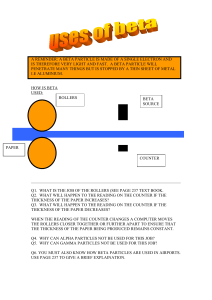
17.1assign - Advancing Physics
... photographs' and answer the questions about what you have seen. Activity 20P Presentation 'Who, what and when?' (described below) should be started early on as it can be an ongoing activity that develops throughout the chapter, work with other students to make it bigger and better! The people who ma ...
... photographs' and answer the questions about what you have seen. Activity 20P Presentation 'Who, what and when?' (described below) should be started early on as it can be an ongoing activity that develops throughout the chapter, work with other students to make it bigger and better! The people who ma ...
Lecture 4: Charged Particle Motion
... + so, with current density and velocity, we can determine the charge density of an electron beam. Relativistic motion Let's back up, for non-relativistic particles, if a force acts on a particle, its velocity can change ...
... + so, with current density and velocity, we can determine the charge density of an electron beam. Relativistic motion Let's back up, for non-relativistic particles, if a force acts on a particle, its velocity can change ...
Particle Physics Matter, Energy, Space, Time
... at these issues, and developed a strategic plan for the next twenty years • It concluded that particle physics is about to enter a new era … – Exploring physics beyond the Standard Model – Addressing deep new questions about the nature of matter and energy, space and time ...
... at these issues, and developed a strategic plan for the next twenty years • It concluded that particle physics is about to enter a new era … – Exploring physics beyond the Standard Model – Addressing deep new questions about the nature of matter and energy, space and time ...
heavyions - Indico
... laboratory in Darmstadt has 5 scientific pillars, one of which is the study of nuclear matter with heavy-ion beams at laboratory energies 8-40 GeV per nucleon (lower end of SPS energy range). ...
... laboratory in Darmstadt has 5 scientific pillars, one of which is the study of nuclear matter with heavy-ion beams at laboratory energies 8-40 GeV per nucleon (lower end of SPS energy range). ...
5.0. Wave Mechanics
... 5.0. Wave Mechanics One cornerstone of quantum theory is the particle-wave duality [the other is the principle of uncertainty]. For example, in optical phenomena such as diffraction and interference, light behaves like waves. In collision processes such as photo-electric and Compton effects, light b ...
... 5.0. Wave Mechanics One cornerstone of quantum theory is the particle-wave duality [the other is the principle of uncertainty]. For example, in optical phenomena such as diffraction and interference, light behaves like waves. In collision processes such as photo-electric and Compton effects, light b ...
here - TeacherWeb
... Put Answers in Your Lab Journal In 1910 when this experiment was first conducted, negative electrons had already been discovered, but no other atomic building particles were known. Since atoms were neutral - no charge - there had to be positive charge to balance the electrons. Procedure Open phet.co ...
... Put Answers in Your Lab Journal In 1910 when this experiment was first conducted, negative electrons had already been discovered, but no other atomic building particles were known. Since atoms were neutral - no charge - there had to be positive charge to balance the electrons. Procedure Open phet.co ...
CH17 Self Assessment
... use hand rule to explain how to determine nature of charge or direction of magnetic field given the other and the track for subatomic particles compare tracks in terms of the mass, charge (size or nature), speed, or energy of the particle compare decreasing relative strengths and ranges of effect of ...
... use hand rule to explain how to determine nature of charge or direction of magnetic field given the other and the track for subatomic particles compare tracks in terms of the mass, charge (size or nature), speed, or energy of the particle compare decreasing relative strengths and ranges of effect of ...
Introduction: what is quantum field theory ?
... 1012 eV . To convert the unit of energy back to a unit of length or time, we need to insert the relevant powers of c and ~. For example, the length scale λ associated to a mass m is the Compton wavelength ...
