Thesis_fulltext - University of Canterbury
... Also, since the hot-spot temperature is the key factor for limiting the power rating of the PCPT, the second part of the research investigates a thermal model to simulate the change of the hot-spot temperature for the designed PCPT. The cooling fluid of the PCPT applied in this project was BIOTEMP®. ...
... Also, since the hot-spot temperature is the key factor for limiting the power rating of the PCPT, the second part of the research investigates a thermal model to simulate the change of the hot-spot temperature for the designed PCPT. The cooling fluid of the PCPT applied in this project was BIOTEMP®. ...
Lecture 19: SRAM
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
ppt - CMOS VLSI Design
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
Lecture 17 - Harvey Mudd College
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
SRAMs
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
Lecture 15
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
Conext Core XC Series Grid Tie Photovoltaic Inverter: Operation
... Configuration, servicing, and maintenance must be performed by authorized service personnel only. Authorized service personnel meet the requirements for a qualified installer, and they have received specific training from the manufacturer on servicing the Conext Core XC Series. Do not open doors or ...
... Configuration, servicing, and maintenance must be performed by authorized service personnel only. Authorized service personnel meet the requirements for a qualified installer, and they have received specific training from the manufacturer on servicing the Conext Core XC Series. Do not open doors or ...
Power challenges may end the multicore era
... The first step in projecting gains from more cores is developing a model that captures future transistor scaling trends. To highlight the challenges of nonideal device scaling, first we present a simplified overview of historical Dennard scaling and the more recent scaling trends. Historical device ...
... The first step in projecting gains from more cores is developing a model that captures future transistor scaling trends. To highlight the challenges of nonideal device scaling, first we present a simplified overview of historical Dennard scaling and the more recent scaling trends. Historical device ...
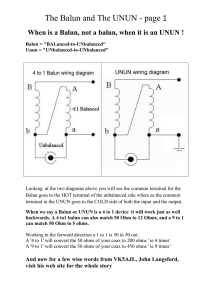
NONLINEAR MAGNETIC SWITCHES FOR PULSE GENERATION
... coercive force, H , so that a smaI I reverse current will reset the core. ' c' For cores requiring larger bias currents, application of the reset current through a bias winding provides the necessary negative flux bias. The use of a bias winding also provides more control over the exact pre-switch c ...
... coercive force, H , so that a smaI I reverse current will reset the core. ' c' For cores requiring larger bias currents, application of the reset current through a bias winding provides the necessary negative flux bias. The use of a bias winding also provides more control over the exact pre-switch c ...
ppt - University of California, Berkeley
... – RAS cycle fetched rows of data from cell array blocks (long access time, around 100ns) – Subsequent CAS cycles quickly access data from row buffers if within an address page (page is around 256 Bytes) ...
... – RAS cycle fetched rows of data from cell array blocks (long access time, around 100ns) – Subsequent CAS cycles quickly access data from row buffers if within an address page (page is around 256 Bytes) ...
Document
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
... For large shift registers, keep data in SRAM instead Move read/write pointers to RAM rather than data – Initialize read address to first entry, write to last – Increment address on each cycle Din ...
MAX5039, MAX5040
... The MAX5039/MAX5040 control the output voltage of the CORE and I/O supplies during power-up, powerdown, and brownout situations. They ensure that the two power supplies rise or fall at the same rate, limiting the voltage difference between the CORE and I/O supplies. This eliminates stresses on the p ...
... The MAX5039/MAX5040 control the output voltage of the CORE and I/O supplies during power-up, powerdown, and brownout situations. They ensure that the two power supplies rise or fall at the same rate, limiting the voltage difference between the CORE and I/O supplies. This eliminates stresses on the p ...
i ?g 255` i
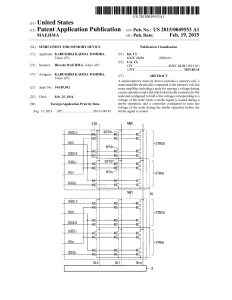
... [0019] The data circuit and page buffer 3 temporarily stores data read from the memory cell array 1, receives write data from the outside of the memory 10, and writes the received data into the selected memory cell. The data circuit and page buffer 3 includes a sense ampli?er 3a. The sense ampli?er ...
