Chapter 3-1 Guided Notes Name___________________ Square
... Whole Numbers- All __________ numbers and _____________. Integers- Set of whole numbers and their _____________ or negatives {-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3} Rational Numbers -any number that can be written as a __________________________ Can be a fraction Irrational Numbers - any number that cannot be writ ...
... Whole Numbers- All __________ numbers and _____________. Integers- Set of whole numbers and their _____________ or negatives {-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3} Rational Numbers -any number that can be written as a __________________________ Can be a fraction Irrational Numbers - any number that cannot be writ ...
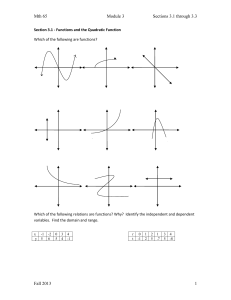
Mth 65 Module 3 Sections 3.1 through 3.3 Section 3.1
... The function above is called a _______________________________function. The shape of the graph is called a ___________________________. Each parabola has a _______________(maximum or minimum) and an axis of symmetry (always a ______________________ line which passes through the vertex). State the ve ...
... The function above is called a _______________________________function. The shape of the graph is called a ___________________________. Each parabola has a _______________(maximum or minimum) and an axis of symmetry (always a ______________________ line which passes through the vertex). State the ve ...
5012040 MATH GRADE 2 - The Beverly Institute Home Page
... focuses on the rate of change from one element to the next. Example: Next = Now + 2; Next = Now x 4. In the explicit form of pattern generalization, the formula or rule is related to the order of the terms in the sequence and focuses on the relationship between the independent variable and the depen ...
... focuses on the rate of change from one element to the next. Example: Next = Now + 2; Next = Now x 4. In the explicit form of pattern generalization, the formula or rule is related to the order of the terms in the sequence and focuses on the relationship between the independent variable and the depen ...
Grade 7- Chapter 4
... _____________________________________ Equivalent fractions represent the same portion of the whole, but may be written differently. Ex: 2/4 = ½. You can simplify fractions by dividing the numerator and denominator by the same common factor. Ex: With 10/12 you can divide the numerator and denomin ...
... _____________________________________ Equivalent fractions represent the same portion of the whole, but may be written differently. Ex: 2/4 = ½. You can simplify fractions by dividing the numerator and denominator by the same common factor. Ex: With 10/12 you can divide the numerator and denomin ...
Exercise 4.1
... The selling price of a computer is $ 13 000. Customers can pay $2 200 as down payment, and pay the remaining cost in 12 equal instalments. How much is each instalment? ...
... The selling price of a computer is $ 13 000. Customers can pay $2 200 as down payment, and pay the remaining cost in 12 equal instalments. How much is each instalment? ...
The Unexpected Appearance of Pi in Diverse Problems
... It is clear that if X is replaced by the set N of all natural ...
... It is clear that if X is replaced by the set N of all natural ...
MATH 1200: Tutorial 5, July 14 and July 21 Factorization is Not
... Inagine yourself in a world (referred to as the E-Zone) where the only numbers that are known are the even numbers. So, in this world, the only numbers that exist are E = {. . . , −8, −6, −4, −2, 0, 2, 4, 8, 10, . . .} . Notice that in the E-zone we can add, subtract, and multiply numbers just as us ...
... Inagine yourself in a world (referred to as the E-Zone) where the only numbers that are known are the even numbers. So, in this world, the only numbers that exist are E = {. . . , −8, −6, −4, −2, 0, 2, 4, 8, 10, . . .} . Notice that in the E-zone we can add, subtract, and multiply numbers just as us ...
MATH 0305
... 15. A family began a trip of 516 miles at 8am. They arrived at their final destination at 5:30pm. If they took two 15-minute breaks and took one hour for lunch, what was their average driving rate? ...
... 15. A family began a trip of 516 miles at 8am. They arrived at their final destination at 5:30pm. If they took two 15-minute breaks and took one hour for lunch, what was their average driving rate? ...