Astronomy in Korea - Royal Asiatic Society
... [page 8] Chosen 朝鮮 which means, “It received the sunlight earlier than the others.” Pi-sa 秘詞 an astronomical or astrological work was written in 2247 B. C. by Sin Chi 神誌, who may be styled the first astronomer of Chosen. This work is listed in the Mun-hon-pi-go 文獻備考 1908, Book 246, p. 29, with some ...
... [page 8] Chosen 朝鮮 which means, “It received the sunlight earlier than the others.” Pi-sa 秘詞 an astronomical or astrological work was written in 2247 B. C. by Sin Chi 神誌, who may be styled the first astronomer of Chosen. This work is listed in the Mun-hon-pi-go 文獻備考 1908, Book 246, p. 29, with some ...
Exploration of the Universe
... 1. What astronomical observations allow us to know the time of day, the date, direction and the timing of ocean tides? 2. What is the difference between an asterism and a constellation? 3. How would observations of stars differ from the observations of planets? 4. What is retrograde motion? 5. What ...
... 1. What astronomical observations allow us to know the time of day, the date, direction and the timing of ocean tides? 2. What is the difference between an asterism and a constellation? 3. How would observations of stars differ from the observations of planets? 4. What is retrograde motion? 5. What ...
Focus On Middle School Astronomy Student
... The practice of astronomy changed dramatically after the invention of the telescope, a scientific tool that uses lenses to magnify distant objects. In the 1600’s Galileo (ga-lǝ-lā’-ō), an Italian scientist considered to be the first modern astronomer, used the telescope to look at the planets. Galil ...
... The practice of astronomy changed dramatically after the invention of the telescope, a scientific tool that uses lenses to magnify distant objects. In the 1600’s Galileo (ga-lǝ-lā’-ō), an Italian scientist considered to be the first modern astronomer, used the telescope to look at the planets. Galil ...
8th Grade - Astronomy
... trillion miles). Astronomers use the light-year to measure distances between the stars. Light-year Light travels at about 300,000 kilometers a second. A light-year is a unit of distance not time. Example: Our next nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri which is 4.2 light-years from Earth. (p. 602 ...
... trillion miles). Astronomers use the light-year to measure distances between the stars. Light-year Light travels at about 300,000 kilometers a second. A light-year is a unit of distance not time. Example: Our next nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri which is 4.2 light-years from Earth. (p. 602 ...
Some 250 years ago, the philosopher Immanuel Universal
... coordinate grid, and shares wordthe eleventh century. ing with another traditional astroAmong the manuscripts was an nomical text, Yue Ling, or Monthly exquisite star chart. It shows the Ordinances, which has been dated entire sky as visible from China, to around 300 bc. Yet it remains the earliest- ...
... coordinate grid, and shares wordthe eleventh century. ing with another traditional astroAmong the manuscripts was an nomical text, Yue Ling, or Monthly exquisite star chart. It shows the Ordinances, which has been dated entire sky as visible from China, to around 300 bc. Yet it remains the earliest- ...
Observing
... The Changing Sky North Pole of the Earth is pointed at Polaris (the North or Pole star), which stays stationary as the other stars move around it ...
... The Changing Sky North Pole of the Earth is pointed at Polaris (the North or Pole star), which stays stationary as the other stars move around it ...
Riaz - protostar sha.. - University of Hertfordshire
... molecular cloud, with the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) 4-m telescope in Chile. They found an odd feature in their image – a shadowed dark lane just to the west of the protostar with a thickness of about 54 billion kilometres (360 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun). Silho ...
... molecular cloud, with the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) 4-m telescope in Chile. They found an odd feature in their image – a shadowed dark lane just to the west of the protostar with a thickness of about 54 billion kilometres (360 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun). Silho ...
"Science, Mesopotamian" In: The Encyclopedia of Ancient History
... diaries and related observational texts from Babylonia are the fruits of a systematic program of observation that began near 750 BCE and continued until the first century CE. Diaries usually contain six months of observations, each month beginning with a section covering daily positions, lunar pheno ...
... diaries and related observational texts from Babylonia are the fruits of a systematic program of observation that began near 750 BCE and continued until the first century CE. Diaries usually contain six months of observations, each month beginning with a section covering daily positions, lunar pheno ...
Maya .(English)
... Moon’s orbit is 27.322days Moon marker – twice a day and skip one each cycle ...
... Moon’s orbit is 27.322days Moon marker – twice a day and skip one each cycle ...
The Sun
... does fusion. Fusion happens in the core (center) of the sun. The sun is just one of many billions of stars in the Milky Way galaxy. ...
