6.1 Organizing the Elements
... Early chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups. Mendeleev arranged the elements in his periodic table in order of increasing atomic mass. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Three classes of elements are metals, nonmetals ...
... Early chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups. Mendeleev arranged the elements in his periodic table in order of increasing atomic mass. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Three classes of elements are metals, nonmetals ...
Ch. 23
... • Metallic calcium serves mainly as an alloying agent • Essential for living systems Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 ...
... • Metallic calcium serves mainly as an alloying agent • Essential for living systems Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 ...
Topic 2: ATomic STrucTure - Manitoba Education and Training
... waves. These waves consist of an electric field and a magnetic field that are perpendicular to each other. The different components (gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves, visible light, and others) of the electromagnetic spectrum vary due to differences in wavelength and frequency, but they all travel at ...
... waves. These waves consist of an electric field and a magnetic field that are perpendicular to each other. The different components (gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves, visible light, and others) of the electromagnetic spectrum vary due to differences in wavelength and frequency, but they all travel at ...
Trace Elements in Coal
... trace elements by level of concern and was based on the potential hazards of these elements to biological systems arising from coal combustion. Amendments to the US Clean Air Act designated a number of trace elements as hazardous air pollutants associated with the operation of industrial plant which ...
... trace elements by level of concern and was based on the potential hazards of these elements to biological systems arising from coal combustion. Amendments to the US Clean Air Act designated a number of trace elements as hazardous air pollutants associated with the operation of industrial plant which ...
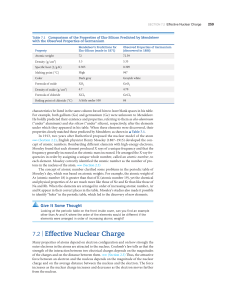
7.2 | Effective Nuclear Charge
... (“under” aluminum) and eka-silicon (“under” silicon), respectively, after the elements under which they appeared in his table. When these elements were discovered, their properties closely matched those predicted by Mendeleev, as shown in ▲ Table 7.1. In 1913, two years after Rutherford proposed the ...
... (“under” aluminum) and eka-silicon (“under” silicon), respectively, after the elements under which they appeared in his table. When these elements were discovered, their properties closely matched those predicted by Mendeleev, as shown in ▲ Table 7.1. In 1913, two years after Rutherford proposed the ...
The Electronegativity and the Global Hardness Are Periodic
... electronegativity was started with the seminal work of Pauling [16,17] who suggested for the first time a scientific definition of electronegativity as “the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons toward itself”. Though the electronegativity has been defined in many different ways after ...
... electronegativity was started with the seminal work of Pauling [16,17] who suggested for the first time a scientific definition of electronegativity as “the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons toward itself”. Though the electronegativity has been defined in many different ways after ...
The Periodic Table
... The Pauli Principle: two electrons with the same spin cannot occupy the same orbital. In other words, no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers (the same 'address'). Hund's Rule: the most stable arrangement of electrons in subshells is the one with the greatest number of parallel spi ...
... The Pauli Principle: two electrons with the same spin cannot occupy the same orbital. In other words, no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers (the same 'address'). Hund's Rule: the most stable arrangement of electrons in subshells is the one with the greatest number of parallel spi ...
Chemical Periodicity
... line at the right side of the table shown below separates the elements into two groups: the metals and the nonmetals. The elements that are on the left of this line tend to be metals, while those to the right tend to be nonmetals. The elements that are directly on the diagonal line are metalloids. M ...
... line at the right side of the table shown below separates the elements into two groups: the metals and the nonmetals. The elements that are on the left of this line tend to be metals, while those to the right tend to be nonmetals. The elements that are directly on the diagonal line are metalloids. M ...
Chemistry Part - teko classes bhopal
... forms a pattern of interlocking hexagonal rings. The carbon atoms are difficult to separate from one another. So graphite also has high melting point. However, the bonds between the layers are weak. The layers are able to slide easily over one another, rather like pack of cards. This makes graphite ...
... forms a pattern of interlocking hexagonal rings. The carbon atoms are difficult to separate from one another. So graphite also has high melting point. However, the bonds between the layers are weak. The layers are able to slide easily over one another, rather like pack of cards. This makes graphite ...
Class XI worksheet - Indian School Muscat
... 12 Explain why cations are smaller and anions are larger in radii than the parent atoms. 13 What are the various factors due to which the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements tends to decrease down the group? 14 Write the general outer electronic configuration of i. s block elements ii. p ...
... 12 Explain why cations are smaller and anions are larger in radii than the parent atoms. 13 What are the various factors due to which the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements tends to decrease down the group? 14 Write the general outer electronic configuration of i. s block elements ii. p ...
Periodic Table Review
... When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. ...
... When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties. ...
ExamView - Periodic Trends Study Guide.tst
... ____ 30. What is the element with the highest electronegativity value? a. cesium b. helium c. calcium d. fluorine ____ 31. Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius? a. Li b. K c. O d. S ____ 32. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state ...
... ____ 30. What is the element with the highest electronegativity value? a. cesium b. helium c. calcium d. fluorine ____ 31. Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius? a. Li b. K c. O d. S ____ 32. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state ...
Chapter 5
... • The p-block elements together with the s-block elements are called the main-group elements. • The properties of elements of the p block vary greatly. • At its right-hand end, the p block includes all of the nonmetals except hydrogen and helium. • All six of the metalloids are also in the p block. ...
