to a positive ...
chapt4 - Northside Middle School
... Atomic Number = number of protons # of protons determines kind of atom the same as the number of electrons in the neutral atom Mass Number = the number of protons ...
... Atomic Number = number of protons # of protons determines kind of atom the same as the number of electrons in the neutral atom Mass Number = the number of protons ...
Atomic Structure
... • He was right in saying matter is made up of atoms • He was right in saying there are different kinds of atoms with different mass and other properties • He was "almost" right in saying atoms of a given element are ...
... • He was right in saying matter is made up of atoms • He was right in saying there are different kinds of atoms with different mass and other properties • He was "almost" right in saying atoms of a given element are ...
Chapter 3
... Stoichiometry and Limiting Reagent 4 wheels + 1 steering wheel + 2 airbags one 4passenger car • Given 57 wheels, 13 steering wheels and 24 airbags, how many passengers (max) can ride to opening day of the Twins game? % mass of each atom in the cmp, find the EF. • 12 cars can be made 48 passenge ...
... Stoichiometry and Limiting Reagent 4 wheels + 1 steering wheel + 2 airbags one 4passenger car • Given 57 wheels, 13 steering wheels and 24 airbags, how many passengers (max) can ride to opening day of the Twins game? % mass of each atom in the cmp, find the EF. • 12 cars can be made 48 passenge ...
quantum mechanical model of the atom
... Bohr’s Model of the Atom • Bohr’s model explained the hydrogen’s spectral lines, but failed to explain any other element’s lines. • For this and other reasons, the Bohr model was replaced with a more sophisticated model called the quantum-mechanical or wavemechanical model. ...
... Bohr’s Model of the Atom • Bohr’s model explained the hydrogen’s spectral lines, but failed to explain any other element’s lines. • For this and other reasons, the Bohr model was replaced with a more sophisticated model called the quantum-mechanical or wavemechanical model. ...
Directed Reading
... ______ 39. The mass of one proton is equal to the combined mass of how many electrons? a. less than 1 b. about 184 c. about 1,840 d. much more than 1,840 ______ 40. When calculating an atom’s approximate mass, how is the mass of electrons figured? a. It is ignored. b. It is figured at 1 over 1,840. ...
... ______ 39. The mass of one proton is equal to the combined mass of how many electrons? a. less than 1 b. about 184 c. about 1,840 d. much more than 1,840 ______ 40. When calculating an atom’s approximate mass, how is the mass of electrons figured? a. It is ignored. b. It is figured at 1 over 1,840. ...
Review AGº = -RTlnKº Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc at 25 ºC
... Because changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy are state functions, we can use any pathway to calculate the change in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy of an overall reaction. Hess’s Law: ΔH for a process is equal to the sum of ΔH for any set of steps, i.e., for any path that equals the over ...
... Because changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy are state functions, we can use any pathway to calculate the change in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy of an overall reaction. Hess’s Law: ΔH for a process is equal to the sum of ΔH for any set of steps, i.e., for any path that equals the over ...
cOO The.Parts of the Atom J
... Isotopes s e e m to have a mind of their own and can't s e e m to follow any rules. So, of course, there are no set number of isotopes any one element can have. The best "balance" of protons and neutrons s e e m s to do a better job of holding the nucleus together. There is a trend, however—light el ...
... Isotopes s e e m to have a mind of their own and can't s e e m to follow any rules. So, of course, there are no set number of isotopes any one element can have. The best "balance" of protons and neutrons s e e m s to do a better job of holding the nucleus together. There is a trend, however—light el ...
nucleus
... The number of neutrons can vary, although there are often the same number of neutrons as there are protons. ...
... The number of neutrons can vary, although there are often the same number of neutrons as there are protons. ...