Unit 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements in the Periodic Table
... Moving across a period from left to right, the melting point rises through the metals and metalloids and then drops abruptly to low values for the non-metals. Giant metallic structures : Metals usually have high melting points. In the metal lattice, each positively charged ion is attracted to the ‘c ...
... Moving across a period from left to right, the melting point rises through the metals and metalloids and then drops abruptly to low values for the non-metals. Giant metallic structures : Metals usually have high melting points. In the metal lattice, each positively charged ion is attracted to the ‘c ...
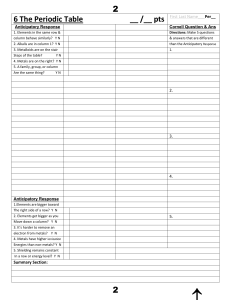
6 The Periodic Tableааааааааааааааааааааааааа__ /__ pts First
... 7. Why would you expect lithium (Li) and sulfur (S) to have different chemical and physical properties? 8. What characterizes the electron configurations of transition metals such as silver (Ag) and iron (Fe)? ...
... 7. Why would you expect lithium (Li) and sulfur (S) to have different chemical and physical properties? 8. What characterizes the electron configurations of transition metals such as silver (Ag) and iron (Fe)? ...
Test Review
... a noble gas. Too reactive to exist in nature freely. Must be stored in mineral oil. Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, not as reactive as alkali metals. Form +2 ions, losing 2 electrons to look like a noble gas. Halogens – Group 7, most reactive metals on the periodic table. Form -1 ions, gaining 1 el ...
... a noble gas. Too reactive to exist in nature freely. Must be stored in mineral oil. Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, not as reactive as alkali metals. Form +2 ions, losing 2 electrons to look like a noble gas. Halogens – Group 7, most reactive metals on the periodic table. Form -1 ions, gaining 1 el ...
Chapter 6
... When atoms lose electrons and form positively charged ions, they become smaller, and are called cations. They become smaller because the loss of the electrons means that the number of protons is greater than the number of electrons. Therefore, the electrons will be pulled more tightly to the nuc ...
... When atoms lose electrons and form positively charged ions, they become smaller, and are called cations. They become smaller because the loss of the electrons means that the number of protons is greater than the number of electrons. Therefore, the electrons will be pulled more tightly to the nuc ...
Nomenclature Powerpoint
... He actually arranged them such that elements with similar properties were located in the table underneath each other; thus, making it easier to observe the “periodicity.” ...
... He actually arranged them such that elements with similar properties were located in the table underneath each other; thus, making it easier to observe the “periodicity.” ...
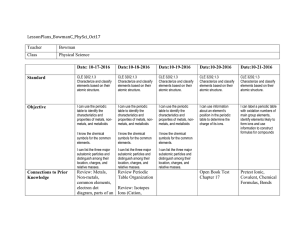
Oct 17-Oct 21
... I can use the periodic table to identify the characteristics and properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids ...
... I can use the periodic table to identify the characteristics and properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY
... The carbonates of alkaline earth metals are relatively less stable. On heating, they decompose to give corresponding oxide and CO 2 gas. The decomposition temperature for alkaline earth metal carbonates increases as we go down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements Their anomalous ...
... The carbonates of alkaline earth metals are relatively less stable. On heating, they decompose to give corresponding oxide and CO 2 gas. The decomposition temperature for alkaline earth metal carbonates increases as we go down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements Their anomalous ...
Elements and Their Properties
... image on paper therefore, they are used to make photographic film and paper. ...
... image on paper therefore, they are used to make photographic film and paper. ...
chapter-5-periodic-classification-of-elements
... the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. 16. Write any one of the strength of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table. Answer: One of the stre ...
... the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. 16. Write any one of the strength of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table. Answer: One of the stre ...
Ch. 5.1 History of the periodic table ppt.
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. – By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. – By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
The Periodic Table!
... Found in compounds that are in the Earth’s Crust More dense and harder than alkali metals ...
... Found in compounds that are in the Earth’s Crust More dense and harder than alkali metals ...
ppt - Ms Jilesen
... An isotope is a variation of an element (same protons) but can have diff. # of neutrons ...
... An isotope is a variation of an element (same protons) but can have diff. # of neutrons ...
A Periodic Table Logic Problem
... Objectives: To analyze the properties and relationships of 26 elements Identify each element’s place in the periodic table based on these properties and relationships. Introduction: When elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition ...
... Objectives: To analyze the properties and relationships of 26 elements Identify each element’s place in the periodic table based on these properties and relationships. Introduction: When elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition ...