... • The p-block elements together with the s-block elements are called the main-group elements. • The properties of elements of the p block vary greatly. • At its right-hand end, the p block includes all of the nonmetals except hydrogen and helium. • All six of the metalloids are also in the p block. ...
Chemistry Benchmark 1 Review
... 77. How many sublevels and orbitals are possible in the third energy level? 78. Write the ground state electron configuration of sulfur and draw its electron-dot structure. 79. Two elements A and B have atomic numbers 8 and 17 respectively. Identify their groups in the periodic table. 80. An element ...
... 77. How many sublevels and orbitals are possible in the third energy level? 78. Write the ground state electron configuration of sulfur and draw its electron-dot structure. 79. Two elements A and B have atomic numbers 8 and 17 respectively. Identify their groups in the periodic table. 80. An element ...
Exam View Benchmark Review sheet for 1st nine weeks
... 77. How many sublevels and orbitals are possible in the third energy level? 78. Write the ground state electron configuration of sulfur and draw its electron-dot structure. 79. Two elements A and B have atomic numbers 8 and 17 respectively. Identify their groups in the periodic table. 80. An element ...
... 77. How many sublevels and orbitals are possible in the third energy level? 78. Write the ground state electron configuration of sulfur and draw its electron-dot structure. 79. Two elements A and B have atomic numbers 8 and 17 respectively. Identify their groups in the periodic table. 80. An element ...
1 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
... electron configurations. Since the families of elements were organized by their chemical behavior, it is predictable that the individual members of each chemical family will have similar electron configurations. If you examine a periodic table, you will often find a number written above each group ( ...
... electron configurations. Since the families of elements were organized by their chemical behavior, it is predictable that the individual members of each chemical family will have similar electron configurations. If you examine a periodic table, you will often find a number written above each group ( ...
Lewis Reeve Gibbes and the Classification of the Elements
... achieving the "synoptical" presentation of chemical relationships which was the objective of its author. It is important to remember that the development of a single relationship amongst all the elements was not uppermost in Gibbes' mind; to him the numerous attempts which had been made in previous ...
... achieving the "synoptical" presentation of chemical relationships which was the objective of its author. It is important to remember that the development of a single relationship amongst all the elements was not uppermost in Gibbes' mind; to him the numerous attempts which had been made in previous ...
Chapter 4 - Northside Middle School
... • Generally, the transition metals are less reactive than the alkali metals and the alkaline-earth metals are. • Some transition metals are so unreactive that they seldom form compounds with other elements. ...
... • Generally, the transition metals are less reactive than the alkali metals and the alkaline-earth metals are. • Some transition metals are so unreactive that they seldom form compounds with other elements. ...
Document
... Humans and their ancestors have used stone tools made from brittle minerals for about 2.5 million years. The shattering of brittle minerals such as flint produced sharp edges useful for cutting and weaponry. Sometimes tools could be repaired by breaking a new cutting edge but the brittleness often m ...
... Humans and their ancestors have used stone tools made from brittle minerals for about 2.5 million years. The shattering of brittle minerals such as flint produced sharp edges useful for cutting and weaponry. Sometimes tools could be repaired by breaking a new cutting edge but the brittleness often m ...
CHAPTER 2
... • Bohr’s model of the atom when applied to atoms with more than one electron failed to explain their line spectra • One major change from Bohr’s model is that electrons do not move in orbits • Atomic orbitals - regions in space with a high probability of finding an electron • Electrons move rapidly ...
... • Bohr’s model of the atom when applied to atoms with more than one electron failed to explain their line spectra • One major change from Bohr’s model is that electrons do not move in orbits • Atomic orbitals - regions in space with a high probability of finding an electron • Electrons move rapidly ...
Periodic Table Quiz 1
... Periodic Properties Practice Quiz NAME__________________________________ Period ___________Date____________ Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. electron affinity f. periodic law b. ionization energy g. cation c. group h. period d. metal i. non-metal e. transition metal j. a ...
... Periodic Properties Practice Quiz NAME__________________________________ Period ___________Date____________ Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. electron affinity f. periodic law b. ionization energy g. cation c. group h. period d. metal i. non-metal e. transition metal j. a ...
Quantum Thorj and th Atom - Crossroads chemistry 40S
... electron can move only from one allowable orbit to another, and therefore, can emit or absorb only certain amounts of energy. I The four electron transitions that account for visible lines in hydrogen’s atomic emission spectrum are shown in Figure 5-lOb. For example, electrons dropping from the thir ...
... electron can move only from one allowable orbit to another, and therefore, can emit or absorb only certain amounts of energy. I The four electron transitions that account for visible lines in hydrogen’s atomic emission spectrum are shown in Figure 5-lOb. For example, electrons dropping from the thir ...
Chapter 3, Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table Ans
... they have the same shape and the same energy; they are oriented differently in space What requirement must be met in order for two electrons to coexist in the same orbital? ...
... they have the same shape and the same energy; they are oriented differently in space What requirement must be met in order for two electrons to coexist in the same orbital? ...
Chapter 5 PRACTICE TEST
... The discovery of the noble gases changed Mendeleev's periodic table by adding a new a. period. c. group. b. series. d. sublevel block. In the modern periodic table, elements are ordered according to a. decreasing atomic mass. c. increasing atomic number. b. Mendeleev's original design. d. the date o ...
... The discovery of the noble gases changed Mendeleev's periodic table by adding a new a. period. c. group. b. series. d. sublevel block. In the modern periodic table, elements are ordered according to a. decreasing atomic mass. c. increasing atomic number. b. Mendeleev's original design. d. the date o ...