The Electron - webhosting.au.edu
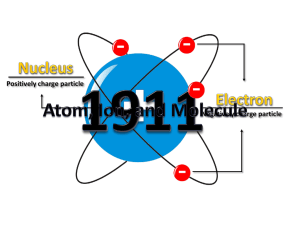
... Nucleus…a dense central core within the atom Proton…positively charged particles in the nucleus Source: whenever “. Came close to a nucleus in the scattering experiment, it experienced a large repulsive and therefore a large deflection. (i.e nucleus is composed of positively charged particles, whic ...
... Nucleus…a dense central core within the atom Proton…positively charged particles in the nucleus Source: whenever “. Came close to a nucleus in the scattering experiment, it experienced a large repulsive and therefore a large deflection. (i.e nucleus is composed of positively charged particles, whic ...
Passive Dynamics and Particle Systems COS 426, Spring 2014 Princeton University
... • Collision detection Intersect ray with scene Compute up to Δt at time of first collision, and then continue from there ...
... • Collision detection Intersect ray with scene Compute up to Δt at time of first collision, and then continue from there ...
How Atoms Work - Distribution Access
... wavelength — Measurement of the distance between two consecutive high points or low points on a wave. (Continued) ...
... wavelength — Measurement of the distance between two consecutive high points or low points on a wave. (Continued) ...
Quantum Theory
... location of an electron. The more we know about one, the less we know about the other. High energy light gives a better location, but disrupts the velocity. Low energy light disturbs the velocity less, but gives high uncertainty of location. Lower energy light gives worse resolution. The uncertainty ...
... location of an electron. The more we know about one, the less we know about the other. High energy light gives a better location, but disrupts the velocity. Low energy light disturbs the velocity less, but gives high uncertainty of location. Lower energy light gives worse resolution. The uncertainty ...
PY 482: Computation for Experimental Particle Physics
... 4. Course Objectives: To provide an introduction to the experimental methods used in modern high energy particle physics. The course will start with a survey of modern experimental particle physics where students will familiarize themselves with the Standard Model of particle physics. We will then c ...
... 4. Course Objectives: To provide an introduction to the experimental methods used in modern high energy particle physics. The course will start with a survey of modern experimental particle physics where students will familiarize themselves with the Standard Model of particle physics. We will then c ...
A modern view of forces - HEP Educational Outreach
... directly proportional to the EM coupling constant, aem! • In general, all force carriers will “couple to” particles with some “strength”. – The particle in question must have the “right charge” (more on this as we go) – The larger the coupling constant, the large the energy level splittings, larger ...
... directly proportional to the EM coupling constant, aem! • In general, all force carriers will “couple to” particles with some “strength”. – The particle in question must have the “right charge” (more on this as we go) – The larger the coupling constant, the large the energy level splittings, larger ...
The Structure of Matter The Standard Model of Elementary Particles
... Gauge bosons: particles that mediate (or transmit) the force between a pair of particles The 4 fundamental forces have different ranges and a different boson is responsible for each force. The mass of the boson establishes the range of the force. The bosons carry the force between particles. The Hig ...
... Gauge bosons: particles that mediate (or transmit) the force between a pair of particles The 4 fundamental forces have different ranges and a different boson is responsible for each force. The mass of the boson establishes the range of the force. The bosons carry the force between particles. The Hig ...
WestFest: Sixty Years of Fireballs
... 1. “…only states that are easily accessible from the initial state may actually attain statistical equilibrium…” 2. “…photons (which) could be created will certainly not have time to develop (statistical equilibrium)…” 3. “Notice the additional conservation law for the difference of the number of nu ...
... 1. “…only states that are easily accessible from the initial state may actually attain statistical equilibrium…” 2. “…photons (which) could be created will certainly not have time to develop (statistical equilibrium)…” 3. “Notice the additional conservation law for the difference of the number of nu ...
Introduction to Statistical Issues in Particle Physics - SLAC
... several. One will be the predicted distribution if X is not present. Another may be the prediction if X is present in the amount, and with the properties, predicted by an expected theory such as the ‘Standard Model’ [1] of Particle Physics. There may also be predictions obtained within the framework ...
... several. One will be the predicted distribution if X is not present. Another may be the prediction if X is present in the amount, and with the properties, predicted by an expected theory such as the ‘Standard Model’ [1] of Particle Physics. There may also be predictions obtained within the framework ...
ATLAS experiment

ATLAS (A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS) is one of the seven particle detector experiments (ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, TOTEM, LHCb, LHCf and MoEDAL) constructed at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), a particle accelerator at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) in Switzerland. The experiment is designed to take advantage of the unprecedented energy available at the LHC and observe phenomena that involve highly massive particles which were not observable using earlier lower-energy accelerators. It is hoped that it will shed light on new theories of particle physics beyond the Standard Model.ATLAS is 46 metres long, 25 metres in diameter, and weighs about 7,000 tonnes; it contains some 3000 km of cable. The experiment is a collaboration involving roughly 3,000 physicists from over 175 institutions in 38 countries. The project was led for the first 15 years by Peter Jenni and between 2009 and 2013 was headed by Fabiola Gianotti. Since 2013 it has been headed by David Charlton. It was one of the two LHC experiments involved in the discovery of a particle consistent with the Higgs boson in July 2012.