File
... d. Be sure to include the charge of the particles, the location where the particles are found, and their mass in relation to each other”. Word atom element atomic symbol proton electron neutron nucleus atomic number mass number average atomic mass isotope ions valence electrons atomic energy levels ...
... d. Be sure to include the charge of the particles, the location where the particles are found, and their mass in relation to each other”. Word atom element atomic symbol proton electron neutron nucleus atomic number mass number average atomic mass isotope ions valence electrons atomic energy levels ...
Periodic Trends Reading
... top of Group 1, lithium is the least reactive, sodium is more reactive, and potassium is still more reactive. In other words, there is a trend toward great reactivity as you move down the alkali metals in Group 1. Understanding a trend among the elements allows you to make predictions about the chem ...
... top of Group 1, lithium is the least reactive, sodium is more reactive, and potassium is still more reactive. In other words, there is a trend toward great reactivity as you move down the alkali metals in Group 1. Understanding a trend among the elements allows you to make predictions about the chem ...
File - Ms. Robbins` PNHS Science Classes
... electrons. Metallic bonding occurs between atoms of sulfur sodium fluoride carbon 69. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet str ...
... electrons. Metallic bonding occurs between atoms of sulfur sodium fluoride carbon 69. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet str ...
Chapter 3 Physical Science - St. Pius X Classical Academy
... Organizing the Elements Mendeleev’s Periodic Table In his periodic table, Mendeleev left blank spaces. He predicted that the blank spaces would be filled by elements that had not yet been discovered. He even correctly predicted the properties of those new elements. ...
... Organizing the Elements Mendeleev’s Periodic Table In his periodic table, Mendeleev left blank spaces. He predicted that the blank spaces would be filled by elements that had not yet been discovered. He even correctly predicted the properties of those new elements. ...
(34 points)
... (E) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 ___28. An impossible electronic configuration ___29. The ground-state configuration for the atoms of a transition element ___30. The ground-state configuration of a negative ion of a halogen ___31. The ground-state configuration of a common ion of an alkaline earth el ...
... (E) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 ___28. An impossible electronic configuration ___29. The ground-state configuration for the atoms of a transition element ___30. The ground-state configuration of a negative ion of a halogen ___31. The ground-state configuration of a common ion of an alkaline earth el ...
Periodic Table
... Remember that the atomic number found on the periodic table is equal to the number of electrons in an atom. ...
... Remember that the atomic number found on the periodic table is equal to the number of electrons in an atom. ...
Science Questions
... Reason: Any metal will combine chemically with any non-metal to form ionic bonds that hold the molecule together. ...
... Reason: Any metal will combine chemically with any non-metal to form ionic bonds that hold the molecule together. ...
Regions of the Periodic Table
... (The “extra” section below the rest of the table.) are part of the transition metals have a partially-filled f sub-level officially have 2 valence electrons, but can shift electrons between s, d, and f sub-levels. Usually form ions with +3 charges. are rare noble gases: elements in group 18 ...
... (The “extra” section below the rest of the table.) are part of the transition metals have a partially-filled f sub-level officially have 2 valence electrons, but can shift electrons between s, d, and f sub-levels. Usually form ions with +3 charges. are rare noble gases: elements in group 18 ...
Effective Nuclear Charge
... atom’s valence electrons increases by one for each element from left to right in a period Down a Group: The effective nuclear charge felt by an atom’s valence electrons stays constant for each element going down a group ...
... atom’s valence electrons increases by one for each element from left to right in a period Down a Group: The effective nuclear charge felt by an atom’s valence electrons stays constant for each element going down a group ...
5-1 Development of the Periodic Table
... Ionic Radii – the size of an ion. • Cation – a positive ion:Na+,Mg2+,Fe2+, Fe3+, – Formed by the loss of an electron – Cations are smaller than their neutral atom. • As an electron is lost, the effective nuclear charge is greater, causing the electron cloud to become pulled closer to the nucleus, m ...
... Ionic Radii – the size of an ion. • Cation – a positive ion:Na+,Mg2+,Fe2+, Fe3+, – Formed by the loss of an electron – Cations are smaller than their neutral atom. • As an electron is lost, the effective nuclear charge is greater, causing the electron cloud to become pulled closer to the nucleus, m ...
Document
... stronger than the alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. They are less reactive than alkali metals, but they too are too reactive to be found free in nature. ...
... stronger than the alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. They are less reactive than alkali metals, but they too are too reactive to be found free in nature. ...
Period 2 element
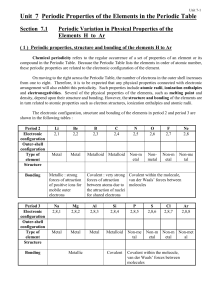
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.