... [0019] The data circuit and page buffer 3 temporarily stores data read from the memory cell array 1, receives write data from the outside of the memory 10, and writes the received data into the selected memory cell. The data circuit and page buffer 3 includes a sense ampli?er 3a. The sense ampli?er ...
Evaluation of Magnetic Materials for Very High Frequency Power
... Note that the capacitance of the probe that measures the output voltage should be as small as possible, as it adds to the resonant capacitor value. The probe capacitance can be estimated from the data sheet. Here we include it with other parasitic capacitances and have considered its influence in ou ...
... Note that the capacitance of the probe that measures the output voltage should be as small as possible, as it adds to the resonant capacitor value. The probe capacitance can be estimated from the data sheet. Here we include it with other parasitic capacitances and have considered its influence in ou ...
an investigation of the boost inductor volume applied to pfc converters
... elements between the high dv/dt tracks of the board to the converter case [5, 6], while the differential mode noise is more affected by the switching ripple and the boost inductor leakage capacitance [7]. Therefore, the common mode noise generation can only be reduced by a layout modification, in su ...
... elements between the high dv/dt tracks of the board to the converter case [5, 6], while the differential mode noise is more affected by the switching ripple and the boost inductor leakage capacitance [7]. Therefore, the common mode noise generation can only be reduced by a layout modification, in su ...
Powder Material for Inductor Cores
... Hysteresis losses are heat losses which occurs when the domains are aligning with the applied field. The heat is created from the friction of the movement. In switching applications, such as, transformers and electric motors it is important to have narrow hysteresis loops i.e large flux density from ...
... Hysteresis losses are heat losses which occurs when the domains are aligning with the applied field. The heat is created from the friction of the movement. In switching applications, such as, transformers and electric motors it is important to have narrow hysteresis loops i.e large flux density from ...
Practical Paper 1
... The method of measuring unknown impedance using the twoprobe approach was first reported for power mains impedance measurements [4]. To briefly describe the method, Fig. 1 shows the basic measurement setup to measure the unknown impedance ZX . The setup involves an injecting probe, a receiving probe ...
... The method of measuring unknown impedance using the twoprobe approach was first reported for power mains impedance measurements [4]. To briefly describe the method, Fig. 1 shows the basic measurement setup to measure the unknown impedance ZX . The setup involves an injecting probe, a receiving probe ...
Compact Contactless Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicles
... 2. The capacitances of the resonant capacitors are independent of the output power. 3. If the primary voltage/current is constant, the secondary voltage/current will also be constant regardless of the load change. 4. The theoretical equation for the efficiency can be easily derived. This enables the ...
... 2. The capacitances of the resonant capacitors are independent of the output power. 3. If the primary voltage/current is constant, the secondary voltage/current will also be constant regardless of the load change. 4. The theoretical equation for the efficiency can be easily derived. This enables the ...
Magnetic-core memory

Magnetic-core memory was the predominant form of random-access computer memory for 20 years between about 1955 and 1975. Such memory is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.Core uses tiny magnetic toroids (rings), the cores, through which wires are threaded to write and read information. Each core represents one bit of information. The cores can be magnetized in two different ways (clockwise or counterclockwise) and the bit stored in a core is zero or one depending on that core's magnetization direction. The wires are arranged to allow for an individual core to be set to either a one or a zero and for its magnetization to be changed by sending appropriate electric current pulses through selected wires. The process of reading the core causes the core to be reset to a zero, thus erasing it. This is called destructive readout. When not being read or written, the cores maintain the last value they had, even when power is turned off. This makes them nonvolatile.Using smaller cores and wires the memory density of core slowly increased, and by the late 1960s a density of about 32 kilobits per cubic meter was typical. However, reaching this density required extremely careful manufacture, almost always carried out by hand in spite of repeated major efforts to automate the process. The cost declined over this period from about $1 per bit to about 1 cent per bit. The introduction of the first semiconductor memory SRAM chips in the late 1960s began to erode the core market. The first successful DRAM, the Intel 1103 which arrived in quantity in 1972 at 1 cent per bit, marked the beginning of the end of core. Improvements in semiconductor manufacturing led rapid increases in storage and decreases in price that drove core from the market by around 1974.Although core memory is obsolete, any computer memory is still occasionally called ""core""; in particular, a file recording the contents of memory after a system error is usually called a core dump.