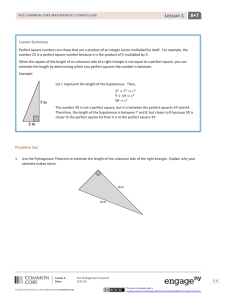
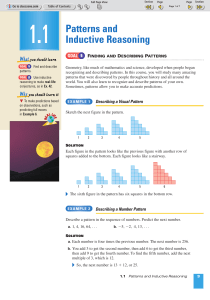
Year 5 Week 7 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... process, counting in 25s and recording sequence. Count on or back in 4s or 5s from any number. Write start number, eg 63. Divide class into 4 teams: Team A counts forwards in 4s, B in 5s; C counts backwards in 4s; D in 5s. Chn write numbers in their sequence. Give teams 1 minute. Each team recites n ...
... process, counting in 25s and recording sequence. Count on or back in 4s or 5s from any number. Write start number, eg 63. Divide class into 4 teams: Team A counts forwards in 4s, B in 5s; C counts backwards in 4s; D in 5s. Chn write numbers in their sequence. Give teams 1 minute. Each team recites n ...
Document
... The ordered pairs of the function f are reversed to produce the ordered pairs of the inverse relation. Example: Given the function f = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 1), (4, 2)}, its domain is {1, 2, 3, 4} and its range is {1, 2, 3}. The inverse relation of f is {(1, 1), (3, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4)}. The domain o ...
... The ordered pairs of the function f are reversed to produce the ordered pairs of the inverse relation. Example: Given the function f = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 1), (4, 2)}, its domain is {1, 2, 3, 4} and its range is {1, 2, 3}. The inverse relation of f is {(1, 1), (3, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4)}. The domain o ...
File - THANGARAJ MATH
... 1. Write the sequence that shows how many branches during each stage. 2. If you wanted to find the total number of branches on the tree at the end of stage 5, explain what would you have to do with the numbers in the sequence? Then do it, do find the total number of branches. ...
... 1. Write the sequence that shows how many branches during each stage. 2. If you wanted to find the total number of branches on the tree at the end of stage 5, explain what would you have to do with the numbers in the sequence? Then do it, do find the total number of branches. ...
Floating point
... – Divide by 2 by shifting right (the point moves to the left) – Multiply by 2 by shifting left (the point moves to the right) – Numbers of form 0.111111…2 represent those just below 1.0 • 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + … + 1/2i + … → 1.0 • We use notation 1.0 – ε to represent them ...
... – Divide by 2 by shifting right (the point moves to the left) – Multiply by 2 by shifting left (the point moves to the right) – Numbers of form 0.111111…2 represent those just below 1.0 • 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + … + 1/2i + … → 1.0 • We use notation 1.0 – ε to represent them ...
Beginning & Intermediate Algebra. 4ed
... Solving Linear Equations Solving Linear Equations in One Variable 1) Multiply both sides by the LCD to clear the equation of ...
... Solving Linear Equations Solving Linear Equations in One Variable 1) Multiply both sides by the LCD to clear the equation of ...
Models for Teaching Addition and Subtraction of Integers
... So if she brings me two checks for $5, no sweat, she helps me by $10, answer = +10. Similarly if she brings me 2 checks for $5 the result is 2 • –5 = –10. Now here is the tricky part: –2 • + 5 = ? Well the – sign means takes away from me. But if we start at zero how can she take anything away? This ...
... So if she brings me two checks for $5, no sweat, she helps me by $10, answer = +10. Similarly if she brings me 2 checks for $5 the result is 2 • –5 = –10. Now here is the tricky part: –2 • + 5 = ? Well the – sign means takes away from me. But if we start at zero how can she take anything away? This ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.