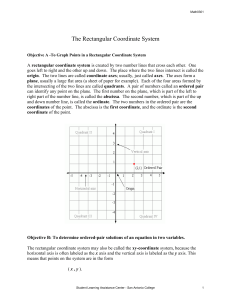
Algebraic Properties
... The order in which to numbers are multiplied does not change their product. Example ...
... The order in which to numbers are multiplied does not change their product. Example ...
Connecticut Curriculum Design Unit Planning Organizer Grade 6
... 6.NS.7. Common models to represent and compare integers include number line models, temperature models and the profit-loss model. On a number line model, the number is represented by an arrow drawn from zero to the location of the number on the number line; the absolute value is the length of this a ...
... 6.NS.7. Common models to represent and compare integers include number line models, temperature models and the profit-loss model. On a number line model, the number is represented by an arrow drawn from zero to the location of the number on the number line; the absolute value is the length of this a ...
Integers and Absolute Value
... distance from 0 but on different sides of 0. Integers are the set of all whole numbers and their opposites. Opposites ...
... distance from 0 but on different sides of 0. Integers are the set of all whole numbers and their opposites. Opposites ...
3.NF.3
... How can different fractions name the same number? How can fractions be compared and evaluated using <, >, or =? Content Statements Different fractions name the same number. Fractions can be compared and evaluated using symbols. ...
... How can different fractions name the same number? How can fractions be compared and evaluated using <, >, or =? Content Statements Different fractions name the same number. Fractions can be compared and evaluated using symbols. ...
Chapter - 1 ( Term-I)
... (i) Every natural no. is whole number. (ii) Every integer is a whole number. (iii) Every rational number is a whole number. (iv) Every irrational number is a real number. (v) Every real number is an irrational number. (vi) Every point on the number line is of the form ...
... (i) Every natural no. is whole number. (ii) Every integer is a whole number. (iii) Every rational number is a whole number. (iv) Every irrational number is a real number. (v) Every real number is an irrational number. (vi) Every point on the number line is of the form ...
Algebraic Expressions and Solving Equations Note
... c) In order to solve an equation, you must isolate the variable, that is, have all of the variables on one side and all of the numbers on the other side. Variables and numbers can be moved from side to side by performing the opposite operation to both sides of the equation. d) All brackets must be e ...
... c) In order to solve an equation, you must isolate the variable, that is, have all of the variables on one side and all of the numbers on the other side. Variables and numbers can be moved from side to side by performing the opposite operation to both sides of the equation. d) All brackets must be e ...
04-05 Match 2 Questions
... Match 2 Team Round 1.) Find the prime factorization of the LCM of 13426, 13818, and 14504 . ...
... Match 2 Team Round 1.) Find the prime factorization of the LCM of 13426, 13818, and 14504 . ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.