divide & conquer algorithms
... there exists an O(N log N) divide-and-conquer solution Assume the points are sorted by x-coordinate (can be done in O(N log N)) 1. partition the points into equal parts using a vertical line in the plane 2. recursively determine the closest pair on left side (Ldist) and the closest pair on the rig ...
... there exists an O(N log N) divide-and-conquer solution Assume the points are sorted by x-coordinate (can be done in O(N log N)) 1. partition the points into equal parts using a vertical line in the plane 2. recursively determine the closest pair on left side (Ldist) and the closest pair on the rig ...
Powerpoint of Notes
... To multiply numbers in scientific notation, multiply the decimals and powers of 10 separately. Then, put the answer in correct scientific notation form. Examples: The Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt contains about 2.3 x 106 blocks of stone. On average, each block weighs about 5 x 103 ponds. About how ...
... To multiply numbers in scientific notation, multiply the decimals and powers of 10 separately. Then, put the answer in correct scientific notation form. Examples: The Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt contains about 2.3 x 106 blocks of stone. On average, each block weighs about 5 x 103 ponds. About how ...
Module 5 Higher Year 11 Spring 496.50KB 2017
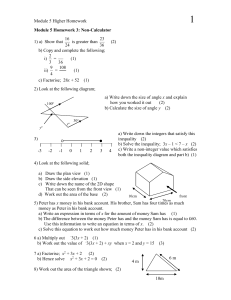
... 9) The area of a circle is п × r2, where п is approximately 3.14 and r is the radius The circumference of a circle is п × D, where D is the diameter a) Calculate the area of a circle with radius 20 cm (use 3.14 as the value of п) (2) b) Calculate the circumference of the same circle (2) c) Given tha ...
... 9) The area of a circle is п × r2, where п is approximately 3.14 and r is the radius The circumference of a circle is п × D, where D is the diameter a) Calculate the area of a circle with radius 20 cm (use 3.14 as the value of п) (2) b) Calculate the circumference of the same circle (2) c) Given tha ...
Here - Mathematical Association of America
... Indian mathematicians were aware of the quadratic formula for solving quadratic equations before such ideas were discussed in Islam. Here is a verse from the Brāhmasphutasiddhānta of Brahmagupta in the seventh century, giving a version of the quadratic formula. The context is the solution of a quadr ...
... Indian mathematicians were aware of the quadratic formula for solving quadratic equations before such ideas were discussed in Islam. Here is a verse from the Brāhmasphutasiddhānta of Brahmagupta in the seventh century, giving a version of the quadratic formula. The context is the solution of a quadr ...
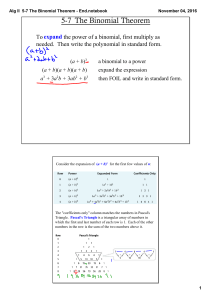
Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
... you've done this step correctly by redistributing through. Let's check it. Trade the terms places for standard form. ...
... you've done this step correctly by redistributing through. Let's check it. Trade the terms places for standard form. ...
CSC - PSBB Schools
... 2. What is an array? Explain with an example. 3. Write the number of bytes occupied by the following variables. a) int a; b) char b[20]; c) int y[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,}; d) char x[]=”Halfyearly\0”; 4. Check if the following declarations are correct. If not, give reasons. a) int b=10,20,30,40}; b) int a[][ ...
... 2. What is an array? Explain with an example. 3. Write the number of bytes occupied by the following variables. a) int a; b) char b[20]; c) int y[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,}; d) char x[]=”Halfyearly\0”; 4. Check if the following declarations are correct. If not, give reasons. a) int b=10,20,30,40}; b) int a[][ ...
U3L8 Synthetic Division with Complex Numbers
... 1. Do Now: Read and markup the following definition. Use the definition to list the complex conjugates of the following complex zeros. The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra States: A polynomial function of a degree n has n zeros(real and non real). Some of these zeros may be repeated. Every polynomial ...
... 1. Do Now: Read and markup the following definition. Use the definition to list the complex conjugates of the following complex zeros. The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra States: A polynomial function of a degree n has n zeros(real and non real). Some of these zeros may be repeated. Every polynomial ...
Addition
Addition (often signified by the plus symbol ""+"") is one of the four elementary, mathematical operations of arithmetic, with the others being subtraction, multiplication and division.The addition of two whole numbers is the total amount of those quantities combined. For example, in the picture on the right, there is a combination of three apples and two apples together; making a total of 5 apples. This observation is equivalent to the mathematical expression ""3 + 2 = 5"" i.e., ""3 add 2 is equal to 5"".Besides counting fruits, addition can also represent combining other physical objects. Using systematic generalizations, addition can also be defined on more abstract quantities, such as integers, rational numbers, real numbers and complex numbers and other abstract objects such as vectors and matrices.In arithmetic, rules for addition involving fractions and negative numbers have been devised amongst others. In algebra, addition is studied more abstractly.Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that order does not matter, and it is associative, meaning that when one adds more than two numbers, the order in which addition is performed does not matter (see Summation). Repeated addition of 1 is the same as counting; addition of 0 does not change a number. Addition also obeys predictable rules concerning related operations such as subtraction and multiplication.Performing addition is one of the simplest numerical tasks. Addition of very small numbers is accessible to toddlers; the most basic task, 1 + 1, can be performed by infants as young as five months and even some non-human animals. In primary education, students are taught to add numbers in the decimal system, starting with single digits and progressively tackling more difficult problems. Mechanical aids range from the ancient abacus to the modern computer, where research on the most efficient implementations of addition continues to this day.