genes-157686-revisions v2_untracked
... Fragile X syndrome was overdiagnosed as a proportion of false ‘positive’ cases were actually expressing FRAXE [fra(Xq28)] which is associated with a much milder, non-syndromic learning disability- the gene at this locus, AFF2, was later shown to have a 5’ trinucleotide GCC repeat which could expand ...
... Fragile X syndrome was overdiagnosed as a proportion of false ‘positive’ cases were actually expressing FRAXE [fra(Xq28)] which is associated with a much milder, non-syndromic learning disability- the gene at this locus, AFF2, was later shown to have a 5’ trinucleotide GCC repeat which could expand ...
Emergent Neutrality in Adaptive Asexual Evolution
... The key derivation of this article concerns the effects of interference interactions on the evolution of the genome state. We develop an approximate calculus for multiple simultaneous mutations. Specifically, we determine how the fixation probability of a specific target mutation is affected by positi ...
... The key derivation of this article concerns the effects of interference interactions on the evolution of the genome state. We develop an approximate calculus for multiple simultaneous mutations. Specifically, we determine how the fixation probability of a specific target mutation is affected by positi ...
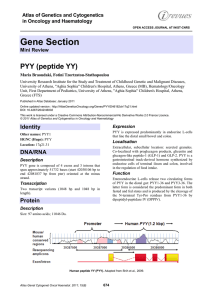
MeCP2 mutations in children with and without
... of MeCP2 mutations.14-24 MeCP2 mutations are predicted to result in a loss of function by either disrupting the methylated DNA– binding properties of the protein or interfering with its association with transcriptional co-repressors.25,26 Most studies have reported a relatively high prevalence of d ...
... of MeCP2 mutations.14-24 MeCP2 mutations are predicted to result in a loss of function by either disrupting the methylated DNA– binding properties of the protein or interfering with its association with transcriptional co-repressors.25,26 Most studies have reported a relatively high prevalence of d ...
User`s Manual - Mendel`s Accountant
... [Sanford et al., 2007. SCPE 8(2): 147-165 - also available on this web site]. Following is a simple outline of how the program operates. 1. Based on user input, Mendel creates a virtual population with the specified number of individuals, mean reproduction rate, mating characteristics, and possible ...
... [Sanford et al., 2007. SCPE 8(2): 147-165 - also available on this web site]. Following is a simple outline of how the program operates. 1. Based on user input, Mendel creates a virtual population with the specified number of individuals, mean reproduction rate, mating characteristics, and possible ...
Screening for Colorectal Cancer - US Preventive Services Task Force
... For all screening modalities, starting screening at age 50 resulted in a balance between life-years gained and colonoscopy risks that was more favorable than commencing screening earlier. Despite the increasing incidence of colorectal adenomas with age, for individuals previously screened the gain i ...
... For all screening modalities, starting screening at age 50 resulted in a balance between life-years gained and colonoscopy risks that was more favorable than commencing screening earlier. Despite the increasing incidence of colorectal adenomas with age, for individuals previously screened the gain i ...
Lesson Overview - Enfield High School
... Effects of Mutations Plant and animal breeders often make use mutations. For example, when a complete set of chromosomes fails to separate during meiosis, the gametes that result may produce triploid (3N) or tetraploid (4N) organisms. The condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes ...
... Effects of Mutations Plant and animal breeders often make use mutations. For example, when a complete set of chromosomes fails to separate during meiosis, the gametes that result may produce triploid (3N) or tetraploid (4N) organisms. The condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes ...
The Role of TP53 in Cervical Carcinogenesis
... which greatly increases the probability that HPVinfected cells will evolve toward malignancy. The induction of p53 destabilization is an exclusive feature of E6 proteins from the high-risk HPV types. Indeed, E6 of the low-risk HPVs, which are seldom associated with malignant lesions, are not able to ...
... which greatly increases the probability that HPVinfected cells will evolve toward malignancy. The induction of p53 destabilization is an exclusive feature of E6 proteins from the high-risk HPV types. Indeed, E6 of the low-risk HPVs, which are seldom associated with malignant lesions, are not able to ...
Mutation at the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene (PAH) and its use
... polymorphisms (IVS2nt19, IVS3nt-22, IVS6nt-55, Q232Q, V245V, L385L, Y414Y); ii) four mutations causing non-PKU HPA (T92I, E390G, R408Q, D415N); iii) 34 mutations causing PKU. Only six mutations (M1V, R261Q, F299C, S349P, R408W and IVS12nt1) occurred in the whole province at relative frequencies > 5% ...
... polymorphisms (IVS2nt19, IVS3nt-22, IVS6nt-55, Q232Q, V245V, L385L, Y414Y); ii) four mutations causing non-PKU HPA (T92I, E390G, R408Q, D415N); iii) 34 mutations causing PKU. Only six mutations (M1V, R261Q, F299C, S349P, R408W and IVS12nt1) occurred in the whole province at relative frequencies > 5% ...
BRCA mutation
A BRCA mutation is a mutation in either of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are tumor suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, while others as benign or of still unknown or uncertain impact. Harmful mutations in these genes may produce a hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome in affected persons. Only 5-10% of breast cancer cases in women are attributed to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations (with BRCA1 mutations being slightly more common than BRCA2 mutations), but the impact on women with the gene mutation is more profound. Women with harmful mutations in either BRCA1 or BRCA2 have a risk of breast cancer that is about five times the normal risk, and a risk of ovarian cancer that is about ten to thirty times normal. The risk of breast and ovarian cancer is higher for women with a high-risk BRCA1 mutation than with a BRCA2 mutation. Having a high-risk mutation does not guarantee that the woman will develop any type of cancer, or imply that any cancer that appears was actually caused by the mutation, rather than some other factor.High-risk mutations, which disable an important error-free DNA repair process (homology directed repair), significantly increase the person's risk of developing breast cancer, ovarian cancer and certain other cancers. Why BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations lead preferentially to cancers of the breast and ovary is not known, but lack of BRCA1 function seems to lead to non-functional X-chromosome inactivation. Not all mutations are high-risk; some appear to be harmless variations. The cancer risk associated with any given mutation varies significantly and depends on the exact type and location of the mutation and possibly other individual factors.Mutations can be inherited from either parent and may be passed on to both sons and daughters. Each child of a genetic carrier, regardless of sex, has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutated gene from the parent who carries the mutation. As a result, half of the people with BRCA gene mutations are male, who would then pass the mutation on to 50% of their offspring, male or female. The risk of BRCA-related breast cancers for men with the mutation is higher than for other men, but still low. However, BRCA mutations can increase the risk of other cancers, such as colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer.Methods to diagnose the likelihood of a patient with mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 getting cancer were covered by patents owned or controlled by Myriad Genetics. Myriad's business model of exclusively offering the diagnostic test led to Myriad growing from being a startup in 1994 to being a publicly traded company with 1200 employees and about $500M in annual revenue in 2012; it also led to controversy over high prices and the inability to get second opinions from other diagnostic labs, which in turn led to the landmark Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics lawsuit.