... 1012 eV . To convert the unit of energy back to a unit of length or time, we need to insert the relevant powers of c and ~. For example, the length scale λ associated to a mass m is the Compton wavelength ...
Beyong the Higgs
... the data, the nearly Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (nMSSM) is ruled out, while the Constrained Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (CMSSM) is disfavoured by the high diphoton rate measured. The Next-toMinimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (NMSSM) fits the data naturally and actually gives ...
... the data, the nearly Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (nMSSM) is ruled out, while the Constrained Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (CMSSM) is disfavoured by the high diphoton rate measured. The Next-toMinimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (NMSSM) fits the data naturally and actually gives ...
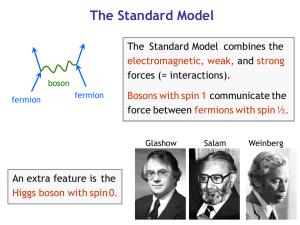
Bosons
... This convergence is improved by introducing a new symmetry called supersymmetry, which predicts a new set of supersymmetric particles with masses >1TeV.The coupling constants converge to a value close to the number 1/8 . ...
... This convergence is improved by introducing a new symmetry called supersymmetry, which predicts a new set of supersymmetric particles with masses >1TeV.The coupling constants converge to a value close to the number 1/8 . ...
unit 5: particle physics
... Because of their spin, all leptons are….. The leptons of each family or generation are assigned a lepton number. Since there are 3 families, there are 3 lepton numbers Lepton number (L): ...
... Because of their spin, all leptons are….. The leptons of each family or generation are assigned a lepton number. Since there are 3 families, there are 3 lepton numbers Lepton number (L): ...
Exercise Sheet 1 to Particle Physics I
... [Find all relevant numbers from PDG webpage: click on the “Physical Constants” link.] 2) Determine, as for exercise 1, in natural units the inverse mean life times (also called decay width Γ = τ −1 ) of the neutron (n), muon (µ− ), the pions (π +,−,0 ) and the rho meson (ρ). Search through the PDG p ...
... [Find all relevant numbers from PDG webpage: click on the “Physical Constants” link.] 2) Determine, as for exercise 1, in natural units the inverse mean life times (also called decay width Γ = τ −1 ) of the neutron (n), muon (µ− ), the pions (π +,−,0 ) and the rho meson (ρ). Search through the PDG p ...
Standard model of particle physics
... and physicists detected new particles in the higher atmosphere, e.g. muons and pions. These new particles initiated new conservation laws and quantities, like the strangeness. These was discovered as secondary radiation in pictures of Figure 1: First picture of anticloud chambers. matter: the track ...
... and physicists detected new particles in the higher atmosphere, e.g. muons and pions. These new particles initiated new conservation laws and quantities, like the strangeness. These was discovered as secondary radiation in pictures of Figure 1: First picture of anticloud chambers. matter: the track ...
REVIEW and REINFORCEMENT Structure of the Atom
... REVIEW and REINFORCEMENT Structure of the Atom ...
... REVIEW and REINFORCEMENT Structure of the Atom ...
ATLAS experiment

ATLAS (A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS) is one of the seven particle detector experiments (ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, TOTEM, LHCb, LHCf and MoEDAL) constructed at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), a particle accelerator at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) in Switzerland. The experiment is designed to take advantage of the unprecedented energy available at the LHC and observe phenomena that involve highly massive particles which were not observable using earlier lower-energy accelerators. It is hoped that it will shed light on new theories of particle physics beyond the Standard Model.ATLAS is 46 metres long, 25 metres in diameter, and weighs about 7,000 tonnes; it contains some 3000 km of cable. The experiment is a collaboration involving roughly 3,000 physicists from over 175 institutions in 38 countries. The project was led for the first 15 years by Peter Jenni and between 2009 and 2013 was headed by Fabiola Gianotti. Since 2013 it has been headed by David Charlton. It was one of the two LHC experiments involved in the discovery of a particle consistent with the Higgs boson in July 2012.