references
... In [1-3], the Generalized Waring Problem (GWP) was formulated for the first time and its complete solution was given in the form of the following statement. THEOREM 1. For any m 0, r 2 there exist: (i) the least finite number of summands, g(m, r) < , and (ii) the finite invariant set, Z(m, r) ...
... In [1-3], the Generalized Waring Problem (GWP) was formulated for the first time and its complete solution was given in the form of the following statement. THEOREM 1. For any m 0, r 2 there exist: (i) the least finite number of summands, g(m, r) < , and (ii) the finite invariant set, Z(m, r) ...
1332CentralTendency&Dispersion.pdf
... To calculate sample variance, we must calculate the deviation of each score in the sample as above as well as the square of each deviation as below. x ...
... To calculate sample variance, we must calculate the deviation of each score in the sample as above as well as the square of each deviation as below. x ...
Grade 6 PCS Eligible Content
... Interpret and compute quotients of fractions (including mixed numbers), and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions. Examples: (1)Given a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4), explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = (a/b) × (d/c) = ...
... Interpret and compute quotients of fractions (including mixed numbers), and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions. Examples: (1)Given a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4), explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = (a/b) × (d/c) = ...
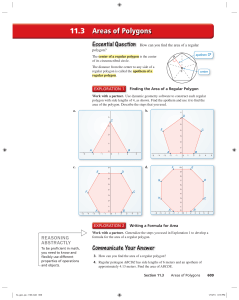
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.