An auxiliary line is a line that is added to a figure to aid in a proof. An
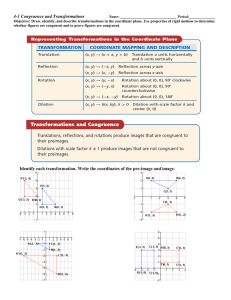
... Consider the triangle whose vertices are A(-3, 2), B(-1, -4), and C(3, 0). Use a piece of graph paper to perform the following transformations. Make sure to draw an x and y-axis below. 1. Plot the original triangle in pencil. Use the color blue to perform a translation 5 units to the left and 2 ...
... Consider the triangle whose vertices are A(-3, 2), B(-1, -4), and C(3, 0). Use a piece of graph paper to perform the following transformations. Make sure to draw an x and y-axis below. 1. Plot the original triangle in pencil. Use the color blue to perform a translation 5 units to the left and 2 ...
Triangle Inequality Properties / Hinge Theorem
... ©E G2C0K1y6X iKSuMtQas PSjo]fbtcwoaEr\eo vLVLiCh._ Q tAxlIlE zrKiRgdh\tFsF Nrzets_eOrKvteHdq.q E _MnawdHeh ewHigtMhz QISnzfBiznEirtzek bGyegoXm\estTrryS. ...
... ©E G2C0K1y6X iKSuMtQas PSjo]fbtcwoaEr\eo vLVLiCh._ Q tAxlIlE zrKiRgdh\tFsF Nrzets_eOrKvteHdq.q E _MnawdHeh ewHigtMhz QISnzfBiznEirtzek bGyegoXm\estTrryS. ...
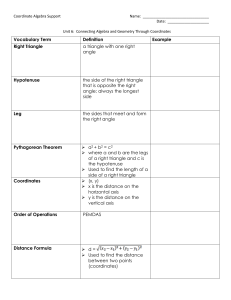
Vocabulary Term Definition Example Right Triangle a triangle with
... of a right triangle and c is the hypotenuse Used to find the length of a side of a right triangle (x, y) x is the distance on the horizontal axis y is the distance on the vertical axis ...
... of a right triangle and c is the hypotenuse Used to find the length of a side of a right triangle (x, y) x is the distance on the horizontal axis y is the distance on the vertical axis ...
Geometry Chapter 5 Review
... 36. A triangle has sides 2 and 8 inches. Write an inequality to show the range of values for the third side. ...
... 36. A triangle has sides 2 and 8 inches. Write an inequality to show the range of values for the third side. ...
Section 9.3 notes
... A polygon is a closed plane figure with at least three sides. The sides meet only at their endpoints. A triangle is a polygon with three sides. You can classify triangles by angle measures. You can also classify triangles by side lengths. Tick marks are used to indicate congruent sides of a figure. ...
... A polygon is a closed plane figure with at least three sides. The sides meet only at their endpoints. A triangle is a polygon with three sides. You can classify triangles by angle measures. You can also classify triangles by side lengths. Tick marks are used to indicate congruent sides of a figure. ...
Medians, Altitudes, and Angle Bisectors
... triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side, then it is a median. If a segment is a median, then it divides the side to which it is drawn into two congruent segments. ...
... triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side, then it is a median. If a segment is a median, then it divides the side to which it is drawn into two congruent segments. ...
Notes 4.2 _Day 1(Filled In).jnt
... If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, the remaining pair of angles are also congruent. ...
... If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, the remaining pair of angles are also congruent. ...
Task - Illustrative Mathematics
... BMC and so are congruent. Since these two angles make a line and are congruent they must each be right angles. We can therefore apply the Pythagorean theorem to △AMC to find |MC|: ...
... BMC and so are congruent. Since these two angles make a line and are congruent they must each be right angles. We can therefore apply the Pythagorean theorem to △AMC to find |MC|: ...
Incircle and excircles of a triangle
Incircle redirects here. For incircles of non-triangle polygons, see Tangential quadrilateral or Tangential polygon.In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle contained in the triangle; it touches (is tangent to) the three sides. The center of the incircle is called the triangle's incenter.An excircle or escribed circle of the triangle is a circle lying outside the triangle, tangent to one of its sides and tangent to the extensions of the other two. Every triangle has three distinct excircles, each tangent to one of the triangle's sides.The center of the incircle, called the incenter, can be found as the intersection of the three internal angle bisectors. The center of an excircle is the intersection of the internal bisector of one angle (at vertex A, for example) and the external bisectors of the other two. The center of this excircle is called the excenter relative to the vertex A, or the excenter of A. Because the internal bisector of an angle is perpendicular to its external bisector, it follows that the center of the incircle together with the three excircle centers form an orthocentric system.Polygons with more than three sides do not all have an incircle tangent to all sides; those that do are called tangential polygons. See also Tangent lines to circles.