... does fusion. Fusion happens in the core (center) of the sun. The sun is just one of many billions of stars in the Milky Way galaxy. ...
Astronomy Impacts our Daily Lives
... that there ever will be. From the effects of the smallest atoms to the appearance of the Universe on the largest ...
... that there ever will be. From the effects of the smallest atoms to the appearance of the Universe on the largest ...
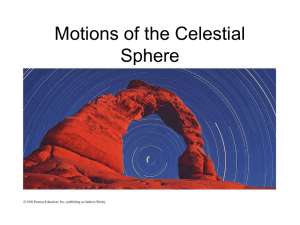
Motions of the Celestial Sphere
... in arcs across the sky that are not perpendicular to horizon. ...
... in arcs across the sky that are not perpendicular to horizon. ...
NOVA COLLEGE-WIDE COURSE CONTENT SUMMARY PHY 150
... human introspection may aid in pursuit for extraterrestrial intelligence within our galaxy ...
... human introspection may aid in pursuit for extraterrestrial intelligence within our galaxy ...
Planetarium Key Points
... Geographic Latitude is the elevation of the visible pole and, roughly, of Polaris The motion of the sphere seems uniform, for this reason it was the source for time telling, but the time scale that comes from is NOT uniform: rotation is slowing down, the day is longer and longer at the rate of 2 ...
... Geographic Latitude is the elevation of the visible pole and, roughly, of Polaris The motion of the sphere seems uniform, for this reason it was the source for time telling, but the time scale that comes from is NOT uniform: rotation is slowing down, the day is longer and longer at the rate of 2 ...
File
... points of Venus and Jupiter, Humans were sacrificed on the first appearance, when Venus was at its dimmest magnitude. They observed the moon (ixchel): Was as important as the sun!, Ixchel the moon goddess battled the sun and made him go into the underworld every night! They observed the stars: The s ...
... points of Venus and Jupiter, Humans were sacrificed on the first appearance, when Venus was at its dimmest magnitude. They observed the moon (ixchel): Was as important as the sun!, Ixchel the moon goddess battled the sun and made him go into the underworld every night! They observed the stars: The s ...
Chapter 18 review answers
... 2. Farmers looked to the sky to track the movements of the sun and stars and to determine when to plant. They looked at the constellations. P 482 3. The calendar is made up of days (24 hours), months (28-31 days) and the unit of a year (12 months). 4. A day is the time it takes the earth to rotate o ...
... 2. Farmers looked to the sky to track the movements of the sun and stars and to determine when to plant. They looked at the constellations. P 482 3. The calendar is made up of days (24 hours), months (28-31 days) and the unit of a year (12 months). 4. A day is the time it takes the earth to rotate o ...
Document
... How do you locate places on the Earth? Latitude and Longitude Latitude: angle measured from the Equator (0o), up or down, N-S Longitude: angle measured from the Prime ...
... How do you locate places on the Earth? Latitude and Longitude Latitude: angle measured from the Equator (0o), up or down, N-S Longitude: angle measured from the Prime ...
Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS) Observation
... • Course material will be covered in two weekly lessons (Mo/We), 1hr15m long; studying from my notes and selected papers, texts. • It includes homework. • The syllabus of the course will soon be online, together with most of the material covered in class. The Web site is: www.astro.umass.edu/~mauro/ ...
... • Course material will be covered in two weekly lessons (Mo/We), 1hr15m long; studying from my notes and selected papers, texts. • It includes homework. • The syllabus of the course will soon be online, together with most of the material covered in class. The Web site is: www.astro.umass.edu/~mauro/ ...
chapter2 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... astronomy Landmarks on the celestial sphere are projections of those on the Earth ...
... astronomy Landmarks on the celestial sphere are projections of those on the Earth ...
Seasonal Motion
... Example: In Winter sun in Sagittarius, Gemini at night sky; in summer sun in Gemini, Sagittarius at night sky ...
... Example: In Winter sun in Sagittarius, Gemini at night sky; in summer sun in Gemini, Sagittarius at night sky ...
a light year is
... a) the characteristic size of light , b) the distance the Earth travels around the sun in one year c) the distance light travels in one year, d) the time it takes light to travel around the Earth's orbit 2. Constellations are a) apparent patterns or designs of stars in the sky , b) physical, related ...
... a) the characteristic size of light , b) the distance the Earth travels around the sun in one year c) the distance light travels in one year, d) the time it takes light to travel around the Earth's orbit 2. Constellations are a) apparent patterns or designs of stars in the sky , b) physical, related ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.